Verteporfin photodynamic therapy for neovascular age-related ...
Verteporfin photodynamic therapy for neovascular age-related ...
Verteporfin photodynamic therapy for neovascular age-related ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
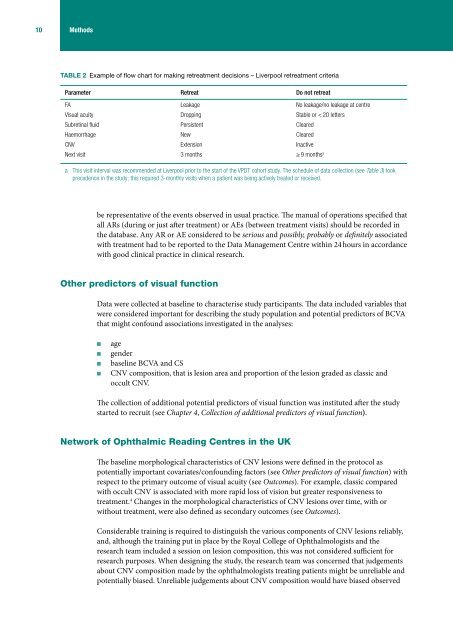
10 MethodsTABLE 2 Example of flow chart <strong>for</strong> making retreatment decisions – Liverpool retreatment criteriaParameter Retreat Do not retreatFA Leak<strong>age</strong> No leak<strong>age</strong>/no leak<strong>age</strong> at centreVisual acuity Dropping Stable or < 20 lettersSubretinal fluid Persistent ClearedHaemorrh<strong>age</strong> New ClearedCNV Extension InactiveNext visit 3 months ≥ 9 months aa This visit interval was recommended at Liverpool prior to the start of the VPDT cohort study. The schedule of data collection (see Table 3) tookprecedence in the study; this required 3-monthly visits when a patient was being actively treated or received.be representative of the events observed in usual practice. The manual of operations specified thatall ARs (during or just after treatment) or AEs (between treatment visits) should be recorded inthe database. Any AR or AE considered to be serious and possibly, probably or definitely associatedwith treatment had to be reported to the Data Man<strong>age</strong>ment Centre within 24 hours in accordancewith good clinical practice in clinical research.Other predictors of visual functionData were collected at baseline to characterise study participants. The data included variables thatwere considered important <strong>for</strong> describing the study population and potential predictors of BCVAthat might confound associations investigated in the analyses:■■■■■■■■<strong>age</strong>genderbaseline BCVA and CSCNV composition, that is lesion area and proportion of the lesion graded as classic andoccult CNV.The collection of additional potential predictors of visual function was instituted after the studystarted to recruit (see Chapter 4, Collection of additional predictors of visual function).Network of Ophthalmic Reading Centres in the UKThe baseline morphological characteristics of CNV lesions were defined in the protocol aspotentially important covariates/confounding factors (see Other predictors of visual function) withrespect to the primary outcome of visual acuity (see Outcomes). For example, classic comparedwith occult CNV is associated with more rapid loss of vision but greater responsiveness totreatment. 4 Changes in the morphological characteristics of CNV lesions over time, with orwithout treatment, were also defined as secondary outcomes (see Outcomes).Considerable training is required to distinguish the various components of CNV lesions reliably,and, although the training put in place by the Royal College of Ophthalmologists and theresearch team included a session on lesion composition, this was not considered sufficient <strong>for</strong>research purposes. When designing the study, the research team was concerned that judgementsabout CNV composition made by the ophthalmologists treating patients might be unreliable andpotentially biased. Unreliable judgements about CNV composition would have biased observed