Climate Change and Tourism - UNEP - Division of Technology ...
Climate Change and Tourism - UNEP - Division of Technology ...
Climate Change and Tourism - UNEP - Division of Technology ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
50 <strong>Climate</strong> <strong>Change</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Tourism</strong> – Responding to Global Challenges<br />
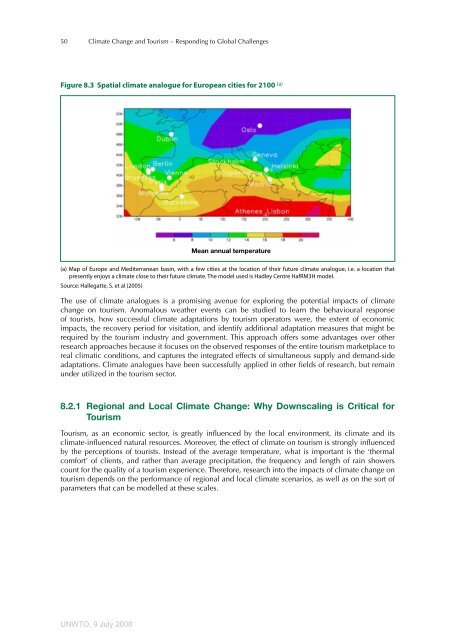
Figure 8.3 Spatial climate analogue for European cities for 2100 (a)<br />
(a) Map <strong>of</strong> Europe <strong>and</strong> Mediterranean basin, with a few cities at the location <strong>of</strong> their future climate analogue, i.e. a location that<br />
presently enjoys a climate close to their future climate. The model used is Hadley Centre HafRM3H model.<br />
Source: Hallegatte, S. et al (2005)<br />
The use <strong>of</strong> climate analogues is a promising avenue for exploring the potential impacts <strong>of</strong> climate<br />
change on tourism. Anomalous weather events can be studied to learn the behavioural response<br />
<strong>of</strong> tourists, how successful climate adaptations by tourism operators were, the extent <strong>of</strong> economic<br />
impacts, the recovery period for visitation, <strong>and</strong> identify additional adaptation measures that might be<br />
required by the tourism industry <strong>and</strong> government. This approach <strong>of</strong>fers some advantages over other<br />
research approaches because it focuses on the observed responses <strong>of</strong> the entire tourism marketplace to<br />
real climatic conditions, <strong>and</strong> captures the integrated effects <strong>of</strong> simultaneous supply <strong>and</strong> dem<strong>and</strong>-side<br />
adaptations. <strong>Climate</strong> analogues have been successfully applied in other fields <strong>of</strong> research, but remain<br />
under utilized in the tourism sector.<br />
8.2.1 Regional <strong>and</strong> Local <strong>Climate</strong> <strong>Change</strong>: Why Downscaling is Critical for<br />
<strong>Tourism</strong><br />
<strong>Tourism</strong>, as an economic sector, is greatly influenced by the local environment, its climate <strong>and</strong> its<br />
climate-influenced natural resources. Moreover, the effect <strong>of</strong> climate on tourism is strongly influenced<br />
by the perceptions <strong>of</strong> tourists. Instead <strong>of</strong> the average temperature, what is important is the ‘thermal<br />
comfort’ <strong>of</strong> clients, <strong>and</strong> rather than average precipitation, the frequency <strong>and</strong> length <strong>of</strong> rain showers<br />
count for the quality <strong>of</strong> a tourism experience. Therefore, research into the impacts <strong>of</strong> climate change on<br />
tourism depends on the performance <strong>of</strong> regional <strong>and</strong> local climate scenarios, as well as on the sort <strong>of</strong><br />
parameters that can be modelled at these scales.<br />
UNWTO, 9 July 2008<br />
Mean annual temperature