(BAT) Reference Document for the Production of Chlor-alkali ...
(BAT) Reference Document for the Production of Chlor-alkali ...
(BAT) Reference Document for the Production of Chlor-alkali ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chapter 4<br />
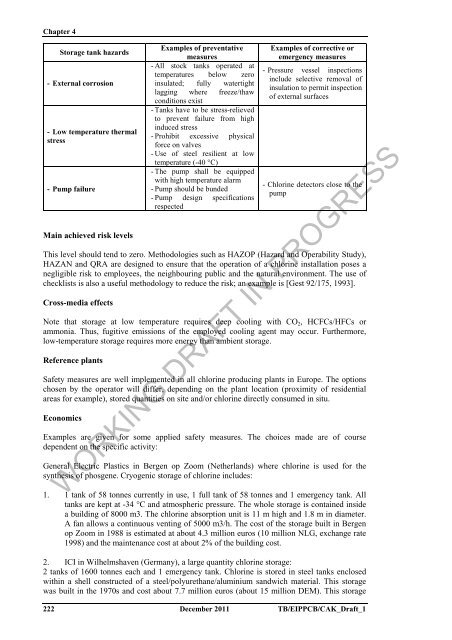
Storage tank hazards<br />
- External corrosion<br />
- Low temperature <strong>the</strong>rmal<br />
stress<br />
- Pump failure<br />
Main achieved risk levels<br />
Examples <strong>of</strong> preventative<br />
measures<br />
- All stock tanks operated at<br />
temperatures below zero<br />
insulated; fully watertight<br />
lagging where freeze/thaw<br />
conditions exist<br />
- Tanks have to be stress-relieved<br />
to prevent failure from high<br />
induced stress<br />
- Prohibit excessive physical<br />
<strong>for</strong>ce on valves<br />
- Use <strong>of</strong> steel resilient at low<br />
temperature (-40 °C)<br />
- The pump shall be equipped<br />
with high temperature alarm<br />
- Pump should be bunded<br />
- Pump design specifications<br />
respected<br />
Examples <strong>of</strong> corrective or<br />
emergency measures<br />
- Pressure vessel inspections<br />
include selective removal <strong>of</strong><br />
insulation to permit inspection<br />
<strong>of</strong> external surfaces<br />
- <strong>Chlor</strong>ine detectors close to <strong>the</strong><br />
pump<br />
This level should tend to zero. Methodologies such as HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Study),<br />
HAZAN and QRA are designed to ensure that <strong>the</strong> operation <strong>of</strong> a chlorine installation poses a<br />
negligible risk to employees, <strong>the</strong> neighbouring public and <strong>the</strong> natural environment. The use <strong>of</strong><br />
checklists is also a useful methodology to reduce <strong>the</strong> risk; an example is [Gest 92/175, 1993].<br />
Cross-media effects<br />
Note that storage at low temperature requires deep cooling with CO2, HCFCs/HFCs or<br />
ammonia. Thus, fugitive emissions <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> employed cooling agent may occur. Fur<strong>the</strong>rmore,<br />
low-temperature storage requires more energy than ambient storage.<br />
<strong>Reference</strong> plants<br />
Safety measures are well implemented in all chlorine producing plants in Europe. The options<br />
chosen by <strong>the</strong> operator will differ, depending on <strong>the</strong> plant location (proximity <strong>of</strong> residential<br />
areas <strong>for</strong> example), stored quantities on site and/or chlorine directly consumed in situ.<br />
Economics<br />
Examples are given <strong>for</strong> some applied safety measures. The choices made are <strong>of</strong> course<br />
dependent on <strong>the</strong> specific activity:<br />
General Electric Plastics in Bergen op Zoom (Ne<strong>the</strong>rlands) where chlorine is used <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
syn<strong>the</strong>sis <strong>of</strong> phosgene. Cryogenic storage <strong>of</strong> chlorine includes:<br />
WORKING DRAFT IN PROGRESS<br />
1. 1 tank <strong>of</strong> 58 tonnes currently in use, 1 full tank <strong>of</strong> 58 tonnes and 1 emergency tank. All<br />
tanks are kept at -34 °C and atmospheric pressure. The whole storage is contained inside<br />
a building <strong>of</strong> 8000 m3. The chlorine absorption unit is 11 m high and 1.8 m in diameter.<br />
A fan allows a continuous venting <strong>of</strong> 5000 m3/h. The cost <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> storage built in Bergen<br />
op Zoom in 1988 is estimated at about 4.3 million euros (10 million NLG, exchange rate<br />
1998) and <strong>the</strong> maintenance cost at about 2% <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> building cost.<br />
2. ICI in Wilhelmshaven (Germany), a large quantity chlorine storage:<br />
2 tanks <strong>of</strong> 1600 tonnes each and 1 emergency tank. <strong>Chlor</strong>ine is stored in steel tanks enclosed<br />
within a shell constructed <strong>of</strong> a steel/polyurethane/aluminium sandwich material. This storage<br />
was built in <strong>the</strong> 1970s and cost about 7.7 million euros (about 15 million DEM). This storage<br />
222 December 2011 TB/EIPPCB/CAK_Draft_1