Ionic Bonding
Ionic Bonding
Ionic Bonding
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Ionic</strong> <strong>Bonding</strong>
q Students know atoms combine toform molecules by sharing electrons toform covalent or metallic bonds or byexchanging electrons to form ionicbonds.q Students know salt crystals, suchas NaCl, are repeating patterns ofpositive and negative ions heldtogether by electrostatic attraction.
Bondsq Forces that hold groups of atomstogether and make them functionas a unit.v <strong>Ionic</strong> bonds – transfer ofelectronsv Covalent bonds – sharing ofelectrons
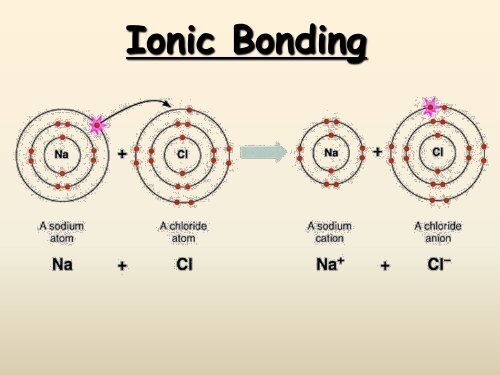
<strong>Ionic</strong> <strong>Bonding</strong>:The Formation of Sodium Chlorideq Sodium has 1 valence electronq Chlorine has 7 valence electronsq An electron transferred giveseach an octetNa: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1Cl: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 5
<strong>Ionic</strong> <strong>Bonding</strong>:The Formation of Sodium ChlorideThis transfer forms ions, eachwith an octet:Na + 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6Cl - 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6
<strong>Ionic</strong> <strong>Bonding</strong>:The Formation of Sodium ChlorideThe resulting ions come togetherdue to electrostatic attraction(opposites attract):Na + Cl -The net charge on the compoundmust equal zero
<strong>Ionic</strong> BondsMetal to NonmetalHigh ENDMetal forms cationNonmetal forms anion
MetalMonatomicCationsIon nameLithium Li + LithiumSodium Na + SodiumPotassium K + PotassiumMagnesium Mg 2+ MagnesiumCalcium Ca 2+ CalciumBarium Ba 2+ BariumAluminum Al 3+ Aluminum
NonmetalMonatomicAnionsIon NameFluorine F - FluorideChlorine Cl - ChlorideBromine Br - BromideIodine I - IodideOxygen O 2- OxideSulfur S 2- SulfideNitrogen N 3- NitridePhosphorus P 3- Phosphide
Sodium Chloride Crystal Lattice<strong>Ionic</strong> compounds formsolid crystals at ordinarytemperatures.<strong>Ionic</strong> compounds organizein a characteristiccrystal lattice ofalternating positive andnegative ions.All salts are ionic compounds and form crystals.
<strong>Ionic</strong> solids are brittleStrong repulsion breaks crystal apart.Force+ - + -+ - + -- + - ++ - + -- + - +
Characteristics of Ion <strong>Bonding</strong> in a Crystal LatticeVisual Concept
Properties of <strong>Ionic</strong> CompoundsStructure:Crystalline solidsMelting point: Generally highBoiling Point:ElectricalConductivity:Solubility inwater:Generally highExcellent conductors,molten and aqueousGenerally soluble
Lattice Energy- the ionic bond---the energy released when thecrystal lattice formation is formed---Lattice energies are listed as negativevalues to indicate that energy is given offwhen ions come together to form the ioniccrystal.The greater the latticeenergy… the stronger the ionicbonding!
VocabularyCOMPOUND2 elementsbinarycompoundNaClmore than 2elementsternarycompoundNaNO 3
VocabularyION1 atom 2 or more atomsmonatomicIonNa +polyatomicIonNO 3-
lithium atomLilithium ione - Li +e -e -3p +loss ofone valenceelectrone - 3p +e -e -fluorine atomFe -e -e - e -e -e - e - e -9p +e - gain ofone valenceelectrone -e - e -fluoride ionF 1-e - e -9p +e - e -e -e - e -
Formation of Cationlithium atomLilithium ionLi +e - e -e -3p +loss ofone valenceelectrone - 3p +e -
Formation of Anionfluorine atomFfluoride ionF 1-e -e -e -gain ofe - one valenceelectrone - 9p +e -e -e - e - e -e -e - e -e - e -9p +e - e -e -e - e -
Formation of <strong>Ionic</strong> Bondlithium ionLi +fluoride ionF 1-e -e - e -e - 3p +e -e - e -9p +e - e -e -e - e -
<strong>Ionic</strong> bonding: Li + Cl1e -3p +4n 0 2e- 1e -7e - 8e - 2e - 17p+ 18n03p +4n 02e - 8e - 8e - 2e 17p +18n 0lithium atom chlorine atom lithium ion chloride ionLi Cl [Li] + [ Cl ]–
<strong>Ionic</strong> bonding: Li + C<strong>Ionic</strong> compound formation equationLi + Cl → [Li] + [ Cl ] –
<strong>Ionic</strong> bonding: Mg + OMgO[Mg] 2+ [ O] 2–1e -12p +12n 02e - 8e - 2e -6e - 2e - 8p +8n012p +12n 02e - 8e -8e - 2e - 8p +8n01e -
Lewis DotDiagrams andBONDING (<strong>Ionic</strong> )
How do we show the valence electrons fordifferent elements?* dot diagrams were developedby American, G.N. Lewis, inthe 1920's* they are called Lewisstructure or Lewis dotdiagrams
Electron-Dot NotationTo keep track of valenceelectrons, it is helpful touse electron-dotnotation.Electron-dot notationshows only the valenceelectrons of an atom ofa particular element,indicated by dots placedaround the elementssymbol. The inner-shellelectrons are notshown.
Electron-Dot NotationClick below to watch the Visual Concept.Visual Concept
Hydrogen has one valence electronNitrogen has five valenceelectrons.
Write the electron dotdiagram for• Na• Mg• C• O• F• Ne• He1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 11s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 21s 2 2s 2 2p 21s 2 2s 2 2p 41s 2 2s 2 2p 51s 2 2s 2 2p 61s 2NaNeMgHeCOF
<strong>Ionic</strong> <strong>Bonding</strong>transfer of electronNa+1 -1ClNaCl
<strong>Ionic</strong> <strong>Bonding</strong>• All the electrons must be accountedfor!Ca +2 +2PP -3Ca-3Ca +2
<strong>Ionic</strong> <strong>Bonding</strong>Ca 2+ Ca P P 3-Ca 2+ 3 2Formula UnitCa 2+ P 3-Ca 2+Ca 2+Ca 2+P 3-P 3-
<strong>Ionic</strong> Formation EquationCa+ P3[Ca] +2 2[ P ] –3
* monatomic ions can bewritten with dot diagrams* as before, dots are used todemonstrate e-* symbol is in [brackets] torepresent ions* charge is placed on theupper right corner
Do the dot diagrams forNa, Mg, Al, P, S, Cl ions
+1-1
PracticeDraw the Lewis Dot Diagrams forthe following compounds:1. Lithium iodide2. Calcium chloride3. Potassium oxideExample: Magnesium Chloride[Mg] +2 2[ Cl ] -1
Polyatomic IonsAn example of a polyatomic ion is the ammonium ion:. It is sometimes written as toNH++4[NH ]show that the group of atoms as a whole has a charge of+1.The charge of the ammonium ion is determined asfollows:seven protons in the nitrogen atomplus the four protons in the four hydrogen atomsgive the ammonium ion a total positive charge of+11.4
When nitrogen and hydrogenatoms combine to form anammonium ion, one of theirelectrons is lost, giving thepolyatomic ion a total negativecharge of -10.The total charge is therefore(+11) + (-10) = +1.
Some examples of Lewis structures of polyatomicions are shown below.