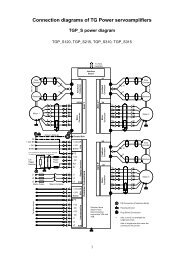
Table of Contents - TG Drives
Table of Contents - TG Drives
Table of Contents - TG Drives
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
80<br />
Reg, PID regulator<br />
GENERAL<br />
EXTENDED REGISTER GROUPS<br />
The regulator performs a central function in the system. It determines the torque<br />
needed to make the motor follow the speed and position commands at all times. It<br />
is a parallel PID type <strong>of</strong> regulator with several feed forward functions. It can be<br />
used in several configurations dependant on the applications characteristics.<br />
It operates with 1 kHz update rate.<br />
The output is a normalized value <strong>of</strong> the torque calculated each servo cycle. This<br />
output is then used by the commutation logic to create two sinusoidal currents.<br />
FUNCTION<br />
Reg.PosErr<br />
Reg.SpdErr<br />
Reg.IErr<br />
Reg.SpdErr<br />
Reg.TorqLim<br />
Reg.TorqPLim<br />
Reg.TorqNLim<br />
Reg.TorqTime<br />
Reg.TorqCLim<br />
Reg.PGain<br />
Reg.IGain<br />
Reg.DGain<br />
RELATED ITEMS<br />
Pg.Apos<br />
Pg.ASpeed<br />
EXAMPLE USAGE<br />
.<br />
Reg.TorqLim,8000<br />
Reg.TorqCLim,2000<br />
Reg.TorqTime,500<br />
or Reg.Mode,64<br />
.<br />
The inputs to the regulator are the command values for<br />
position, speed and acceleration. Each ms the difference<br />
between the command values and the actual values are<br />
calculated.<br />
The acceleration is used only for the feed forward parts.<br />
The position error is used in the Proportional and the Integral<br />
part, and the speed error is used in the Derivative part. The<br />
feed forward parts are Inertia compensation, Viscous friction,<br />
Static friction and Torque.<br />
These parts makes up the output which is passed trough a<br />
limiting function. There are three different limits, maximum<br />
positive torque (Reg.TorqPLim), maximum negative torque<br />
(Reg.TorqNLim) and maximum continuous torque<br />
(Reg.TorqLim). The output torque is always limited to the<br />
range bounded by Reg.TorqPLim and Reg.TorqNLim.<br />
If enabled, an additional function will limit the output to<br />
Reg.TorqLim. If the output has been larger than this limit for<br />
more than Reg.TorqTime [ms]. This can be seen as a<br />
dynamic torque limit.<br />
By adjusting these limits to proper values, the motor can be<br />
protected from excessive overheating, permitting the thermal<br />
sensor in the motor windings to be able to react fast enough.<br />
The gain and other tuning parameters must be calculated<br />
and/or established by testing for each application.<br />
Command value for position.<br />
Command value for speed.<br />
;set maximum torque limit<br />
;set continuos limit to 25 %<br />
;allow 500 ms <strong>of</strong> max. torque<br />
;activate dynamic torque limit<br />
User's Manual 5.1 Inmotion Technologies AB<br />
Doc. No.9032 0027 01 (B), Rev. 11.07.2001