Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Name Class DateSECTION 3-1 REVIEWWATERVOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms.1. polar compound2. hydrogen bond3. cohesion4. adhesionMULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank.1. In a water molecule,HRW material copyrighted under notice appearing earlier in this work.a. all of the atoms have a slight positivecharge.b. the oxygen atom has a slight negativecharge and the hydrogen atoms havea slight positive charge.2. When sodium chloride is dissolved in water, the sodium ionsa. are attracted to the oxygen atomsof water molecules.b. are attracted to the hydrogen atomsof water molecules.3. Hydrogen bondsa. <strong>for</strong>m between hydrogen atoms indifferent molecules.b. are strong bonds.c. the oxygen atom has a slight positivecharge and the hydrogen atoms havea slight negative charge.d. all of the atoms have a slight negativecharge.c. are attracted to each other.d. do not dissociate from the sodiumchloride.c. hold water molecules to one another.d. hold the two hydrogen atoms togetherin a molecule of hydrogen gas, H 2 .4. When a glass is filled to the brim with water, the water appears to bulge from the sides ofthe glass due toa. capillarity. b. thermal energy. c. adhesion. d. cohesion.5. When liquid water is heated, most of the energy that the water initially absorbs is used toa. raise the temperature of the water.b. break the covalent bonds between thehydrogen and oxygen atoms in water.c. make the water boil.d. break the hydrogen bonds between thewater molecules.Modern <strong>Biology</strong> Study Guide15
Name Class DateSHORT ANSWER Answer the questions in the space provided.1. Why is water a good solvent?2. What kinds of substances besides water can be involved in hydrogen bonding?3. What property of water allows it to stick to a dry surface, such as a wooden countertop?4. How does water help cells keep an even temperature despite temperature changes inthe environment?5. Critical Thinking Explain why water <strong>for</strong>ms large, round drops as it falls from a faucet with aslow leak.6. Critical Thinking <strong>Water</strong> is often called the universal solvent because it dissolves most substancesthat are important to living things. What does this suggest about the nature of those substances?STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS The diagram below represents a single water molecule.Draw three other water molecules near it, and use dashed lines to indicate where hydrogenbonds would <strong>for</strong>m between the molecule shown below and the ones you drew.HOHHRW material copyrighted under notice appearing earlier in this work.16 Section 3-1 Review
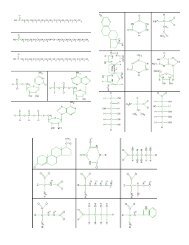
HRW material copyrighted under notice appearing earlier in this work.6. Since a tenfold increase in H 3 O ion concentrationreflects a decrease of one pH unit, a 100-foldincrease in concentration reflects a decrease oftwo pH units. There<strong>for</strong>e, the new pH would be 5.5.STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS1. a, alkaline; b, neutral; c, acidicSection 3-1VOCABULARY REVIEW1. A polar compound is one with an uneven distributionof positive and negative charges.2. A hydrogen bond is an attraction between ahydrogen atom in one molecule and a region ofnegative charge on another molecule.3. Cohesion is an attractive <strong>for</strong>ce between particlesof the same kind.4. Adhesion is an attractive <strong>for</strong>ce between unlikesubstances.MULTIPLE CHOICE1. b 2. a 3. c 4. d 5. dSHORT ANSWER1. <strong>Water</strong>’s polar nature allows it to dissolve otherpolar substances as well as ionic compounds.2. Any molecule that has a region of negative chargeor a hydrogen atom with a slight positive chargecan be involved in hydrogen bonding.3. Adhesion allows water to stick to a dry surface.4. Because of its hydrogen bonds, water must gain orlose a relatively large amount of energy <strong>for</strong> its temperatureto change. It there<strong>for</strong>e tends to resisttemperature changes.5. Cohesive <strong>for</strong>ces cause the water molecules in eachdrop to move as close as possible to one another,making the drop round.6. It suggests that the substances are most oftenpolar molecules or ionic compounds.STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONSDrawings should show two water molecules below andone above the central water molecule. The moleculesbelow should have their H atoms facing away from thecentral molecule, and the molecule above should haveone of its H atoms pointing toward the central molecule.Dashed lines should be drawn between eachH atom in the central molecule and the O atom in eachof the lower water molecules, and between the O atomin the central molecule and the nearer H atom in theupper water molecule.Section 3-2VOCABULARY REVIEW1. An organic compound is a compound containingcarbon atoms covalently bonded to other carbonatoms and to other elements. Examples: anycarbon-containing compound, such as benzene,ethanol, glycerol, glucose, fructose, sucrose, ATP,and ADP.2. A functional group is a cluster of atoms in a compoundthat influences the properties of that compound.Examples: hydroxyl group, phosphategroup.3. An alcohol is an organic compound with ahydroxyl group attached to one of its carbonatoms. Examples: ethanol, methanol, glycerol.4. A monomer is a simple molecule that can bond toothers of its kind to <strong>for</strong>m more complex molecules.Examples: glucose, fructose.5. A polymer is a complex molecule that consists ofrepeated, linked units. Example: sucrose.MULTIPLE CHOICE1. a 2. c 3. b 4. a 5. dSHORT ANSWER1. The hydroxyl group on alcohols is polar, and thismakes alcohols polar compounds. Alcohols canthere<strong>for</strong>e <strong>for</strong>m hydrogen bonds.2. carbon atom, monomer, polymer, macromolecule3. The glucose molecule releases a hydroxide ion,OH , and the fructose molecule releases ahydrogen ion, H . These two ions combine toproduce water, H 2 O.4. The hydrolysis products are ADP and inorganicphosphate. Energy is released.5. With seven electrons in its outermost energy level,carbon could not <strong>for</strong>m double or triple bonds withother atoms, so far fewer organic compoundscould be <strong>for</strong>med.STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS1. Forward reaction: reactants, glucose and fructose;products, sucrose and H 2 O. 2. condensationreaction 3. Reverse reaction: reactants,sucrose and H 2 O; products, glucose and fructose.4. hydrolysisSection 3-3VOCABULARY REVIEW1. A monosaccharide is a simple sugar containingcarbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of 1:2:1;a polysaccharide is a complex molecule composedof three or more monosaccharides.2. Hydrophilic means “water-loving,” or attracted towater; hydrophobic means “water-fearing,” ortending not to interact with water molecules.3. A nucleotide is a compound containing a phosphategroup, a five-carbon sugar, and a ringshapednitrogen base; a nucleic acid is a verylarge polymer of nucleotides.MULTIPLE CHOICE1. c 2. a 3. d 4. b 5. dSHORT ANSWER1. The storage <strong>for</strong>m is glycogen, and the quick-energy<strong>for</strong>m is glucose. Glycogen consists of hundredsof glucose molecules linked in a highlybranched chain.2. Starch, 1; proteins, 20; nucleic acids, 4.3. Phospholipid composes most of the cell membrane.The hydrophobic tails of the phospholipidsprovide a barrier between the inside and outsideof the cell.4. Steroids are lipids. Examples: testosterone andcholesterol.5. Wax serves as a waterproof layer, limitingwater loss and preventing insects fromdrying out.STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS1. a, substrate; b, enzyme; c, productsModern <strong>Biology</strong> Study Guide Answer Key3