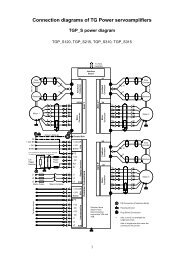
Table of Contents - TG Drives
Table of Contents - TG Drives
Table of Contents - TG Drives
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
142<br />
LAN1, Local area network 1<br />
EXTENDED REGISTER GROUPS<br />
A user controls how to handle ’Remote Frame’ responses on transmit descriptors.<br />
See MsgObjLAN1.Status and MsgObjLAN1.Frame.<br />
LAN1, POWER UP<br />
On power up the low-level protocol initializes itself and sets up CAN<br />
communications rate at the content <strong>of</strong> EEprom.8.<br />
A user can change the can frequency. See LAN1.Ini.<br />
LAN1, HIGH LEVEL COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS.<br />
No higher-level communication protocols are implemented that require their own<br />
groups.<br />
A higher protocol uses some user defined ”live” message objects and the<br />
underlying protocol uses these to implement communication services, as:<br />
• On-demand data, (server/client relation ship).<br />
• Broadcast data.<br />
• Sporadic data.<br />
• Periodic data.<br />
• Data synchronization.<br />
• Large data messages, up/download <strong>of</strong> application code.<br />
• User defined services. (User defined protocol).<br />
• Multi data services, uses a communication area, when more that one<br />
parameter is required before a service can be performed.<br />
LAN1 COMMUNICATION SCENARIOS.<br />
Server uses periodic receive objects to trigger the slave owning the object to<br />
transmit its data. A slave transmits data on demand from the server.<br />
Server<br />
Client # 1<br />
Client # 2<br />
Client # 3<br />
Node # 1<br />
Node # 2<br />
Node # 3<br />
Node # 4<br />
All nodes use periodic receives objects to trigger the owner <strong>of</strong> the object to transmit<br />
its data. Any node can send or receive sporadic ’alert’ message objects.<br />
i<br />
All message objects must have a unique object ID. Make sure<br />
that each and every node/server use unique transmits object<br />
IDs. In other words, there cannot be more than one unit that<br />
transmit an object with the same ID, at the same time.<br />
Sporadic message objects have the disadvantage that the<br />
user must be sure that these messages will not clogging the<br />
network. And the firmware cannot handle back-to-back<br />
messages. The time between two messages sent back-to-back<br />
User's Manual 5.1 Inmotion Technologies AB<br />
Doc. No.9032 0027 01 (B), Rev. 11.07.2001