The probable impacts of climate change on poverty - UNDP
The probable impacts of climate change on poverty - UNDP
The probable impacts of climate change on poverty - UNDP
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
6.8.1 Impacts <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Climate Change <strong>on</strong> Health- Percepti<strong>on</strong><br />
Human health suffers from different climatic variability and shocks in different ways. <str<strong>on</strong>g>The</str<strong>on</strong>g> experts informed that<br />
health is affected, especially during and after shocks like flood and cycl<strong>on</strong>e. Slow <strong>on</strong>sets <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> climatic system have<br />
also <str<strong>on</strong>g>impacts</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>on</strong> health. Flood affects sources <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> drinking water and sanitati<strong>on</strong> system through c<strong>on</strong>taminati<strong>on</strong><br />
which lead to out break <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> diarrhoea, cholera, skin diseases including scabies, drowning, snake bite and even<br />
death. Cycl<strong>on</strong>e, sea level rise and salinity intrusi<strong>on</strong> cause outbreaks <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> diarrhoea, cholera and other water borne<br />
diseases, use <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> saline water causes hypertensi<strong>on</strong>, increase blood pressure, corrosive effects due to salt in air,<br />
scabies and other skin diseases. Besides that, drought, erratic rainfall and temperature variati<strong>on</strong> increase vector<br />
borne diseases, heat stroke, malnutriti<strong>on</strong>, fever etc. Cold wave creates respiratory problem, especially that <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
children and the old.<br />
It is already proven that different types <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> diseases breakout during and after flood. In future, these <str<strong>on</strong>g>impacts</str<strong>on</strong>g> will<br />
be more frequent and severe since intensity and frequency <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> flood will increase. Similarly, cycl<strong>on</strong>e and storm<br />
surge will affect human health and lives severely with the increasing intensity and frequency <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> cycl<strong>on</strong>e. Besides<br />
this, temperature variati<strong>on</strong>, erratic rainfall will increase incidence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> vector borne diseases like dengue, malaria.<br />
Lack <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> fresh water in drought pr<strong>on</strong>e and coastal areas will increase malnutriti<strong>on</strong>, extreme <strong>poverty</strong>, bring <str<strong>on</strong>g>change</str<strong>on</strong>g>s<br />
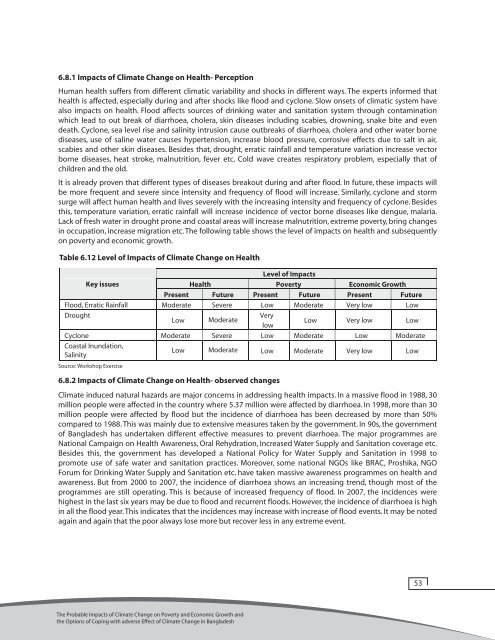
in occupati<strong>on</strong>, increase migrati<strong>on</strong> etc. <str<strong>on</strong>g>The</str<strong>on</strong>g> following table shows the level <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>impacts</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>on</strong> health and subsequently<br />
<strong>on</strong> <strong>poverty</strong> and ec<strong>on</strong>omic growth.<br />
Table 6.12 Level <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Impacts <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Climate Change <strong>on</strong> Health<br />
Key issues<br />
Health<br />
Level <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Impacts<br />
Poverty Ec<strong>on</strong>omic Growth<br />
Present Future Present Future Present Future<br />
Flood, Erratic Rainfall Moderate Severe Low Moderate Very low<br />
Low<br />
Drought<br />
Low Moderate<br />
Very<br />
low<br />
Low Very low<br />
Low<br />
Cycl<strong>on</strong>e Moderate Severe Low Moderate Low Moderate<br />
Coastal Inundati<strong>on</strong>,<br />
Salinity<br />
Low Moderate Low Moderate Very low Low<br />
Source: Workshop Exercise<br />
6.8.2 Impacts <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Climate Change <strong>on</strong> Health- observed <str<strong>on</strong>g>change</str<strong>on</strong>g>s<br />
Climate induced natural hazards are major c<strong>on</strong>cerns in addressing health <str<strong>on</strong>g>impacts</str<strong>on</strong>g>. In a massive flood in 1988, 30<br />
milli<strong>on</strong> people were affected in the country where 5.37 milli<strong>on</strong> were affected by diarrhoea. In 1998, more than 30<br />
milli<strong>on</strong> people were affected by flood but the incidence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> diarrhoea has been decreased by more than 50%<br />
compared to 1988. This was mainly due to extensive measures taken by the government. In 90s, the government<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Bangladesh has undertaken different effective measures to prevent diarrhoea. <str<strong>on</strong>g>The</str<strong>on</strong>g> major programmes are<br />
Nati<strong>on</strong>al Campaign <strong>on</strong> Health Awareness, Oral Rehydrati<strong>on</strong>, Increased Water Supply and Sanitati<strong>on</strong> coverage etc.<br />
Besides this, the government has developed a Nati<strong>on</strong>al Policy for Water Supply and Sanitati<strong>on</strong> in 1998 to<br />
promote use <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> safe water and sanitati<strong>on</strong> practices. Moreover, some nati<strong>on</strong>al NGOs like BRAC, Proshika, NGO<br />
Forum for Drinking Water Supply and Sanitati<strong>on</strong> etc. have taken massive awareness programmes <strong>on</strong> health and<br />
awareness. But from 2000 to 2007, the incidence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> diarrhoea shows an increasing trend, though most <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the<br />
programmes are still operating. This is because <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> increased frequency <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> flood. In 2007, the incidences were<br />
highest in the last six years may be due to flood and recurrent floods. However, the incidence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> diarrhoea is high<br />
in all the flood year. This indicates that the incidences may increase with increase <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> flood events. It may be noted<br />
again and again that the poor always lose more but recover less in any extreme event.<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>The</str<strong>on</strong>g> Probable Impacts <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Climate Change <strong>on</strong> Poverty and Ec<strong>on</strong>omic Growth and<br />
the Opti<strong>on</strong>s <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Coping with adverse Effect <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Climate Change in Bangladesh<br />
53