May 2011 - Career Point
May 2011 - Career Point May 2011 - Career Point
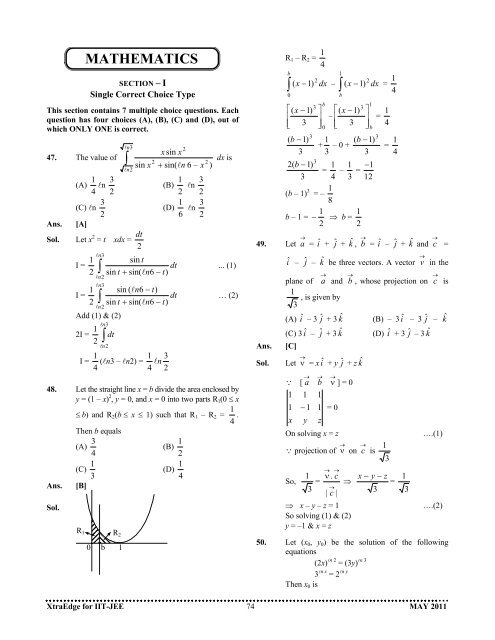
MATHEMATICSSECTION – ISingle Correct Choice TypeThis section contains 7 multiple choice questions. Eachquestion has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D), out ofwhich ONLY ONE is correct.ln3x sin x47. The value of∫dx is22sin x + sin( ln6 – x )Ans.Sol.(A) 41 ln 23(C) ln 23[A]ln2Let x 2 = t xdx = 2dtl 31 n ln2l 31 n 2ln2sin tI =∫dt2 sin t + sin( ln6− t)sin ( ln6− t)I =∫dtsin t + sin( ln6− t)Add (1) & (2)2I =1 l n 32 ∫l n 2dt1 1 3I = (ln3 – ln2) = l n4 4 22(B) 21 ln 23(D) 61 ln 23... (1)… (2)48. Let the straight line x = b divide the area enclosed byy = (1 – x) 2 , y = 0, and x = 0 into two parts R 1 (0 ≤ xAns.Sol.≤ b) and R 2 (b ≤ x ≤ 1) such that R 1 – R 2 = 41 .Then b equals(A) 43(C) 31[B]R 1R 20 b 1(B) 21(D) 41R 1 – R 2 = 41b22 1∫( x − 1) dx –∫( x − 1) dx = 40⎡(x − 1)⎢⎣ 3( b −1)3333⎤⎥⎦b01b⎡(x − 1)– ⎢⎣ 33⎤⎥⎦1 ( b −1)+ – 0 + 3 32( b −1)1 1 −1= – =3 4 3 12(b – 1) 3 1= – 8b – 1 =1 1− ⇒ b =2 21b= 413= 4149. Let → a = î + ĵ + kˆ , → b = î – ĵ + kˆ and → c =Ans.Sol.î – ĵ – kˆ be three vectors. A vector → v in theplane of → a and → b , whose projection on → c is1 , is given by3(A) î – 3 ĵ + 3 kˆ (B) – 3 î – 3 ĵ – kˆ(C) 3 î – ĵ + 3 kˆ (D) î + 3 ĵ – 3 kˆ[C]Let → ν = x î + y ĵ + z kˆQ [ → a → b → ν ] = 011x1− 1 1 = 0y1zOn solving x = zQ projection of → ν on → c is→νc→131 . c x − y − zSo, = ⇒ =3→| |3⇒ x – y – z = 1So solving (1) & (2)y = –1 & x = z13….(1)….(2)50. Let (x 0 , y 0 ) be the solution of the followingequations(2x) ln 2 = (3y) ln 33 ln x = 2 ln yThen x 0 isXtraEdge for IIT-JEE 74 MAY 2011
(A) 61(B) 31So, m + 3 = ± 3 (1 – 3 m)(C) 21(D) 6Ans. [C]Sol. (2x) ln 2 = ( 3y) ln 3ln 2 (ln 2 + ln x) = ln 3 (ln 3 + ln y)ln 2 . ln x – ln 3 ln y = (ln 3) 2 – (ln 2) 2 .....(1)3 ln x = 2 ln yln x . ln 3 = lny . ln 2ln3ln y = ln x.....(2)ln2Solving (1) & (2)1ln x = – ln 2 ⇒ x = 251. Let α and β be the roots of x 2 – 6x – 2 = 0, withα > β. If a n = α n – β n for n ≥ 1, then the value ofa10– 2a82a9is(A) 1 (B) 2(C) 3 (D) 4Ans. [C]Sol. ∴ x 2 – 6x – 2 = 0 has roots α, βSo, α 2 – 2 = 6α & β 2 – 2 = 6βa n = α n – β n=8So,2α ( αa2( α10− 2a2a9− 2) − β9− β8)8( β92=( α10− 2) α=8− β102( α) − 2( α9− β89)8− β(6α)− β (6β)= 3.9 92( α − β )52. A straight line L through the point (3, –2) isinclined at an angle 60° to the line 3 x + y = 1.If L also intersects the x-axis, then the equation ofL is(A) y + 3 x + 2 – 3 3 = 0(B) y – 3 x + 2 + 3 3 = 0(C) 3 y – x + 3 + 2 3 = 0(D) 3 y + x – 3 + 2 3 = 0Ans. [B]Sol. Let the slope of the line is mm + 3tan 60º =1 − 3m3 =m +1 −33m8)m + 3 = 3 – 3m m + 3 = – 3 + 3mm = 0 m = 3hence linehence liney = – 2 y + 2 = 3 (x – 3)y – 3 x + 2 + 3 3 = 0as line intersects x-axisSo line will be, y – 3 x + 2 + 3 3 = 053. Let P = {θ : sin θ – cos θ = 2 cos θ} andQ = {θ : sin θ + cos θ = 2 sin θ} be two sets.Then(A) P ⊂ Q and Q – P ≠ ∅(B) Q ⊄ P(C) P ⊄ Q(D) P = QAns. [D]Sol. P : sin θ – cos θ = 2 cos θsin θ = ( 2 + 1) cos θtan θ = 2 + 1tan θ = tan 67 21 °3πθ = nπ + , n ∈ I8Q : sin θ + cos θ = 2 sin θcos θ = ( 2 – 1) sin θ1tanθ =2 − 1= 2 + 1θ = nπ +∴ P = Q3π , n ∈ I8…(1)…(2)SECTION – IIMultiple Correct Choice TypeThis section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Eachquestion has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D), out ofwhich ONE OR MORE may be correct.54. The vector(s) which is/are coplanar with vectorsî + ĵ + 2 kˆ and î + 2 ĵ + kˆ , and perpendicularto the vector î + ĵ + kˆ is /are(A) ĵ – kˆ(B) – î + ĵ(C) î – ĵ(D) – ĵ + kˆXtraEdge for IIT-JEE 75 MAY 2011
- Page 26 and 27: Hence, E x = -∴∂V∂ xE = - ayi
- Page 28 and 29: For (x - a) 2 + (y - b) 2 = r 2 , t
- Page 30 and 31: (If the velocities are not along th
- Page 32 and 33: KEY CONCEPTPhysicalChemistryFundame
- Page 34 and 35: ⎛ n ⎞ ⎛ n ⎞Correction term
- Page 36 and 37: Kinetic Isotope Effects :The kineti
- Page 38 and 39: (m / 32) 1Moles fraction of O 2 ==(
- Page 40 and 41: `tà{xÅtà|vtÄ V{tÄÄxÇzxá1 Se
- Page 42 and 43: Students' ForumExpert’s Solution
- Page 44 and 45: MATHSCOMPLEX NUMBERMathematics Fund
- Page 46 and 47: MATHSMATRICES &DETERMINANTSMathemat
- Page 48 and 49: aBased on New PatternIIT-JEE 2012Xt
- Page 50 and 51: dxO12. The time of crossing the riv
- Page 52 and 53: 6. Choose the INCORRECT statement f
- Page 54 and 55: 7. If the equation 3x 4 - 16x 3 + 3
- Page 56 and 57: Based on New PatternIIT-JEE 2013Xtr
- Page 58 and 59: 17. A stone is projected from level
- Page 60 and 61: 16. Half a mole of photon is used t
- Page 62 and 63: 17. Ifsin 3θcos 2θ2-147137= 0Then
- Page 64 and 65: IIT-JEE 2011PAPER-I (PAPER & SOLUTI
- Page 66 and 67: 9. Amongst the given options, the c
- Page 68 and 69: 22. The total number of alkenes pos
- Page 70 and 71: 1 2 × 8∆U = × [V - 0]22 2 + 81
- Page 72 and 73: shown in the figure. We use the sig
- Page 74 and 75: 40. A block is moving on an incline
- Page 78 and 79: Ans.Sol.[A,D]r = xiˆ + yj ˆ + zk
- Page 80 and 81: ⎡323 21× ⎤=⎡32 1⎤1 C2C21 C
- Page 82 and 83: XtraEdge for IIT-JEE 80 MAY 2011
- Page 84 and 85: Ans. [A]Sol. ∆T = k f × m × i
- Page 86 and 87: SECTION - IVMatrix match TypeThis s
- Page 88 and 89: Ans.[D]m 1 = 0.01 kgvH = 5mm 2 = 0.
- Page 90 and 91: 31. A series R-C circuit is connect
- Page 92 and 93: P3PBAColumn-I(A) Pipe closed at one
- Page 94 and 95: 21/ x45. If lim [1 + xl n(1 + b )]
- Page 96 and 97: So f(x) is monotonically decreasing
- Page 98 and 99: (C)25 / 6πI = x dxn ∫sec πl 327
- Page 100 and 101: Subscription Offer for Students'Xtr
- Page 102: XtraEdge for IIT-JEE 100 MAY 2011
MATHEMATICSSECTION – ISingle Correct Choice TypeThis section contains 7 multiple choice questions. Eachquestion has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D), out ofwhich ONLY ONE is correct.ln3x sin x47. The value of∫dx is22sin x + sin( ln6 – x )Ans.Sol.(A) 41 ln 23(C) ln 23[A]ln2Let x 2 = t xdx = 2dtl 31 n ln2l 31 n 2ln2sin tI =∫dt2 sin t + sin( ln6− t)sin ( ln6− t)I =∫dtsin t + sin( ln6− t)Add (1) & (2)2I =1 l n 32 ∫l n 2dt1 1 3I = (ln3 – ln2) = l n4 4 22(B) 21 ln 23(D) 61 ln 23... (1)… (2)48. Let the straight line x = b divide the area enclosed byy = (1 – x) 2 , y = 0, and x = 0 into two parts R 1 (0 ≤ xAns.Sol.≤ b) and R 2 (b ≤ x ≤ 1) such that R 1 – R 2 = 41 .Then b equals(A) 43(C) 31[B]R 1R 20 b 1(B) 21(D) 41R 1 – R 2 = 41b22 1∫( x − 1) dx –∫( x − 1) dx = 40⎡(x − 1)⎢⎣ 3( b −1)3333⎤⎥⎦b01b⎡(x − 1)– ⎢⎣ 33⎤⎥⎦1 ( b −1)+ – 0 + 3 32( b −1)1 1 −1= – =3 4 3 12(b – 1) 3 1= – 8b – 1 =1 1− ⇒ b =2 21b= 413= 4149. Let → a = î + ĵ + kˆ , → b = î – ĵ + kˆ and → c =Ans.Sol.î – ĵ – kˆ be three vectors. A vector → v in theplane of → a and → b , whose projection on → c is1 , is given by3(A) î – 3 ĵ + 3 kˆ (B) – 3 î – 3 ĵ – kˆ(C) 3 î – ĵ + 3 kˆ (D) î + 3 ĵ – 3 kˆ[C]Let → ν = x î + y ĵ + z kˆQ [ → a → b → ν ] = 011x1− 1 1 = 0y1zOn solving x = zQ projection of → ν on → c is→νc→131 . c x − y − zSo, = ⇒ =3→| |3⇒ x – y – z = 1So solving (1) & (2)y = –1 & x = z13….(1)….(2)50. Let (x 0 , y 0 ) be the solution of the followingequations(2x) ln 2 = (3y) ln 33 ln x = 2 ln yThen x 0 isXtraEdge for IIT-JEE 74 MAY <strong>2011</strong>