- Page 2 and 3:
Tsubaki: RecognizedProvider forBasi
- Page 4 and 5:
RThe Powerful Tsubaki LineBecause i
- Page 6 and 7:
ContentsBefore UseNotes on Using Ro
- Page 8 and 9:
Before UseT S U B A K I D R I V E C
- Page 10 and 11:
GlossaryT S U B A K I D R I V E C H
- Page 12 and 13:
T S U B A K I D R I V E C H A I NRo
- Page 14 and 15:
T S U B A K I D R I V E C H A I NRo
- Page 16:
Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 19 and 20:
T S U B A K I D R I V E C H A I N4.
- Page 21 and 22:
"World’s No. 1"kilowatt ratings b
- Page 23 and 24:
Standard Roller ChainsOld-New Chain
- Page 27 and 28:
Standard Roller ChainsRS25, BF25-H
- Page 29 and 30:
Standard Roller ChainsRS35 Sprocket
- Page 31 and 32:
Standard Roller ChainsRS40 Sprocket
- Page 33 and 34:
Standard Roller ChainsRS50 Sprocket
- Page 35 and 36:
Standard Roller ChainsRS60 Sprocket
- Page 37 and 38:
Standard Roller ChainsRS80 Sprocket
- Page 39 and 40:
Standard Roller ChainsRS100 Sprocke
- Page 41 and 42:
Standard Roller ChainsRS120 Sprocke
- Page 43:
Standard Roller ChainsRS140 Sprocke
- Page 46 and 47:
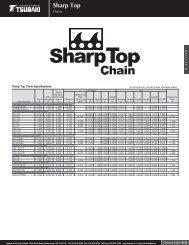
Standard Roller Chains RS Roller Ch
- Page 48 and 49:
Standard Roller Chains RS Roller Ch
- Page 50 and 51:
Standard Roller Chains RS Roller Ch
- Page 52 and 53:
Standard Roller ChainsRF320-T, RF40
- Page 56 and 57:
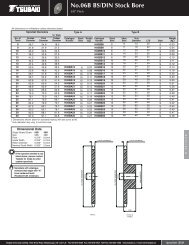
Standard Roller ChainsBS/DIN Standa
- Page 58 and 59:
BS/DIN Standard RS Roller ChainsKil
- Page 60 and 61:
BS/DIN Standard RS Roller ChainsKil
- Page 62 and 63:
Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 64 and 65:
Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 66 and 67:
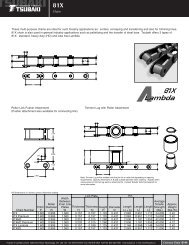
Lube-Free Roller ChainsLambda Chain
- Page 68 and 69:
Lube-Free Roller ChainsX-Lambda Cha
- Page 70 and 71:
Lube-Free Roller ChainsKilowatt Rat
- Page 72 and 73:
Lube-Free Roller ChainsHeavy Duty L
- Page 74 and 75:
Lube-Free Roller ChainsCurved Lambd
- Page 76 and 77:
Lube-Free Roller ChainsKilowatt Rat
- Page 78 and 79:
T S U B A K I D R I V E C H A I NHe
- Page 80 and 81:
Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 82 and 83:
Heavy Duty Roller Chains RS-HT Chai
- Page 84 and 85:
Heavy Duty Roller Chains RS-HT Chai
- Page 86 and 87:
Heavy Duty Roller Chains RS-HT Chai
- Page 88 and 89: Heavy Duty Roller Chains RS-HT Chai
- Page 90 and 91: Heavy Duty Roller Chains SUPER Roll
- Page 92 and 93: Heavy Duty Roller Chains SUPER Roll
- Page 94 and 95: Heavy Duty Roller Chains SUPER Roll
- Page 96 and 97: Heavy Duty Roller Chains SUPER Roll
- Page 98 and 99: Heavy Duty Roller Chains ULTRA SUPE
- Page 100 and 101: T S U B A K I D R I V E C H A I NBe
- Page 102 and 103: Corrosion Resistant Roller ChainsOl
- Page 104 and 105: Corrosion Resistant Roller Chains S
- Page 106 and 107: Corrosion Resistant Roller Chains S
- Page 108 and 109: Corrosion Resistant Roller ChainsTi
- Page 110 and 111: Corrosion Resistant Roller Chains L
- Page 112 and 113: Corrosion Resistant Roller ChainsLo
- Page 114 and 115: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 116 and 117: Specialty Roller ChainsLeaf ChainsB
- Page 118 and 119: Specialty Roller ChainsLeaf ChainsB
- Page 120 and 121: Specialty Roller ChainsPin Gear Att
- Page 122 and 123: Pin Gear SprocketBefore Use For Saf
- Page 124 and 125: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 126 and 127: 2 ETS Type: Straight type, with idl
- Page 128 and 129: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 130 and 131: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 132 and 133: Roller Chain SelectionBefore Use Fo
- Page 134 and 135: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 136 and 137: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 140 and 141: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 142 and 143: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 144 and 145: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 146 and 147: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 148 and 149: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 150 and 151: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 152 and 153: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 154 and 155: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 156 and 157: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 158 and 159: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 160 and 161: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 162 and 163: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 164 and 165: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 166 and 167: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 168 and 169: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 170 and 171: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 172 and 173: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 174 and 175: Before Use For Safe UseStandard Rol
- Page 176 and 177: 175MEMO