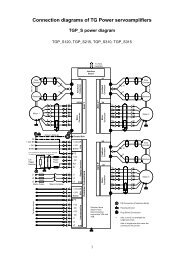
Table of Contents - TG Drives
Table of Contents - TG Drives
Table of Contents - TG Drives
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
PL2 Native position language<br />
INTRODUCTION<br />
This manual pertains to programming DMC 2 motion controller products and<br />
contains a language reference that explains instructions, extended registers,<br />
language syntax and compiler functions.<br />
Typefaces used in this manual:<br />
Mono spaced This typeface represents text as it appears on the screen (in<br />
ECT) or in a program and is also used to indicate items the<br />
programmer may type.<br />
Italics Italics are used to emphasize certain words, such as new<br />
terms.<br />
Bold PL2 reserved word<br />
GENERAL<br />
Program A Program is comprised <strong>of</strong> a collection <strong>of</strong> Program<br />
Statements.<br />
i<br />
Program<br />
Statement<br />
The DMC 2 product family allows a Program to be stored in<br />
volatile memory,(RAM) or in nonvolatile memory<br />
(FLASHPROM). The program can also be a file that is<br />
stored on a computer when the development environment<br />
(ECT) is used.<br />
A program statement is one line <strong>of</strong> text that contains a<br />
mnemonic for an instruction. Each instruction has its own<br />
syntax. (The compiler checks for the correct syntax. The<br />
controller has a built in one-line compiler.)<br />
Line The sequential number where a program instruction is stored.<br />
(1-8191)<br />
Mnemonic A mnemonic is a text synonym for an instruction. The DMC 2<br />
Mnemonic<br />
Operator<br />
family <strong>of</strong> products directly interprets Mnemonics.<br />
Note: Occasionally, instructions refer to the Mnemonic for the<br />
instruction.<br />
An operator used together with a Mnemonic to define the<br />
Instruction.<br />
Argument One or several arguments are used with a Mnemonic to define<br />
the Instruction.<br />
Expression<br />
Operator<br />
Used with a Mnemonic and Argument(s) to define an action<br />
that should take place during execution <strong>of</strong> the Instruction.<br />
Routine A part <strong>of</strong> a program, usually designated to perform a certain<br />
function, is called a Routine.<br />
A Program is typically made up <strong>of</strong> many Routines.<br />
Parameter stack Part <strong>of</strong> the memory organized as a FILO for parameter<br />
storage.<br />
[Mnemonic] Designates an optional Mnemonic.<br />
Example: The Let Mnemonic can usually be omitted.<br />
Syntax There are different ways to combine a Mnemonic together with<br />
arguments and an operator. This will yield different<br />
User's Manual 5.1 Inmotion Technologies AB<br />
Doc. No.9032 0027 01 (B), Rev. 11.07.2001 25