Lecture 2 - Basic Components Of An Electric Drives System
Lecture 2 - Basic Components Of An Electric Drives System
Lecture 2 - Basic Components Of An Electric Drives System
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
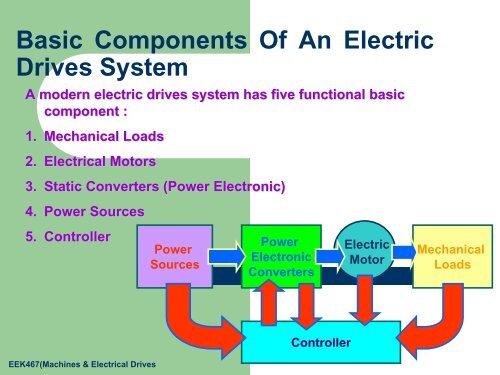
<strong>Basic</strong> <strong>Components</strong> <strong>Of</strong> <strong>An</strong> <strong>Electric</strong><strong>Drives</strong> <strong>System</strong>A modern electric drives system has five functional basiccomponent :1. Mechanical Loads2. <strong>Electric</strong>al Motors3. Static Converters (Power Electronic)4. Power Sources5. ControllerPowerSourcesPowerElectronicConverters<strong>Electric</strong>MotorMechanicalLoadsEEK467(Machines & <strong>Electric</strong>al <strong>Drives</strong>Controller
The basic criterion in selecting an electric motor for a givendrives application :1. Power level and performance required by the loads during steady-state state anddynamic operation.Ex: In application for which a high starting torque is needed a dc series motormight be a better choice than an ac induction motor.In Constant speed applications, synchronous motor be more suitable than inductionor dc motors2. Environmental factors (determine the motor type)Ex: In food processing, chemical industries, aviation, where the environment mustbe clean and free from arcs, dc motor can not be used unless they areencapsulated.3. The cost of the electric motors.In general, brushless dc motors are more expensive, whereas squirrel cageinduction motors are the choppers4. The function of converters (wave forms)Ex: If the power source is an ac type and the motor is a dc machine. The convertertransforms the ac waveform to dc. (stability, efficiency and performance of motorthat using this converter.
1. Mechanical LoadsMechanical loads exhibit wide variations of speed-torque characteristics, Generallycan be expressed as :⎛T = CTr⎜⎝nnr⎟ ⎞⎠k……….1Where : C is proportionality constantT r is the loads torquen r is speed of loadn is operating speedP = TωThe mechanical power P of the loadtorque T is given by :P =Tω2πnω = 2πf=60
Type of the Mechanical Loads:1. Torque Independent of Speed (torque constant)The power linear dependent of speed, Ex: Hoist or the pumping ofwater or gas against constant pressure.2. Torque Linearly Dependent on SpeedEx: Motor driving a dc generator connected toa fixed-resistance load, and the field of thegenerator is constant.3. Torque Proportional to the Squareof SpeedEx: fans, centrifugal pumps, andpropeller.4. Torque Inversely Proportional to SpeedEx: Milling and boring machines. Theload usually requires a large torque atstarting speed and at low speeds.
2. <strong>Electric</strong> Motors Speed-Torque Characteristics<strong>Electric</strong> motors have wide variation of speed-torque characteristicsCurve I : Synchronous or reluctance motor (Constant speed)Curve II : Shunt or separately excited dcmotor (speed slightly reducedwhen the load torque increase)Curve III : Series dc motor (speed is highat light loading condition and lowat heavy loading)Curve IV : Induction motor (during steadystate, they operation at the linearportion of speed-torquecharacteristic speed is high at lightloading, the maximum developedtorque is limited to T maxIn electric drive application, electric motors should be selected to match theintended performance of loads. Ex: In constant speed application, thesynchronous motor is probably the best option.
3. Power SourcesTwo major type of power sources are used in industrialapplications:1. Alternating Current (ac), single phase or three-phase, 60Hz or60 Hz, 240V/415V, 220V/380V, 120V/90V, 11kV/415V, etc.2. Direct Current (dc)Extensive industrial installation usually have more than one typeof power sources at different voltages and frequencies,Commercial airplanes, for examples, may have a 400Hz acsources in additional a 270 volt sources.
4. ConvertersThe main function of converters is to transform the waveform of a powersources to that the required by an electric motor in order to achieve thedesired performance.Type of Converters :1. dc to ac converter (inverter). The output of this converter isfrequency, current/voltage can be adjusted according to theapplication2. dc to dc converter (dc chopper). The output of this converter isvariable magnitude of voltage.3. ac to dc converter (rectifier). The output of this converter is variablemagnitude of dc voltage, input is single or three-phase ac voltage.4. ac to ac converter (ac chopper). The output of this converter isfrequency and ac variable voltage, the input is constant frequencyand ac voltage.
Motor DC drives <strong>System</strong> by Using Two Static Converters(Rectifiers)
Motor DC drives <strong>System</strong> by Using Three Static Converters (TwoRectifiers and one DC Chopper)
Equivalent Circuit of Separately DC MotorV = RfaafIV = R I += RaT = KdIvaafI+fEgKIav= B ω +T Lω IfVω =a− RKvIafIa=VKva− RaIa( Vf/ Rf)P =T dω
Characteristic of Separately Excited DC Motor
Equivalent Circuit of Series DC Motor(14)Eag= Kavω I = KV = ( R + R ) I += ( R + R ) Iafffaa+vEKω Igvaω IfT = K I I =dvfaK= B ω +T LvI2aP =T dωVa−( Ra+ Rf) IaVa−(Ra+ Rf) Iω ==K IK Ivfvaa
Characteristic of Series Excited DC Motor
Mode : MotoringSeparately DC MotorSeries DC Motor
Mode : Regenerative BrakingSeparately DC MotorSeries DC Motor
Mode : Dynamic BrakingSeparately DC MotorSeries DC Motor
Mode : Plugging BrakingSeparately DC MotorSeries DC Motor