Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
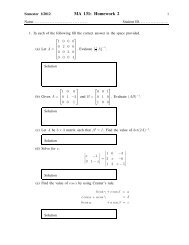
MA112 Section 750001: Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 48Example 3.23 F<strong>in</strong>d the area of the parallelogram with two adjacent sides formed by thevectors u = 〈1,2,−2〉 and v = 〈3,0,1〉.Solution .........Example 3.24 F<strong>in</strong>d the area of the triangle that is determ<strong>in</strong>ed by the po<strong>in</strong>ts P 1 (2,2,0),P 2 (−1,0,2), and P 3 (0,4,3).Solution .........Scalar Triple ProductsIf u = 〈u 1 ,u 2 ,u 3 〉, v = 〈v 1 ,v 2 ,v 3 〉, and w = 〈w 1 ,w 2 ,w 3 〉 are vectors <strong>in</strong> 3-space, then thenumberu·(v×w)is called the scalar triple product of u, v, and w. This value can be obta<strong>in</strong>ed directlyfrom the formula∣ u 1 u 2 u 3∣∣∣∣∣u·(v×w) =v 1 v 2 v 3(3.20)∣w 1 w 2 w 3Example 3.25 Calculate the scalar triple product u·(v×w) of the vectorsSolution .........u = 3i−2j−5k, v = i+4j−4k, w = 3j+2kGeometric Properties of the Scalar Triple ProductTheorem 3.13 Let u, v and w be nonzero vectors <strong>in</strong> 3-space.(a) The volume V of the parallelepiped that has u, v and w as adjacent edges isV = |u·(v×w)| (3.21)(b) u·(v×w) = 0 if and only if u, v and w lie <strong>in</strong> the same plane.Example 3.26 F<strong>in</strong>d the volume of the parallelepiped with three adjacent edges formed bythe vectors u = 〈7,8,0〉, v = 〈1,2,3〉 and w = 〈4,5,6〉.Solution .........Algebraic Properties of the Scalar Triple Productu·(v×w) = w·(u×v) = v·(w×u)u·v×w = u×v·w