FINAL EXAM: Chapter 6 Review
FINAL EXAM: Chapter 6 Review
FINAL EXAM: Chapter 6 Review
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
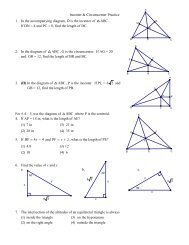
GeometryIV. Decide whether the statement is always, sometimes, or never t~e~ :a) A rectangle is a square. ~2 "~"b) A parallelogram is a trapezoid.c) A rhombus is a parallelogram.V. What special type of quadrilateral is shown? Justify your answer.2,1VII. Use the diagra~ of isosceles trapezoid ABCD to the right to answer the questionsbelow.Use th~ diagram of isosceles trapezoid16. tfAB = 6 and CD = 16, find the length of the mldsegment.17. t:{ m~2DAB = t 12 °, find: ~ measures of the o~he~ angles of ABCDoVIII. What special type of quadrilateral is PQRS? Give the most specific name and justifyanswer. (choose 2 and justify using slope and length (distance)).IX. Find the area of the trmngle or qua~ruateran23. 24.MD/3- ! 2
GeometryName:Date:Per.:<strong>FINAL</strong> <strong>EXAM</strong>: <strong>Chapter</strong> 7 <strong>Review</strong> (Transformations)Summary¯¯¯¯¯¯Identify types of rigid transformationsUseproperties of reflectionsRelate reflections and line symmetryRelate rotations and rotational symmetryUse properties of translationsUse properties of glide reflectionsProblemsI. Does the transformation appear to be an isometry? ExplainII. For questions #1-4, use the diagram.Y $2III. Name the coordinates of the vertices of the image after a clockwise rotation of thegiven number of degrees about the origin.90°270 °MD/6-12
IV~ Describe the translation using (a) coordinate notation and (b) a vector in componentform.Describe the composition of the transformations~ABVII. Use the diagram.Ide,ltffy the traasformation thatmaps figure DEFGHIJ ontofigure MNPQRST.What is fl~e prdmage of S? ~What is the image of D? ~MD/6-12 2
<strong>FINAL</strong> <strong>EXAM</strong>: <strong>Chapter</strong> 8 <strong>Review</strong> (Similarity)Date:Summaryco Write and simplify the ratio of two numbersco Use proportions to solve problemsco Understand properties of proportionsco Identify similar polygons and use properties of similar polygonsoo Prove that two triangles are similar using the definition of similar triangles and the AA Postulate,SSS Similarity Theorem, and SAS Simi~arit ’’ Theoremco Use proportionality theorems to solve problemsoo Identify and draw dilations and use properties of dilationsProblemsI. Solve the proportion.II. Complete the sentence.III. Solve the following problem using a proportion.You buy a 13-inch scale model of the sculpture The Dancer by Edgar Degas. The ratio of the heightof the scale model to the height of the sculpture is 1:3. Find the height of the sculpture.
IV. Use the figures to the right to answer the following questions.Geometry’1. Find the scale factor of z~DEFG to oHJ .~-~-’~JH2. Find the length of DE and the measure of3. Find the ratio of t~e perimeter of ~E to the perimeter of oDEFGV. Determine ~hether the triangles can be proved similar or not. Explain.PR2. F K L/VVI. Find the value of the variable.11 xVII. Identify the dilation, find its scale factor, and find the value of the variable using thediagram below.MD/6-07 2
Name: Date: Per.:Geome/"ry<strong>FINAL</strong> <strong>EXAM</strong>: <strong>Chapter</strong> 9 <strong>Review</strong> (Right Triangles and Trigonometry)¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯Solve proMems involving similar right triangles formed by the altitude drawn to the hypotenuse of aright triangle.Use the Pythagorean Theorem and its converseUse side lengths to classify triangles by their angle measuresFind the side lengths of special right trianglesFind trigonometric ratios of an acute angle.Solve a right triangle.Find the magnitude and direction of a vector.Find the sum of two vectors~ProblemsI. Find the value of each variable.II. The variables r and s represent the lengths of the legs of a right triangle, and t repreSentSlength of the hypotenuse. Find the unknown value. Then tell whether the lengths form aPythagorean triple. ~r = 12, s = 16 .~ ",,°~’ ~ ’: ..... ~ 2. r=B,t=124. r=4, s=6MD/6-07 1
GeometryIII. Decide whether the numbers can represent the side lengths of a triangle. If they can, classifythe triangle as acute, right, or obtuse.8, 12, 20IV. Special Right Trianglesi. An isosceles right triangle has legs of length 3J~. Find the length of the hypotenuse.2. A diagonal of a square is 6 inches long. Find its perimeter and its area.3. A 30 °- 60 ° 90 ° triangle has a hypotenuse of length 12 inches. What are the lengths of thelegs?4. An equilateral triangle has sides of length 18 centimeters. Find the length of an altitude ofthe triangle. Then find the area of the triangle.MD/6-07 2
Name: Date: Per.:Geometr~<strong>FINAL</strong> <strong>EXAM</strong>: <strong>Chapter</strong> 10 <strong>Review</strong> (Circles)Summary¯¯¯¯¯¯Identify segments and lines related to circlesUse properties of tangents of circlesUse properties of arcs and chords of circlesUse properties of inscribed angles and inscribed polygons of circlesUse angles formed by tangents, chords, and secantsFind the lengths of segments of tangents, chords, and lines that intersect a circle.ProblemsI. Name a point, segment, line, or circle that represents the phrase.1. Diameter of C:)P ~b~ 2. Point oftangency ofE)Q ~k, ¢3. Chord of "~P B~=~ 4l, Center of Ire’get cir~ ’ gB. Radius of6. Common tangent ~.~7. Secant 8. Point of tangency of~P and9. Is/-PBC a right angle? Explain. ~,~_~II. Use ®Q in the diagram to find the measure of the indicated arc. AD is a diameter, andm~E = 121 °,III. Kite ABCD is inscribed in ®P. Decide whether the statement is true or false. Explain~ACMD/6-12 1
GeometryIV. Find the value of x.):70 EMD/6-122
Name: Date: Per.:<strong>FINAL</strong> <strong>EXAM</strong>: <strong>Chapter</strong> 11 <strong>Review</strong> (Area of Polygons and Circles)Summary¯¯¯¯¯¯Find the measures of the interior and exterior angles of polygonsFind the areas of equilateral triangles and other regular polygonsCompare perimeters and areas of similar figuresFind the circumference of a circle and the length of an arc of a circle,Find the areas of circles and sectorsFind geometric probability.ProblemsI. Given the number of sides of a regular polygon, find the measure of each interior angle and eachexterior angle.II. Given the measure of each interior angle of a regular n-gon, find the value of n (number ofsides).III. Find the specified area.1. An equilateral triangle has 12 cm sides. Find the area of the triangle.2. A regular hexagon has 5 meter sides, Find the area of the hexagon.MD/6-12
3. A regular decagon has 1+5 foot sides. Find the area of the decagon.GeometryIV. Compete the statement using always, sometimes, or never.If the ratio of the perimeters of two rectangles is 3:5, then the ratio of theirareas is ~ 9:25.2. Two parallelograms are ~ similar~3. Two regular dodecagons with perimeters in the ratio 4 to 7 ~ have areasin the ratio 16 to 49~Find the circumference of ®P and the length of arc AB.+C B AVI. Find the radius of a circle with circumference 12 inches.VII. Find ~ diameter of a circI~ with circumfer~nc~ 15~ meters.MD/6 - 12 2
VIII. Find the area of the shaded region.Geometry+135°iIX. What is the area of a circle with diameter 28 ~ ~-~?’ ~l-’~~X. What is the radius of a c rc e with area 40 square~j~ches?XI. Find the probability that a point Ao selected randomly on JN, is on the given segment.XII. Find the probability that a randomly chosen point in the figure lies in the shaded region.
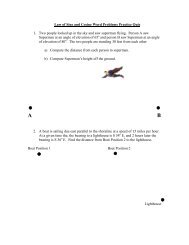
GeometryV. Find the sine, cosine, and the tangent of the acute angles of the triangle shown. Express eachvalue as a decimal rounded to four places.VI. Solve the right triangle. Round decima s to the nearest tenth, E2OFVII. Use the diagram to the right to find the following.VII. Trigonometric Ratios. Sketch a diagram and solve.1. An escalator is 15 m in length with a 37 ° incline. How high is the escalator?2. How far below sea level wilt a porpoise be if it swims a distance of 250 m at a 12 ° angle ofdepression?MD/6 -07
Name: Date: Per,:Geometry<strong>FINAL</strong> <strong>EXAM</strong>: <strong>Chapter</strong> 12 <strong>Review</strong> (Surface Area and Volume)SummaryProblemsUse properties of polyhedraFind the surface area and volume of prismsFind the surface area and volume of cylindersI. Use Euler’s Theorem to find the unknown number. ~, ~ , ~ ~ ~ ....."~1. Faces: 32 2. F~es: ? 3. Faces: 5Vertices: ? Vertices: 6 Vertices:Edges: 90 Edges: 10 Edges:II. Find the surface area of the right prism or right cylinder~ Round your result to two decimalplaces~Note: height = 18 in.MD/6-012 1
III. Find the volume of the described solid.A side of a cube measures 8 centimeters.A right prism has a height of 37.2 meters and regular hexagonal bases, each with abase edge of 21 meters.A right cylinder has a radius of 3.5 inches and a height of 8 inches.IV. Determine the word or words described by the given phrase.1. A line segment formed by the intersection of two faces of a polyhedron.2. A polyhedron with eight faces.3. A polyhedron with two congruen~ faces, called bases, that lie in parallel4. The number of cubic units contained in the interior of a solid.5. A solid with congruent circular bases that lie in parallel planes.MD/~-012 2