21st century classroom rubric - Galileo Educational Network
21st century classroom rubric - Galileo Educational Network
21st century classroom rubric - Galileo Educational Network
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
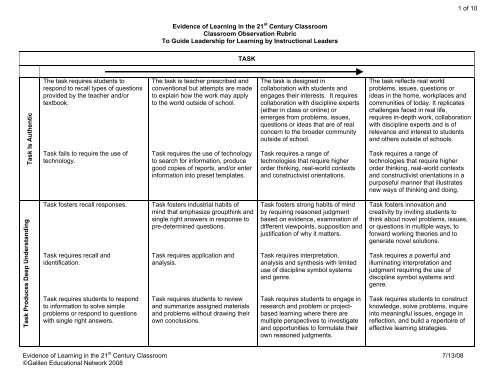
1 of 10Evidence of Learning in the 21 st Century ClassroomClassroom Observation RubricTo Guide Leadership for Learning by Instructional LeadersTASKTask Is AuthenticThe task requires students torespond to recall types of questionsprovided by the teacher and/ortextbook.Task fails to require the use oftechnology.The task is teacher prescribed andconventional but attempts are madeto explain how the work may applyto the world outside of school.Task requires the use of technologyto search for information, producegood copies of reports, and/or enterinformation into preset templates.The task is designed incollaboration with students andengages their interests. It requirescollaboration with discipline experts(either in class or online) oremerges from problems, issues,questions or ideas that are of realconcern to the broader communityoutside of school.Task requires a range oftechnologies that require higherorder thinking, real-world contextsand constructivist orientations.The task reflects real worldproblems, issues, questions orideas in the home, workplaces andcommunities of today. It replicateschallenges faced in real life,requires in-depth work, collaborationwith discipline experts and is ofrelevance and interest to studentsand others outside of schools.Task requires a range oftechnologies that require higherorder thinking, real-world contextsand constructivist orientations in apurposeful manner that illustratesnew ways of thinking and doing.Task Produces Deep UnderstandingTask fosters recall responses.Task requires recall andidentification.Task requires students to respondto information to solve simpleproblems or respond to questionswith single right answers.Task fosters industrial habits ofmind that emphasize groupthink andsingle right answers in response topre-determined questions.Task requires application andanalysis.Task requires students to reviewand summarize assigned materialsand problems without drawing theirown conclusions.Task fosters strong habits of mindby requiring reasoned judgmentbased on evidence, examination ofdifferent viewpoints, supposition andjustification of why it matters.Task requires interpretation,analysis and synthesis with limiteduse of discipline symbol systemsand genre.Task requires students to engage inresearch and problem or projectbasedlearning where there aremultiple perspectives to investigateand opportunities to formulate theirown reasoned judgments.Task fosters innovation andcreativity by inviting students tothink about novel problems, issues,or questions in multiple ways, toforward working theories and togenerate novel solutions.Task requires a powerful andilluminating interpretation andjudgment requiring the use ofdiscipline symbol systems andgenre.Task requires students to constructknowledge, solve problems, inquireinto meaningful issues, engage inreflection, and build a repertoire ofeffective learning strategies.Evidence of Learning in the 21 st Century Classroom 7/13/08©<strong>Galileo</strong> <strong>Educational</strong> <strong>Network</strong> 2008
2 of 10AssessmentAssessment Is ComprehensiveAssessment is summative.Assessment of learning provides alimited picture of student learning.Students fail to use technology toobtain feedback.Assessment is primarily summativein nature; however the teacheruses the information to guideplanning.Assessment of learning provides ageneral picture of student learningand competencies.Students use technology in limitedways to obtain feedback fromsimple applications.Assessment is primarily formative.Formative assessment is used toguide student learning at keypoints throughout the task.Students co-construct criteria, setgoals and they obtain timely,specific feedback about their workto improve learning from peers, selfand the teacher. The teacher usesassessment for learning to informinstructional decisions.Assessment of learning providesan accurate, defensible picture ofstudent learning andcompetencies.Students use technology(interactive, responsive systemsand applications) to improve workand obtain immediate feedbackabout their learning.All assessment is focused onimproving learning. It is integral tothe learning and woven into allaspects of the learning. Studentsco-construct criteria and use it toguide learning, set goals, obtainfeedback from a variety of peopleboth inside and outside the<strong>classroom</strong> to improve theirlearning. The teacher usesassessment to inform instructionaldecisions and reflect upon andimprove practice.Assessment of learning providesan accurate, comprehensive,defensible picture of studentlearning and competencies at thetime the grade is awarded.Students use technology to seekand obtain feedback from multiplesources on an ongoing basis toimprove and guide learning.Teacher uses technology to recordmarks and generate report cards.Teacher and students use a limitedrange of technologies to documentstudent learning.Teacher and students use a widerange of technologies to documentstudent learning through an onlineportfolio.Teacher and students use a widerange of technologies to documentstudent learning through an onlineportfolio which invites the outsideworld to provide commentary onthe work.Evidence of Learning in the 21 st Century Classroom 7/13/08©<strong>Galileo</strong> <strong>Educational</strong> <strong>Network</strong> 2008
4 of 10Learning EnvironmentPhysical Learning Environment Is Conducive ToLearningWalls are bare.Desks are immobile and arrangedto accommodate solitary seatwork.Students and teachers rarely haveaccess to technology.Assistive technologies areunavailable in the <strong>classroom</strong>.Walls are adorned withcommercially produced productsand posters.Furniture is moveable, howeverdesks are only occasionallyarranged to facilitate cooperativegroup work.Students and teachers have limitedaccess to technologies through acomputer lab that must be bookedin advance.Assistive technologies areavailable in the <strong>classroom</strong> butsome features have been disabled.Walls serve as a showcase fordisplaying exemplary student work.Furniture is moveable to enableflexible collaborative group work.Students and teachers have readyaccess to an array of technologiesto support learning needs as theyemerge.Assistive technologies are enabledand available for the use bystudents requiring them.Walls serve as a canvas fordocumenting collective knowledgeand learning processes.Furniture and space arrangementsmaximize flexibility andaccommodate students and theirlearning needs.Students and teachers haveaccess to a wide range oftechnologies i.e.: books online, oniPod, pictures/images taken orcreated, creating own data andanalyze, VC with experts, humanresources that enable them toproduce authentic high qualityproducts and performances.Assistive technologies are enabledand seamlessly incorporated intolearning tasks and activities.Resources MeetLearning NeedsLearning environment isinformation poor, prescribed underthe “1 size fits all model” – there isone path and one uniformoutcome.Learning environment provides fewinformation options and studentsmay choose from these limitedchoices.Learning environment isinformation rich with both print andonline resources and students areencouraged to choose the mostappropriate resources for the taskat hand.Learning environment isinformation rich with online andprint resources and students areencouraged to use resources topush the boundaries of creativityand innovation.Evidence of Learning in the 21 st Century Classroom 7/13/08©<strong>Galileo</strong> <strong>Educational</strong> <strong>Network</strong> 2008
5 of 10Students are disinterested in andsee no relevance to the work theyare asked to complete.Students are compliant but seelittle relevance to the work they areasked to complete.Students can make generalconnections between the work andself, others and/or the real world.Students are deeply involved in thework and know why it matters tothem, to the discipline and/or to thereal world.Learning Is EngagingMost students are off task andsome are acting out.A quiet, somber, joyless climatepervades the <strong>classroom</strong>.Students go through the motions ofcompleting work in order to avoid apoor mark.Some students are off task whileothers are compliantly doing thework.An efficient, respectful andsupportive climate pervades the<strong>classroom</strong>.Students complete work with littleenthusiasm or do just enough toget by.Students do the work but theirprimary motivation is to earngrades.An inviting, nurturing, intellectuallyexciting, climate pervades the<strong>classroom</strong>.Students are motivated by gradesto do a good job.Students are emotionally andintellectually invested in the work(don’t want to stop/put itdown/leave class/school).An intellectually rich, supportiverisk taking, student-directed climatepervades the <strong>classroom</strong>.Students are so excited by learningthat they spend extra time andeffort doing their work. They deriveexcitement and pleasure from thework they are doing and gradesare not their primary motivation.Evidence of Learning in the 21 st Century Classroom 7/13/08©<strong>Galileo</strong> <strong>Educational</strong> <strong>Network</strong> 2008
6 of 10Students are passive anddisengaged from the work they areassigned.Students are compliant but exhibitlittle enthusiasm or ownership forthe work they are assigned.Students are active in their ownlearning and able to managesignificant aspects of it.Students are highly engaged asthey direct and determine thecourse of their own learning.Students Are Self-DirectedStudents fail to have access toassessment criteria to set personalgoals therefore are unable toparticipate in goal setting byidentifying proof of learning andreflecting on the gap betweencurrent achievement and expectedachievement.Students do not have sufficientaccess to assessment criteria whilelearning and therefore have limitedopportunities to participate in goalsetting by identifying proof oflearning and reflecting on the gapbetween current achievement andexpected achievement.Students have sufficient access toassessment criteria and feedbackwhile learning and therefore areable to:• identify proof of learning,• reflect on the gap betweencurrent achievement andexpected achievement,• direct and monitor their ownlearning as it progresses, and• engage in goal setting.Students have sufficient access toassessment criteria and ongoingspecific feedback from a variety ofsources in all aspects of learningand therefore are able to:• identify proof of learning,• reflect on the gap betweencurrent achievement andexpected achievement,• direct major aspects of theirlearning,• develop effective learningstrategies, and• engage in accurate goal setting.Students use agendas orcalendars as prescribed by theteacher.Students use agendas orcalendars to record due dates andreminders.Students use calendars, agendasand project managementapplications (electronic and paper)to manage work flow.Students use calendars and projectmanagement applications(electronic and paper) on aconsistent basis to coordinatelearning with others and managework flow.Evidence of Learning in the 21 st Century Classroom 7/13/08©<strong>Galileo</strong> <strong>Educational</strong> <strong>Network</strong> 2008
7 of 10Relationships/Learning CommunityStudents work alone with someopportunities to orally answerquestions and share ideas aboutthe topic or subject content.Students respond to tasksassigned by the teacher.There is no expectation thatstudents use technology in theirday-to-day work.Students share ideas to buildcollective understanding of thetopic or subject content.Students have opportunities toselect among project optionsprovided by the teacher.There is an expectation thatstudents will use technology tostore individual day-to-day work ina personal online folder.Students interact with each otherabout ideas of a topic underconsideration (the talk is aboutdiscipline subject matter andincludes higher-order thinking suchas making distinctions, applyingideas, forming generalizations,raising questions).Students have opportunities toprovide input into the task design,product and performanceoutcomes.There is an expectation thatstudents will use technology tocontribute to group work usingshared common folders and useonline <strong>classroom</strong> discussionforums.Students engage in considerableinteraction about the ideas of atopic (the talk is about disciplinesubject matter and includes higherorderthinking such as makingdistinctions, applying ideas,forming generalizations, raisingquestions) in which the dialoguebuilds coherently on participants'ideas to promote improvedcollective understanding of a topic.Students have opportunities forsubstantive input into task designand make key decisions regardinglearning approaches andproduct/performance outcomes.There is an expectation thatstudents will use a variety oftechnologies to extend <strong>classroom</strong>interactions, build knowledge andinitiate collaboration with othersbeyond the <strong>classroom</strong>.Evidence of Learning in the 21 st Century Classroom 7/13/08©<strong>Galileo</strong> <strong>Educational</strong> <strong>Network</strong> 2008
8 of 10Role of TeacherTeacher Designs LearningThe teacher is knowledgeableabout Alberta Programs of Studyoutcomes and uses them to deliverinstruction.Teacher fails to assesstechnologies or learning resources.The teacher has a clearunderstanding of Alberta Programsof Study outcomes and uses themto explore ways to employ projectbasedor problem-based learning.Teacher has limited ability toassess technology; therefore,students sometimes useinappropriate technologies andlearning resources.The teacher has an excellentunderstanding of Alberta Programsof Study outcomes and skillfullymaps them to strong project-basedor problem-based learning tasksand activities.Teacher critically assesses themost appropriate technologies andlearning resources to supportstudent learning.The teacher has an exceptionalunderstanding of Alberta Programsof Study outcomes and skillfullymaps them to issues, questionsand problems in the world outsidethe <strong>classroom</strong> walls in aconnected, integrated, crosscurricularmanner.Teacher critically assesses thevalidity of technologies being usedto maximize student learning, levelthe playing field and democratizelearning.Teacher Is ACognitive CoachTeacher asks students to come tohis/her desk if they encounterdifficulties while working quietly attheir desks.The teacher circulates amongstudents as they work to ensurethat they are following directionsand assisting them as needed.The teacher circulates among thestudents as they workcollaboratively, to monitor learning,stimulate discussion, posequestions, provoke thinking orsuggest resources as requested orappropriate.The teacher engages students indialogue, as they work, to extendlearning, stimulate discussion,pose questions, provoke thinking,suggest resources and helpstudents determine their nextlearning steps.Teacher Is A GuideThe teacher provides directions onhow to complete assignments.Teacher provides choices ofproducts that students may use incompleting assignments.The teacher helps students tolearn how, when, and why to usedifferent strategies and provideshints, clues, and other feedback tothe entire class based on anobservation of individual studentsor in anticipation of likely problems.The teacher and other instructionalpartners make their thinkingprocesses public, help students tolearn how, when and why to usedifferent strategies andtechnologies that provide hints,clues, or other feedback on astudent-by-student basis.Evidence of Learning in the 21 st Century Classroom 7/13/08©<strong>Galileo</strong> <strong>Educational</strong> <strong>Network</strong> 2008
9 of 10The teacher has experience usingthe instructional materials.The teacher provides students withopportunities to explore areaswithin the teacher’s expertise.The teacher provides studentsopportunities to explore areasoutside of the teacher’s expertise,but always stays a step ahead ofthe students.The teacher extends his or her ownknowledge and questions alongwith the students’ and invitesstudents to become a part of theinstructional process.The teacher relies on and rarelystrays from prescribed resourceseven if information is outdatedand/or inaccurate.The teacher occasionally bringscurrent events related to curriculumtopics into the <strong>classroom</strong> to sharewith students.The teacher continues to learnabout and stay abreast of newknowledge related to the subjectshe/she teaches.The teacher continues to learnabout and stay abreast of disciplineknowledge as it evolves in realworld contexts.Teacher Is A LearnerThe teacher operates in isolation.The teacher participates in learningcommunities as part of a schoolinitiative but does not use onlinecommunication technologies forprofessional learning.The teacher shares lessons andactivities he/she has created.The teacher participates in learningcommunities as part of a schoolinitiative and occasionally usesonline communication technologiesfor professional learning.The teacher obtains feedbackabout instructional planning fromcolleagues and mentors.The teacher participates in schoolbasedand online learningcommunities to access continuousongoing professional learning toimprove practice.The teacher works in collaborationwith others to design robustlearning tasks and obtain feedbackabout instructional planning fromcolleagues and mentors.The teacher participates in schoolbasedand online learningcommunities to access and extendcontinuous ongoing professionallearning for self, to improvepractice and to advance thelearning of colleagues.Teacher rarely consultseducational research.Teacher is knowledgeable aboutresearch but makes little or noattempt to incorporate ideas intoown practice.Teacher is knowledgeable aboutand acts in accordance withcurrent research.Teacher takes the initiative toinform self about current researchliterature and incorporates it intoteaching and learning practices.Teacher Has A StrongInstructional RepertoireTeacher represents informationand concepts one way.Instruction reflects a “one size fitsall” means of information andconcept representation.Teacher represents informationand concepts in more than oneway.Instruction reflects some aspects ofUDL principles in that students areprovided with multiple, flexiblemeans of expression; howeverinstruction is limited whenrepresenting information andconcepts.Teacher ensures that ideas,concepts and information arerepresented in multiple, flexibleways.Instruction reflects UDL principleswhere a range of learning activitiesand formats are provided by theteacher and available to allstudents to meet their uniquelearning needs.Teacher has an extensiverepertoire of responsive teachingstrategies to represent importantconcepts, information and ideas inrichly textured ways.Instruction reflects seamlessintegration of UDL principles wherethe teacher anticipates the studentlearning needs and plans for andprovides a wide range of learningactivities, formats and technologiesto suit the needs of every student.Evidence of Learning in the 21 st Century Classroom 7/13/08©<strong>Galileo</strong> <strong>Educational</strong> <strong>Network</strong> 2008
10 of 10PublicityTasks and resources are availableonly within the <strong>classroom</strong>.Tasks and resources aresometimes available online forothers to see.Tasks, resources and assessmentcriteria are available online for allto see.Tasks, resources and assessmentcriteria are available online for all tosee and respond to.The Classroom Is Open and PublicPurpose for the learning is oftenunclear and the audience isexclusively the teacher.Tasks and assessment criteriaknown only to teacher.Students’ work is sent home or putup on a bulletin board.Purpose for the learning is notalways clear and the audience isother members of the class and theteacher via presentations.Tasks and assessment criteria canbe easily accessed by studentsand by parents through anewsletter that is sent home.Students present work toclassmates and parents.Purpose and audience for thelearning is clear and transparentfrom the start and open to largerschool community usingtechnology.Task and assessment criteria arepublished online for parents andstudents to view on an as needsbasis.Students respond to and explaintheir work to peers, parents and atleast one other audience outside ofschool using appropriate media.Purpose and audience for thelearning is clear and transparentfrom the start, responsive toemerging needs and open to thelarger globally connectedcommunity.Task and assessment criteria arepublished online along withexemplars of student work.Parents, experts and members ofthe larger community are invited torespond to it.Students use media andelaborated forms of communicationto present work in innovative waysto audiences inside and outside ofthe school and invite feedback.Class newsletters and notices aresent home in paper copy only.Class newsletters and notices areavailable in both paper and viaemail.Class newsletters and notices arepublished online, available as pdfdocuments or sent home in papercopy as requested by parents.Class newsletters and notices arepublished online, available as pdfdocuments, through subscriptionvia a RSS feed or as a paper copyas requested by parents.Evidence of Learning in the 21 st Century Classroom 7/13/08©<strong>Galileo</strong> <strong>Educational</strong> <strong>Network</strong> 2008