Technology of Q 2500 colour TV set
Technology of Q 2500 colour TV set
Technology of Q 2500 colour TV set
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
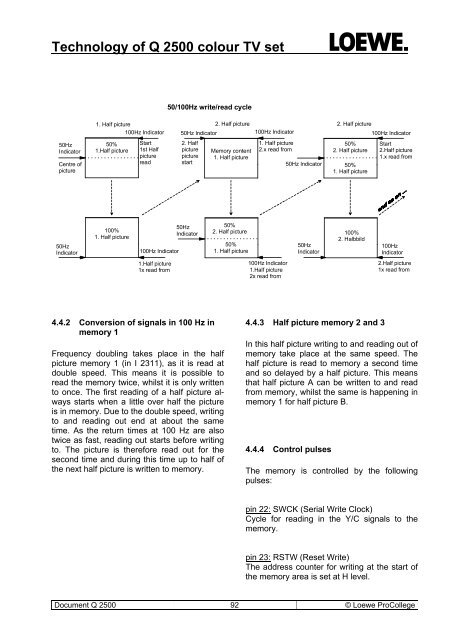
<strong>Technology</strong> <strong>of</strong> Q <strong>2500</strong> <strong>colour</strong> <strong>TV</strong> <strong>set</strong>50/100Hz write/read cycle50HzIndicatorCentre <strong>of</strong>picture1. Half picture 2. Half picture 2. Half picture100Hz Indicator 50Hz Indicator100Hz Indicator100Hz Indicator50%1.Half pictureStart1st Halfpictureread2. HalfpicturepicturestartMemory content1. Half picture1. Half picture2.x read from50Hz Indicator50%2. Half picture50%1. Half pictureStart2.Half picture1.x read from50HzIndicator100%1. Half picture100Hz Indicator50HzIndicator50%2. Half picture50%1. Half picture50HzIndicator100%2. Halbbild100HzIndicator1.Half picture1x read from100Hz Indicator1.Half picture2x read from2.Half picture1x read from4.4.2 Conversion <strong>of</strong> signals in 100 Hz inmemory 1Frequency doubling takes place in the halfpicture memory 1 (in I 2311), as it is read atdouble speed. This means it is possible toread the memory twice, whilst it is only writtento once. The first reading <strong>of</strong> a half picture alwaysstarts when a little over half the pictureis in memory. Due to the double speed, writingto and reading out end at about the sametime. As the return times at 100 Hz are alsotwice as fast, reading out starts before writingto. The picture is therefore read out for thesecond time and during this time up to half <strong>of</strong>the next half picture is written to memory.4.4.3 Half picture memory 2 and 3In this half picture writing to and reading out <strong>of</strong>memory take place at the same speed. Thehalf picture is read to memory a second timeand so delayed by a half picture. This meansthat half picture A can be written to and readfrom memory, whilst the same is happening inmemory 1 for half picture B.4.4.4 Control pulsesThe memory is controlled by the followingpulses:pin 22: SWCK (Serial Write Clock)Cycle for reading in the Y/C signals to thememory.pin 23: RSTW (Re<strong>set</strong> Write)The address counter for writing at the start <strong>of</strong>the memory area is <strong>set</strong> at H level.Document Q <strong>2500</strong> 92 © Loewe ProCollege