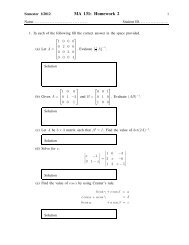
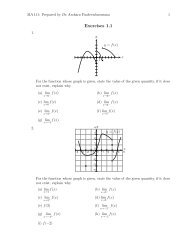
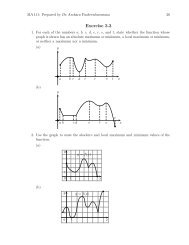
Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
MA112 Section 750001: Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 31Region Descriptionxy-plane Consists of all po<strong>in</strong>ts of the form (x,y,0)xz-plane Consists of all po<strong>in</strong>ts of the form (x,0,z)yz-plane Consists of all po<strong>in</strong>ts of the form (0,y,z)x-axis Consists of all po<strong>in</strong>ts of the form (x,0,0)y-axis Consists of all po<strong>in</strong>ts of the form (0,y,0)z-axis Consists of all po<strong>in</strong>ts of the form (0,0,z)Distance <strong>in</strong> 3-Space; SpheresRecall that <strong>in</strong> 2-space the distance d between the po<strong>in</strong>ts P 1 (x 1 ,y 1 ) and P 2 (x 2 ,y 2 ) isd = √ (x 2 −x 1 ) 2 +(y 2 −y 1 ) 2The distance formula <strong>in</strong> 3-space has the same form, but it has a third term to account forthe added dimension. The distance between the po<strong>in</strong>ts P 1 (x 1 ,y 1 ,z 1 ) and P 2 (x 2 ,y 2 ,z 2 ) isd = √ (x 2 −x 1 ) 2 +(y 2 −y 1 ) 2 +(z 2 −z 1 ) 2Example 3.1 F<strong>in</strong>d the distance d between the po<strong>in</strong>ts (2,−3,4) and (−3,2,−5).Solution .........Recall that the standard equation of a circle <strong>in</strong> 2-space that has center (x 0 ,y 0 ) andradius r is(x−x 0 ) 2 +(y −y 0 ) 2 = r 2Analogously, standard equation of the sphere <strong>in</strong> 3-space that has center (x 0 ,y 0 ,z 0 )and radius r is(x−x 0 ) 2 +(y −y 0 ) 2 +(z −z 0 ) 2 = r 2 (3.1)Iftheterms<strong>in</strong>(3.1)areexpandedandliketermsarecollected, thentheresult<strong>in</strong>gequationhas the formx 2 +y 2 +z 2 +Gx+Hy +Iz +J = 0 (3.2)Example 3.2 F<strong>in</strong>d the center and radius of the sphereSolution .........x 2 +y 2 +z 2 −10x−8y −12z +68 = 0In general, complet<strong>in</strong>g the squares <strong>in</strong> (3.2) produces an equation of the form(x−x 0 ) 2 +(y −y 0 ) 2 +(z −z 0 ) 2 = k 2• If k > 0, then the graph of this equation is a sphere with center (x 0 ,y 0 ,z 0 ) and radius√k.• If k = 0, then the sphere has radius zero, so the graph is the s<strong>in</strong>gle po<strong>in</strong>t (x 0 ,y 0 ,z 0 ).