Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
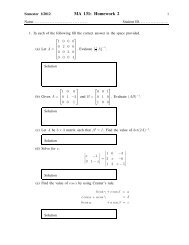
MA112 Section 750001: Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 43That is, we want to f<strong>in</strong>d scalars k 1 and k 2 such thatv = k 1 e 1 +k 2 e 2 (3.7)We can f<strong>in</strong>d k 1 by tak<strong>in</strong>g the dot product of v with e 1 . This yieldsSimilarly,v·e 1 = (k 1 e 1 +k 2 e 2 )·e 1= k 1 (e 1 ·e 1 )+k 2 (e 2 ·e 1 )= k 1 ‖e 1 ‖ 2 +0 = k 1v·e 2 = (k 1 e 1 +k 2 e 2 )·e 2 = k 1 (e 1 ·e 2 )+k 2 (e 2 ·e 2 ) = 0+k 2 ‖e 2 ‖ 2 = k 2Substitut<strong>in</strong>g these expressions for k 1 and k 2 <strong>in</strong> (3.7) yieldsv = (v·e 1 )e 1 +(v·e 2 )e 2 (3.8)In this formula we call (v·e 1 )e 1 and (v·e 2 )e 2 the vector components of v along e 1 ande 2 , respectively; and we call v · e 1 and v · e 2 the scalar components of v along e 1 ande 2 , respectively.If θ denote the angle between v and e 1 , thenv·e 1 = ‖v‖cosθ and v·e 2 = ‖v‖s<strong>in</strong>θand the decomposition (3.7) can be expressed asExample 3.16 Letv = 〈2,3〉, e 1 =v = (‖v‖cosθ)e 1 +(‖v‖s<strong>in</strong>θ)e 2 (3.9)〈 1 √2 ,〉 〈1√ , and e 2 = −√ 1 ,2 2〉1√2F<strong>in</strong>d the scalar components of v along e 1 and e 2 and the vector components of v along e 1and e 2 .Solution .........Example 3.17 A rope is attached to a 100-lb block on a ramp that is <strong>in</strong>cl<strong>in</strong>ed at an angleof 30 ◦ with the ground.30 ◦How much force does the block exert aga<strong>in</strong>st the ramp, and how much force must be appliedto the rope <strong>in</strong> a direction parallel to the ramp to prevent the block from slid<strong>in</strong>g down theramp?Solution .........