Planck Pre-Launch Status Papers - APC - Université Paris Diderot ...
Planck Pre-Launch Status Papers - APC - Université Paris Diderot ...
Planck Pre-Launch Status Papers - APC - Université Paris Diderot ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
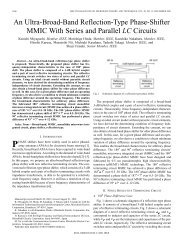
A&A 520, A8 (2010)Fig. 5. Polarisation conversion term due to bandpass mismatch, ( f s − f m )/2, (y-axis) for each LFI RCA, plotted against brightness-temperaturespectral index β (x-axis). The dotted line shows the approximation of Eq. (27).low-frequency cutoff depends on OMT return loss scaled frommeasurements of the similar 44 GHz OMTs; while the 70 GHzmodel barely covers the full bandpass in some cases (e.g. LFI-21, see Fig. 6), and hints at significant gain below its lower limitof 60 GHz, apparently in line with measurements (Zonca et al.Fig. 14).We have repeated the analysisdiscussedabovetocomparethe raw measurements with the QUCS models, where the effectsof ill-determined band edges were removed by using only thecommon frequency range of measurements and models. Evenso, deviation between model and measurements are large enoughthat the derived f s − f m values are frequently of opposite sign.This is a difficult test to pass, since we are concerned with asecond-order effect, the difference of two small terms; neverthelesswe need accuracy at this level to meet our aspirationof polarisation errors below 1%. As discussed by Zonca et al.(2009), work is planned to reduce and quantify uncertainties inthe QUCS models, which will include refined measurement andmodelling of flight spare devices.The flight data themselves can be used to isolate bandpasserrors, by differencing total intensity maps made with differenthorns, and, at 70 GHz, by differencing polarisation mapsmade independently from the three mirror-symmetric horn pairs.In such maps bandpass errors will dominate where foregroundemission is strong. This provides both a check on the predictionsfrom the model bandpasses and, in principle, an opportunity toupdate bandpass parameters, in particular ν eff ,usingtheflightdata.5.3. Cross-polarisation response across the bandpassThe components of J OMT are a subset of the complex amplitudesfrom the scattering matrix measured in laboratory testing of theOMTs (D’Arcangelo et al. 2009b), namely( )J OMT Side arm insertion loss Side arm cross pol≡. (31)Main arm cross pol Main arm insertion loss“Insertion loss” is so named since, when measured in dB, a nonzerovalue represents a departure of J ii from unity.These parameters were measured for the flight model OMTsat IFP-CNR Milan, using a vector network analyser (VNA), asdescribed by D’Arcangelo et al. (2009b). The measured phasedata also included the contribution of the adaptors connectingthe VNA to the OMT under test. The amplitude and phase contributionsfrom the adaptors, essentially a linear phase gradientacross the band, were measured and subtracted. Typical precisionfor the insertion loss signals was