(BAT) Reference Document for the Production of Chlor-alkali ...
(BAT) Reference Document for the Production of Chlor-alkali ...
(BAT) Reference Document for the Production of Chlor-alkali ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Chapter 3<br />
sent to a deposit. In some cases <strong>the</strong> filter cakes are dissolved to be pumped to <strong>the</strong> waste water<br />
treatment unit and <strong>the</strong> sludge <strong>the</strong>refrom is distilled at <strong>the</strong> plant, temporarily stored or sent to a<br />
deposit [ 3, Euro <strong>Chlor</strong> 2011 ].<br />
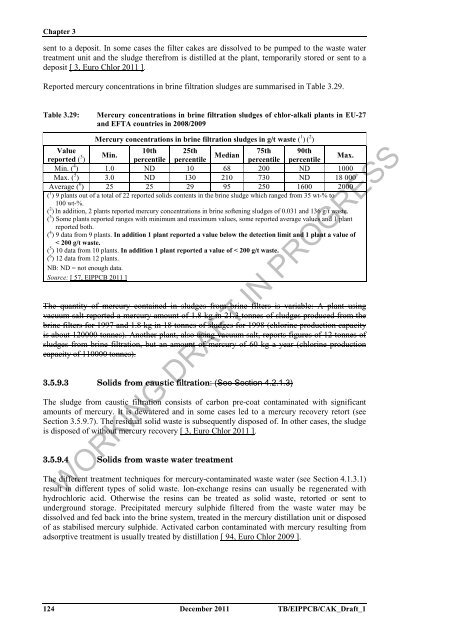
Reported mercury concentrations in brine filtration sludges are summarised in Table 3.29.<br />
Table 3.29: Mercury concentrations in brine filtration sludges <strong>of</strong> chlor-<strong>alkali</strong> plants in EU-27<br />
and EFTA countries in 2008/2009<br />
Mercury concentrations in brine filtration sludges in g/t waste ( 1 ) ( 2 )<br />
Value<br />
reported ( 3 10th 25th<br />
Min.<br />
)<br />
percentile percentile Median<br />
75th 90th<br />
Max.<br />
percentile percentile<br />
Min. ( 4 ) 1.0 ND 10 68 200 ND 1000<br />
Max. ( 5 ) 3.0 ND 130 210 730 ND 18 000<br />
Average ( 6 ) 25 25 29 95 250 1600 2000<br />
( 1 ) 9 plants out <strong>of</strong> a total <strong>of</strong> 22 reported solids contents in <strong>the</strong> brine sludge which ranged from 35 wt-% to<br />
100 wt-%.<br />
( 2 ) In addition, 2 plants reported mercury concentrations in brine s<strong>of</strong>tening sludges <strong>of</strong> 0.031 and 136 g/t waste.<br />
( 3 ) Some plants reported ranges with minimum and maximum values, some reported average values and 1 plant<br />
reported both.<br />
( 4 ) 9 data from 9 plants. In addition 1 plant reported a value below <strong>the</strong> detection limit and 1 plant a value <strong>of</strong><br />
< 200 g/t waste.<br />
( 5 ) 10 data from 10 plants. In addition 1 plant reported a value <strong>of</strong> < 200 g/t waste.<br />
( 6 ) 12 data from 12 plants.<br />
NB: ND = not enough data.<br />
Source: [ 57, EIPPCB 2011 ]<br />
The quantity <strong>of</strong> mercury contained in sludges from brine filters is variable: A plant using<br />
vacuum salt reported a mercury amount <strong>of</strong> 1.8 kg in 21.3 tonnes <strong>of</strong> sludges produced from <strong>the</strong><br />
brine filters <strong>for</strong> 1997 and 1.8 kg in 18 tonnes <strong>of</strong> sludges <strong>for</strong> 1998 (chlorine production capacity<br />
is about 120000 tonnes). Ano<strong>the</strong>r plant, also using vacuum salt, reports figures <strong>of</strong> 12 tonnes <strong>of</strong><br />
sludges from brine filtration, but an amount <strong>of</strong> mercury <strong>of</strong> 60 kg a year (chlorine production<br />
capacity <strong>of</strong> 110000 tonnes).<br />
3.5.9.3 Solids from caustic filtration: (See Section 4.2.1.3)<br />
The sludge from caustic filtration consists <strong>of</strong> carbon pre-coat contaminated with significant<br />
amounts <strong>of</strong> mercury. It is dewatered and in some cases led to a mercury recovery retort (see<br />
Section 3.5.9.7). The residual solid waste is subsequently disposed <strong>of</strong>. In o<strong>the</strong>r cases, <strong>the</strong> sludge<br />
is disposed <strong>of</strong> without mercury recovery [ 3, Euro <strong>Chlor</strong> 2011 ].<br />
3.5.9.4 Solids from waste water treatment<br />
The different treatment techniques <strong>for</strong> mercury-contaminated waste water (see Section 4.1.3.1)<br />
result in different types <strong>of</strong> solid waste. Ion-exchange resins can usually be regenerated with<br />
hydrochloric acid. O<strong>the</strong>rwise <strong>the</strong> resins can be treated as solid waste, retorted or sent to<br />
underground storage. Precipitated mercury sulphide filtered from <strong>the</strong> waste water may be<br />
dissolved and fed back into <strong>the</strong> brine system, treated in <strong>the</strong> mercury distillation unit or disposed<br />
<strong>of</strong> as stabilised mercury sulphide. Activated carbon contaminated with mercury resulting from<br />
adsorptive treatment is usually treated by distillation [ 94, Euro <strong>Chlor</strong> 2009 ].<br />
WORKING DRAFT IN PROGRESS<br />
124 December 2011 TB/EIPPCB/CAK_Draft_1