Relay symbols and device numbers - APE Distribuidor ABB
Relay symbols and device numbers - APE Distribuidor ABB
Relay symbols and device numbers - APE Distribuidor ABB
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
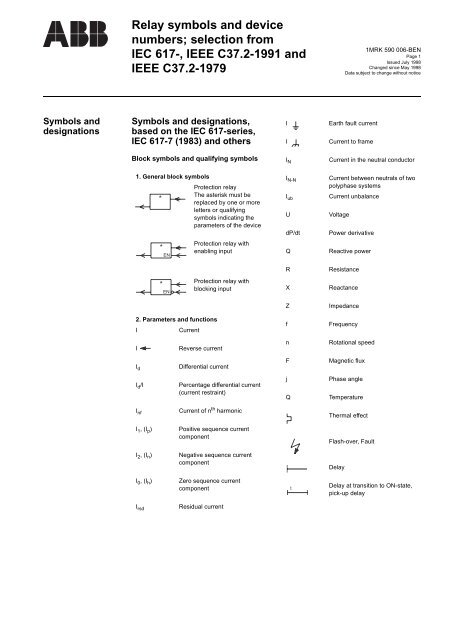
<strong>Relay</strong> <strong>symbols</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>device</strong><strong>numbers</strong>; selection fromIEC 617-, IEEE C37.2-1991 <strong>and</strong>IEEE C37.2-19791MRK 590 006-BENPage 1Issued July 1998Changed since May 1998Data subject to change without noticeSymbols <strong>and</strong>designationsSymbols <strong>and</strong> designations,based on the IEC 617-series,IEC 617-7 (1983) <strong>and</strong> othersIIEarth fault currentCurrent to frameBlock <strong>symbols</strong> <strong>and</strong> qualifying <strong>symbols</strong>I NCurrent in the neutral conductor1. General block <strong>symbols</strong>Protection relayThe asterisk must be*replaced by one or moreletters or qualifying<strong>symbols</strong> indicating theparameters of the <strong>device</strong>I N-NI ubUdP/dtCurrent between neutrals of twopolyphase systemsCurrent unbalanceVoltagePower derivative*ENProtection relay withenabling inputQReactive powerRResistance*ENProtection relay withblocking inputXReactanceZImpedance2. Parameters <strong>and</strong> functionsICurrentfFrequencyIReverse currentnRotational speedI dDifferential currentFMagnetic fluxI d /IPercentage differential current(current restraint)jQPhase angleTemperatureI nfCurrent of n th harmonicThermal effectI 1 , (I p )Positive sequence currentcomponentFlash-over, FaultI 2 , (I n )Negative sequence currentcomponentDelayI 0 , (I h )Zero sequence currentcomponenttDelay at transition to ON-state,pick-up delayI rsdResidual current
<strong>ABB</strong> Network Partner<strong>Relay</strong> <strong>symbols</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong>;selection from IEC 617-, IEEE C37.2-1991<strong>and</strong> IEEE C37.2-19791MRK 590 006-BENPage 2Symbols <strong>and</strong>designations (cont’d) SYNC Synchronizing (check)BLOCKBlocking <strong>device</strong><strong>Relay</strong> with make contact,delayed when the relay isenergized.Pick-up delayLOTCSLock-outTrip circuit supervision<strong>Relay</strong> with brake contact,delayed when the relay isdeenergized.Drop-out delayX/YTranslation of signalA/D or /# Analog to digital conversionUI>Overcurrent relay withshort-circuiting connector> Operation above a set value,e.g. overcurrentCoils< Operation below a set value,e.g. underimpedance<strong>Relay</strong> with one winding>> Operation above a high setstage<strong>Relay</strong> with two windingsExamples of protection relays<strong>Relay</strong>s <strong>and</strong> relay partsR<strong>Relay</strong> contactsOperate <strong>and</strong> reset coilMake contactAuxiliary relay with mechanical contactsBrake contactAuxiliary relay, block symbolChange-over contact(break before make)Change-over contact,delayed when releasing+-EL-ELStatic relay with terminals for external auxiliaryvoltage supply+Switch contactsChange-over contact,delayed when operatingPush-button operatedcontact with automaticreturn
<strong>ABB</strong> Network Partner<strong>Relay</strong> <strong>symbols</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong>;selection from IEC 617-, IEEE C37.2-1991<strong>and</strong> IEEE C37.2-19791MRK 590 006-BENPage 3Test switch contactsIndicationsIndicator with self reset, indicateswhen coil is energized.Annunciator element (target)Indicator light, lamp or led1. Break-contact (voltage supply circuit), lateopening <strong>and</strong> early closing upon insertion<strong>and</strong> withdrawal, respectively, of the test h<strong>and</strong>le.Note that the test switch contactsnumber 1 <strong>and</strong> 18 (12) will not be openedwhen the test h<strong>and</strong>le RTXH 18 (24) isinserted.2. Break-contact (trip circuits), early opening<strong>and</strong> late closing upon insertion <strong>and</strong> withdrawalrespectively, of the test h<strong>and</strong>le.3. Make before break contacts with shortingconnection (CT secondary circuits), lateopening <strong>and</strong> early closing upon insertion<strong>and</strong> withdrawal respectively, of the testh<strong>and</strong>le.Components+UH<strong>and</strong> reset indication, indicateswhen the coil is energized <strong>and</strong>remains visible even when thecoil is not energizedCapacitor, general symbolPolarized capacitorResistor, general symbolPotentiometerResistor with two fixed endterminals <strong>and</strong> one movableterminalVaristorVoltage dependent non-linearresistorFixed trimming resistorResistor with two fixed endterminals <strong>and</strong> one movableterminal for fixed setting(trimming)Diode, semiconductorReference diodeZener diodeVoltage regulator diodeSingle-phase transformer withtwo windings
<strong>ABB</strong> Network Partner<strong>Relay</strong> <strong>symbols</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong>;selection from IEC 617-, IEEE C37.2-1991<strong>and</strong> IEEE C37.2-19791MRK 590 006-BENPage 4Symbols <strong>and</strong>designations (cont’d)Designations5Divider (by 5)I r , U rRated current, voltageI b , U bBase current, voltageB<strong>and</strong>-pass filterI s , U sSet current, voltageL1, L2, L3, N Phase designations200mstTime element delayedon pick-up, 200 msAlternating current, acDirect current, dc70mstTime element delayedon drop-out, 70 msULELAc <strong>and</strong> dcAuxiliary tripping voltageAuxiliary electronic voltageTmintAdjustable timeelement delayed onpick-upRLAuxiliary relay voltage50msLogic elementstTime element nonre-triggable pulseDIRLogic setting signal(including on-off)LOOPDELAYLoop delay output(T) = input (T-1)BCBinary input signalABAB&≥1CCAND gateC = A x BOR gateC = A + BEF 3ΙoSTDEFKLight emitting diode(LED)Earth fault overcurrentdependenttime functionInput invertedAB+-ΣCOutput invertedSignal summationcircuitC = A + (-B)EF 3ΙoSTD3Ιo x 100%Cos(ϕ-65°) FORWARD60%REVERSEEF UCHDirectional earth faultovercurrent functionLevel detector, earthfault voltage check
<strong>ABB</strong> Network Partner<strong>Relay</strong> <strong>symbols</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong>;selection from IEC 617-, IEEE C37.2-1991<strong>and</strong> IEEE C37.2-19791MRK 590 006-BENPage 5IEEE <strong>device</strong><strong>numbers</strong> <strong>and</strong>functionsIEEE <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong> <strong>and</strong> functionsfor switchgear apparatusThe <strong>device</strong>s in switching equipments arereferred to by <strong>numbers</strong>, with appropriate suffixletters when necessary, according to thefunctions they perform.These <strong>numbers</strong> are based on a system adoptedas st<strong>and</strong>ard for automatic switchgear byIEEE, <strong>and</strong> incorporated in AmericanSt<strong>and</strong>ard C37.2-1979. This system is used inconnection diagrams, in instruction books,<strong>and</strong> in specifications.DevicenumberDefinition<strong>and</strong> function1 Master element is the initiating<strong>device</strong>, such as a control switch,voltage relay, float switch etc., thatserves either directly, or through suchpermissive <strong>device</strong>s as protective <strong>and</strong>time-delay relays, to place an equipmentin or out of operation.2 Time-delay starting or closing relayis a <strong>device</strong> that functions to give adesired amount of time delay before orafter any point of operation in a switchingsequence or protective relay system,except as specificallyprovided by <strong>device</strong> functions 48, 62<strong>and</strong> 79 described later.3 Checking or interlocking relay is a<strong>device</strong> that operates in response tothe position of a number of other<strong>device</strong>s, (or to a number of predeterminedconditions), in an equipment toallow an operating sequence to proceed,to stop, or to provide a check ofthe position of these <strong>device</strong>s or ofthese conditions for any purpose.DevicenumberDefinition<strong>and</strong> function6 Starting circuit breaker is a <strong>device</strong>whose principal function is to connecta machine to its source of startingvoltage.7 Rate-of-rise relay is a relay that functionson an excessive rate of rise ofcurrent.8 Control power disconnecting<strong>device</strong> is a disconnecting <strong>device</strong>,such as a knife switch, circuit breaker,or pull-out fuse block, used for thepurpose of respectively connecting<strong>and</strong> disconnecting the source ofcontrol power to <strong>and</strong> from the controlbus or equipment.9 Reversing <strong>device</strong> is used for thepurpose of reversing a machine fieldor for performing any other reversingfunctions.10 Unit sequence switch is used tochange the sequence in which unitsmay be placed in <strong>and</strong> out of service inmultiple-unit equipment.11 Multifunction <strong>device</strong> is a <strong>device</strong> thatperforms three or more comparativelyimportant functions that could only bedesignated by combining several ofthese <strong>device</strong> function <strong>numbers</strong>. All ofthe functions performed by <strong>device</strong> 11shall be defined in the drawing legendor <strong>device</strong> function list.12 Overspeed <strong>device</strong> is usually a directconnectedspeed switch that functionson machine overspeed.4 Master contactor is a <strong>device</strong>,generally controlled by <strong>device</strong> No. 1 orequivalent, <strong>and</strong> the required permissive<strong>and</strong> protective <strong>device</strong>s, that serveto make <strong>and</strong> break the necessary controlcircuits to place an equipment intooperation under the desired conditions<strong>and</strong> to take it out of operation underother or abnormal conditions.5 Stopping <strong>device</strong> is a control <strong>device</strong>used primarily to shut down an equipment<strong>and</strong> hold it out of operation. [This<strong>device</strong> may be manually or electricallyactuated, but excludes the function ofelectrical lockout (see <strong>device</strong> function86) on abnormal conditions.]13 Synchronous-speed <strong>device</strong>, such asa centrifugal speed switch, a slipfrequency relay, a voltage relay, anundercurrent relay, or any other typeof <strong>device</strong> that operates at approximatelythe synchronous speed of amachine.14 Underspeed <strong>device</strong> functions whenthe speed of a machine falls below apre-determined value.
<strong>ABB</strong> Network Partner<strong>Relay</strong> <strong>symbols</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong>;selection from IEC 617-, IEEE C37.2-1991<strong>and</strong> IEEE C37.2-19791MRK 590 006-BENPage 6IEEE <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong><strong>and</strong> functions (cont’d)DevicenumberDefinition<strong>and</strong> function15 Speed or frequency matching<strong>device</strong> functions to match <strong>and</strong> holdthe speed or the frequency of amachine or of a system equal to, orapproximately equal to, that of anothermachine, source, or system.16 Reserved for future application17 Shunting or discharge switchserves to open or to close a shuntingcircuit around any piece of apparatus(except a resistor), such as a machinefield, a machine armature, a capacitor,or a reactor.Note: This excludes <strong>device</strong>s thatperform such shunting operations asmay be necessary in the process ofstarting a machine by <strong>device</strong>s 6 or 42,or their equivalent, <strong>and</strong> also excludes<strong>device</strong> 73 function that serves for theswitching of resistors.18 Accelerating or decelerating<strong>device</strong> is used to close or to cause theclosing of circuits that are used toincrease or decrease the speed of amachine.19 Starting-to-running transitioncontactor is a <strong>device</strong> that operates toinitiate or cause the automatic transferof a machine from the starting to therunning power connection.20 Electrically operated valve is anelectrically operated, controlled, ormonitored valve used in a fluid, air,gas, or vacuum line.Note: The function of the valve may beindicated by the use of the suffixes, seepage 11.21 Distance relay is a relay that functionswhen the circuit admittance,impedance, or reactance increases ordecreases beyond a predeterminedvalue.22 Equalizer circuit breaker is a breakerthat serves to control or to make <strong>and</strong>break the equalizer or the current balancingconnections for a machinefield, or for regulating equipment, in amultiple unit installation.DevicenumberDefinition<strong>and</strong> function23 Temperature control <strong>device</strong> functionsto raise or to lower the temperatureof a machine or other apparatus,or of any medium, when its temperaturefalls below or rises above a predeterminedvalue.Note: An example is a thermostat thatswitches on a space heater in aswitchgear assembly when thetemperature falls to a desired valueas distinguished from a <strong>device</strong> that isused to provide automatic temperatureregulation between close limits<strong>and</strong> would be designated as 90T.24 Volts per hertz relay is a relay thatfunctions when the ratio of voltage tofrequency exceeds a preset value.The relay may have an instantaneousor a time characteristic.25 Synchronizing or synchronismcheck<strong>device</strong> operates when two accircuits are within the desired limits offrequency, phase angle, or voltage topermit or to cause the paralleling ofthese two circuits.26 Apparatus thermal <strong>device</strong> functionswhen the temperature of the protectedapparatus (other than the loadcarryingwindings of machines <strong>and</strong>transformers as covered by <strong>device</strong>function number 49) or of a liquid orother medium exceeds a predeterminedvalue; or when the temperatureof the protected apparatus or of anymedium decreases below a predeterminedvalue.27 Undervoltage relay is a relay thatoperates when its input voltage is lessthan a predetermined value.28 Flame detector is a <strong>device</strong> thatmonitors the presence of the pilot ormain flame in such apparatus as a gasturbine or a steam boiler.29 Isolating contactor is used expresslyfor disconnecting one circuit fromanother for the purposes of emergencyoperation, maintenance, or test.
<strong>ABB</strong> Network Partner<strong>Relay</strong> <strong>symbols</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong>;selection from IEC 617-, IEEE C37.2-1991<strong>and</strong> IEEE C37.2-19791MRK 590 006-BENPage 7DevicenumberDefinition<strong>and</strong> function30 Annunciator relay is a nonautomaticallyreset <strong>device</strong> that gives a numberof separate visual indications upon thefunctioning of protective <strong>device</strong>s <strong>and</strong>that may also be arranged to performa lock-out function.31 Separate excitation <strong>device</strong>connects a circuit, such as the shuntfield of a synchronous converter, to asource of separate excitation duringthe starting sequence; or one whichenergizes the excitation <strong>and</strong> ignitioncircuits of a power rectifier.32 Directional power relay is a relaythat operates on a predeterminedvalue of power flow in a given directionor upon reverse power flow such asthat resulting from the motoring of agenerator upon loss of its primemover.33 Position switch makes or breakscontact when the main <strong>device</strong> or pieceof apparatus that has no <strong>device</strong> functionnumber reaches a given position.34 Master sequence <strong>device</strong> is a <strong>device</strong>such as a motor operated multicontactswitch, or the equivalent, or a programming<strong>device</strong>, such as a computer,that establishes or determines theoperating sequence of the major<strong>device</strong>s in an equipment during starting<strong>and</strong> stopping or during othersequential switching operations.35 Brush-operating or slip-ring shortcircuiting<strong>device</strong> is used for raising,lowering or shifting the brushes of amachine; short-circuiting its slip rings;or engaging or disengaging thecontacts of a mechanical rectifier.36 Polarity or polarizing voltage <strong>device</strong>operates, or permits theoperation of, another <strong>device</strong> on apredetermined polarity only or thatverifies the presence of a polarizingvoltage in an equipment.DevicenumberDefinition<strong>and</strong> function38 Bearing protective <strong>device</strong> functionson excessive bearing temperature oron other abnormal mechanical conditionsassociated with the bearing,such as undue wear, which mayeventually result in excessive bearingtemperature or failure.39 Mechanical condition monitor is a<strong>device</strong> that functions upon the occurrenceof an abnormal mechanicalcondition (except that associated withbearings as covered under <strong>device</strong>function 38), such as excessive vibration,eccentricity, expansion, shock,tilting, or seal failure.40 Field relay functions on a given orabnormally low value or failure ofmachine field current, or on an excessivevalue of the reactive componentof armature current in an ac machineindicating abnormally low field excitation.41 Field circuit breaker is a <strong>device</strong> thatfunctions to apply or remove the fieldexcitation of a machine.42 Running circuit breaker is a <strong>device</strong>whose principal function is to connecta machine to its source of running oroperating voltage. This function mayalso be used for a <strong>device</strong>, such as acontactor, that is used in series with acircuit breaker or other fault protectingmeans, primarily for frequent opening<strong>and</strong> closing of the circuit.43 Manual transfer or selector <strong>device</strong>is a manually operated <strong>device</strong> thattransfers the control circuits in order tomodify the plan of operation of theswitching equipment or of some of the<strong>device</strong>s.44 Unit sequence starting relay is arelay that functions to start the nextavailable unit in multiple unit equipmentupon the failure or nonavailabilityof the normally preceding unit.37 Undercurrent or underpower relayfunctions when the current or powerflow decreases below a predeterminedvalue.45 Atmospheric condition monitor is a<strong>device</strong> that functions upon the occurrenceof an abnormal atmosphericcondition, such as damaging fumes,explosive mixtures, smoke, or fire.
<strong>ABB</strong> Network Partner<strong>Relay</strong> <strong>symbols</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong>;selection from IEC 617-, IEEE C37.2-1991<strong>and</strong> IEEE C37.2-19791MRK 590 006-BENPage 8IEEE <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong><strong>and</strong> functions (cont’d)DevicenumberDefinition<strong>and</strong> function46 Reverse-phase or phase-balancecurrent relay is a relay that functionswhen the polyphase currents are ofreverse phase sequence or when thepolyphase currents are unbalanced orcontain negative phase-sequencecomponents above a given amount.47 Phase-sequence or phase-balancevoltage relay functions upon a predeterminedvalue of polyphasevoltage in the desired phasesequence, or when the polyphase voltagesare unbalanced, or when thenegative phase-sequence voltageexceeds a given amount.48 Incomplete sequence relay is a relaythat generally returns the equipmentto the normal, or off, position <strong>and</strong>locks it out if the normal starting,operating, or stopping sequence isnot properly completed within a predeterminedtime. If the <strong>device</strong> is usedfor alarm purposes only, it should preferablybe designated as 48A (alarm).49 Machine or transformer thermalrelay is a relay that functions when thetemperature of a machine armaturewinding or other load-carrying windingor element of a machine or powertransformer exceeds a predeterminedvalue.50 Instantaneous overcurrent relay is arelay that functions instantaneously onan excessive value of current.51 Ac time overcurrent relay is a relaywith either a definite or inverse timecharacteristic that functions when theac input current exceeds a predeterminedvalue, <strong>and</strong> in which the inputcurrent <strong>and</strong> operating time are independentlyrelated or inversely relatedthrough a substantial portion of theperformance range.52 Ac circuit breaker is a <strong>device</strong> that isused to close <strong>and</strong> interrupt an acpower circuit under normal conditionsor to interrupt this circuit under fault oremergency conditions.DevicenumberDefinition<strong>and</strong> function53 Exciter or dc generator relay is arelay that forces the dc machine fieldexcitation to build up during starting orthat functions when the machine voltagehas built up to a given value.54 Turning gear engaging <strong>device</strong> is anelectrically operated, controlled, ormonitored <strong>device</strong> that functions tocause the turning gear to engage (ordisengage) the machine shaft.55 Power factor relay is a relay thatoperates when the power factor in anac circuit rises above or falls below apredetermined value.56 Field application relay is a relay thatautomatically controls the applicationof the field excitation to an ac motor atsome predetermined point in the slipcycle.57 Short-circuiting or grounding<strong>device</strong> is a primary circuit switching<strong>device</strong> that functions to short circuitor ground a circuit in response to automaticor manual means.58 Rectification failure relay is a <strong>device</strong>that functions if a power recitifier failsto conduct or block properly.59 Overvoltage relay is a relay thatoperates when its input voltage ishigher than a predetermined value.60 Voltage or current balance relay is arelay that operates on a given differencein voltage, or current input or output,of two circuits.61 Density switch or sensor is a <strong>device</strong>that operates on a given value, or agiven rate of change, of gas density.62 Time-delay stopping or openingrelay is a time-delay relay that servesin conjunction with the <strong>device</strong> thatinitiates the shutdown, stopping, oropening operation in an automaticsequence or protective relay system.63 Pressure switch is a switch that operateson given values, or on a givenrate of change, of pressure.
<strong>ABB</strong> Network Partner<strong>Relay</strong> <strong>symbols</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong>;selection from IEC 617-, IEEE C37.2-1991<strong>and</strong> IEEE C37.2-19791MRK 590 006-BENPage 9DevicenumberDefinition<strong>and</strong> function64 Ground detector relay is a relay thatoperates upon failure of machine orother apparatus insulation to ground,or on flashover of a dc machine toground.Note: This function is assigned only toa relay which detects the flow of currentfrom the frame of a machine or enclosingcase or structure of a piece ofapparatus to ground, or detects aground on a normally ungrounded windingor circuit. It is not applied to a <strong>device</strong>connected in the secondary neutral of acurrent transformer, or in the secondaryneutral of current transformers, connectedin the power circuit of a normallygrounded system.65 Governor is the assembly of fluid,electrical, or mechanical controlequipment used for regulating the flowof water, steam, or other media to theprime mover for such purposes asstarting, holding speed or load, orstopping.66 Notching or jogging <strong>device</strong> functionsto allow only a specified numberof operations of a given <strong>device</strong> orequipment, or a specified number ofsuccessive operations within a giventime of each other. It is also a <strong>device</strong>that functions to energize a circuitperiodically or for fractions of specifiedtime intervals, or that is used to permitintermittent acceleration or jogging ofa machine at low speeds for mechanicalpositioning.67 Ac directional overcurrent relay is arelay that functions on a desired valueof ac overcurrent flowing in a predetermineddirection.68 Blocking relay is a relay that initiatesa pilot signal for blocking of tripping onexternal faults in a transmission line orin other apparatus under predeterminedconditions, or that cooperateswith other <strong>device</strong>s to block tripping orto block reclosing on an out-of-stepcondition or on power swings.DevicenumberDefinition<strong>and</strong> function69 Permissive control <strong>device</strong> is generally,a two-position <strong>device</strong> that in oneposition permits the closing of a circuitbreaker, or the placing of an equipmentinto operation, <strong>and</strong> in the otherposition prevents the circuit breaker orthe equipment from being operated.70 Rheostat is a variable resistance<strong>device</strong> used in an electric circuit whichis electrically operated or has otherelectrical accessories, such as auxiliary,position, or limit switches.71 Level switch is a switch that operateson given values, or on a given rate ofchange, of level.72 Dc circuit breaker is used to close<strong>and</strong> interrupt a dc power circuit undernormal conditions or to interrupt thiscircuit under fault or emergency conditions.73 Load-resistor contactor is used toshunt or insert a step of load limiting,shifting, or indicating resistance in apower circuit, or to switch a spaceheater in circuit, or to switch a light, orregenerative load resistor of a powerrectifier or other machine in <strong>and</strong> out ofcircuit.74 Alarm relay is a relay other than anannunciator, as covered under <strong>device</strong>function 30, that is used to operate, orthat operates in connection with, avisual or audible alarm.75 Position changing mechanism is amechanism that is used for moving amain <strong>device</strong> from one position toanother in an equipment; for example,shifting a removable circuit breakerunit to <strong>and</strong> from the connected, disconnected,<strong>and</strong> test positions.76 Dc overcurrent relay is a relay thatfunctions when the current in a dccircuit exceeds a given value.
<strong>ABB</strong> Network Partner<strong>Relay</strong> <strong>symbols</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong>;selection from IEC 617-, IEEE C37.2-1991<strong>and</strong> IEEE C37.2-19791MRK 590 006-BENPage 10IEEE <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong><strong>and</strong> functions (cont’d)DevicenumberDefinition<strong>and</strong> function77 Telemetering <strong>device</strong> is a transmitterused to generate <strong>and</strong> transmit to aremote location an electrical signalrepresenting a measured quantity, or areceiver used to receive the electricalsignal from a remote transmitter <strong>and</strong>convert the signal to represent theoriginal measured quantity.78 Phase-angle measuring or out-ofstepprotective relay is a relay thatfunctions at a predetermined phaseangle between two voltages, orbetween two currents, or betweenvoltage <strong>and</strong> current.79 Ac reclosing relay is a relay thatcontrols the automatic reclosing <strong>and</strong>locking out of an ac circuit interrupter.DevicenumberDefinition<strong>and</strong> function86 Lockout relay is an electricallyoperated h<strong>and</strong> or electrically resetauxiliary relay that is operated uponthe occurrence of abnormal conditionsto maintain associated equipment or<strong>device</strong>s out of service until it is reset.87 Differential protective relay is aprotective relay that functions on apercentage, or phase angle, or otherquantitative difference between twocurrents or some other electricalquantities.88 Auxiliary motor or motor generatoris a <strong>device</strong> used for operating auxiliaryequipment, such as pumps, blowers,exciters, rotating magnetic amplifiers,etc.80 Flow switch is a switch that operateson given values, or on a given rate ofchange, of flow.81 Frequency relay is a relay thatresponds to the frequency of anelectrical quantity, operating whenthe frequency or rate of change offrequency exceeds or is less than apredetermined value.82 Dc load-measuring reclosing relayis a relay that controls the automaticclosing <strong>and</strong> reclosing of a dc circuitinterrupter, generally in response toload circuit conditions.83 Automatic selective control ortransfer relay is a relay that operatesto select automatically betweencertain sources or conditions in anequipment or that performs a transferoperation automatically.84 Operating mechanism is the completeelectrical mechanism or servomechanism,including the operatingmotor, solenoids, position switches,etc., for a tap changer, induction regulator,or any similar piece of apparatusthat otherwise has no <strong>device</strong> functionnumber.85 Carrier or pilot-wire receiver relay isa relay that is operated or restrainedby a signal used in connection withcarrier-current or dc pilot-wire faultdirectional relaying.89 Line switch is used as a disconnecting,load interrupter, or isolating switchin an ac or dc power circuit. (This<strong>device</strong> function number is normallynot necessary unless the switch iselectrically operated or has electricalaccessories, such as an auxiliaryswitch, a magnetic lock, etc.)90 Regulating <strong>device</strong> functions toregulate a quantity or quantities, suchas voltage, current, power, speed,frequency, temperature, <strong>and</strong> load,at a certain value or between certain(generally close) limits for machines,tie lines, or other apparatus.91 Voltage directional relay is a relaythat operates when the voltage acrossan open circuit breaker or contactorexceeds a given value in a given direction.92 Voltage <strong>and</strong> power directional relayis a relay that permits or causes theconnection of two circuits when thevoltage difference between themexceeds a given value in a predetermineddirection <strong>and</strong> causes these twocircuits to be disconnected from eachother when the power flowing betweenthem exceeds a given value in theopposite direction.93 Field-changing contactor functionsto increase or decrease, in one step,the value of field excitation on amachine.
<strong>ABB</strong> Network Partner<strong>Relay</strong> <strong>symbols</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong>;selection from IEC 617-, IEEE C37.2-1991<strong>and</strong> IEEE C37.2-19791MRK 590 006-BENPage 11Devicenumber94 Tripping or trip-free relay functionsto trip a circuit breaker, contactor, orequipment, or to permit immediatetripping by other <strong>device</strong>s; or to preventimmediate reclosing of a circuit interrupterif it should open automatically,even though its closing circuit is maintainedclosed.9596979899Definition<strong>and</strong> functionUsed only for specific applications onindividual installations where none ofthe assigned numbered functions from1 to 94 is suitable.Supervisory control <strong>and</strong> indication.A similar series of <strong>numbers</strong>, prefixedby the letters RE (for “remote”) shallbe used for the interposing relaysperforming functions that are controlleddirectly from the supervisorysystem. Typical examples of such<strong>device</strong> functions are: RE1, RE5 <strong>and</strong>RE94.Note: The user of the “RE” prefix forthis purpose in place of the former200 series of <strong>numbers</strong> now makes itpossible to obtain increased flexibilityof the <strong>device</strong> function numbering system.For example, in pipeline pumpstations, the <strong>numbers</strong> 1 through 99are applied to <strong>device</strong> functions thatare associated with the over-all stationoperation. A similar series of <strong>numbers</strong>,starting with 101 instead of 1, areused for those <strong>device</strong> functions thatare associated with unit 1; a similarseries starting with 201 for <strong>device</strong>functions that are associated with unit2; <strong>and</strong> so on, for each unit in theseinstallations.Devices performing more than onefunctionIf one <strong>device</strong> performs two relatively importantfunctions in an equipment so that it isdesirable to identify both of these functions,this may be done by using a double functionnumber <strong>and</strong> name such as:50/51 Instantaneous <strong>and</strong> Time Overcurrentrelay.Suffix <strong>numbers</strong>If two or more <strong>device</strong>s with the same functionnumber <strong>and</strong> suffix letter (if used) are presentin the same equipment, they may be distinguishedby numbered suffixes as for example,52X-1, 52X-2 <strong>and</strong> 52X-3, when necessary.Suffix lettersSuffix letters are used with <strong>device</strong> function<strong>numbers</strong> for various purposes. In order to preventpossible conflict each suffix letter shouldhave only one meaning in an individualequipment. All other words should use theabbreviations as contained in AmericanSt<strong>and</strong>ard Z32.13-1950, or latest revisionthereof, or should use some other distinctiveabbreviation, or be written out in full eachtime they are used. The meaning of eachsingle suffix letter, or combination of letters,should be clearly designated in the legend onthe drawings or publications applying to theequipment. In cases where the same suffix(consisting of one letter or a combination ofletters) has different meanings in the sameequipment, depending upon the <strong>device</strong> functionnumber with which is used, then thecomplete <strong>device</strong> function number with whichit is used, the complete <strong>device</strong> functionnumber with its suffix letter or letters <strong>and</strong> itscorresponding function name should be listedin the legend in each case, as follows: 90V,Voltage regulator.Lower case (small) suffix letters are used inpractically all instances on electrical diagramsfor the auxiliary, position, <strong>and</strong> limitswitches. Capital letters are generally usedfor all other suffix letters.The letters should generally form part of the<strong>device</strong> function designation, are usually writtendirectly after the <strong>device</strong> function number,as for example, 52CS, 71W, or 49D. When itis necessary to use two types of suffix lettersin connection with one function number, it isoften desirable for clarity to separate them bya slanted line or dash, as for example,20D/CS or 20D-CS.The suffix letters which denote parts of themain <strong>device</strong>, <strong>and</strong> those which cannot or neednot form part of the <strong>device</strong> function designation,are generally written directly below the<strong>device</strong> function number on drawings, as for52CC43Aexample, -------- or ----- .
<strong>ABB</strong> Network Partner<strong>Relay</strong> <strong>symbols</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong>;selection from IEC 617-, IEEE C37.2-1991<strong>and</strong> IEEE C37.2-19791MRK 590 006-BENPage 12IEEE <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong><strong>and</strong> functions (cont’d)Auxiliary <strong>device</strong>sSeparate auxiliary <strong>device</strong>sXY – Auxiliary relay 1)ZRLOCCSCLOPUDPB– Raising relay– Lowering relay– Opening relay or contactor– Closing relay or contactor– Control switch– Auxiliary relay, open (energized whenmain <strong>device</strong> is in open position)– Auxiliary relay, open (energized whenmain <strong>device</strong> is in open position)– “Up” position-switch relay– “Down” position-switch relay– Push button1) In the control of a circuit breaker with so-calledX-Y relay control scheme, the X relay is the<strong>device</strong> whose main contacts are used to energizethe closing coil or the <strong>device</strong> which insome other manner, such as by the release ofstored energy, causes the breaker to close.The contacts of the Y relay provide the antipumpfeature for the circuit breaker.Actuating quantitiesThese letters indicate the condition orelectrical quantity to which the <strong>device</strong>responds, or the medium in which it islocated, such as:ACDEFHJLPPFQSTVVARVBW– Air or Amperes or Alternating– Current– Direct or Discharge– Electrolyte– Frequency, or Flow, or Fault– Explosive– Differential– Level, or Liquid– Power, or Pressure– Power factor– Oil– Speed, or Suction, or Smoke– Temperature– Voltage, Volts, or Vacuum– Reactive power– Vibration– Water, or WattsMain <strong>device</strong>sThese letters denote the location of the main<strong>device</strong> in the circuit, or the type of circuit inwhich the <strong>device</strong> is used or the type of circuitor apparatus with which it is associated, whenthis is necessary, such as:A – Alarm or Auxiliary powerAN – AnodeB – Battery, or Blower, or BusBK – BrakeBL – Block (Valve)BP – BypassBT – Bus tieC – Capacitor, or Condenser, or Compensator,or Carrier current, or Case, orCompressorCA – CathodeCH – Check (Valve)D – Discharge (Valve)E – ExciterF – Feeder, or Field, or Filament, or Filter,or FanG – Generator, or Ground 2)H – Heater, or HousingL – Line, or LogicM – Motor, or MeteringN – Network, or Neutral 2)P – Pump, or Phase comparisonR – Reactor, or Rectifier, or RoomS – Synchronizing, or Secondary, orStrainer, or Sump, or Suction (Valve)T – Transformer, or ThyratronTH – Transformer (high-voltage side)TL – Transformer (low-voltage side)TM – TelemeterU – Unit2) Suffix “N” is generally used in preference to “G”for <strong>device</strong>s connected in the secondary neutralof current transformers, or in the secondary ofa current transformer whose primary winding islocated in the neutral of a machine or powertransformer, except in the case of transmissionline relaying, where the suffix “G” is more commonlyused for those relays which operate onground faults.
<strong>ABB</strong> Network Partner<strong>Relay</strong> <strong>symbols</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong>;selection from IEC 617-, IEEE C37.2-1991<strong>and</strong> IEEE C37.2-19791MRK 590 006-BENPage 13Main <strong>device</strong> partsThese letters denote parts of the main<strong>device</strong>, divided in the two followingcategories:1. All parts, except auxiliary contacts, positionswitches, limit switches, <strong>and</strong> torque limitswitches.BK – BrakeC – Coil, or Condenser, or CapacitorCC – Closing coilHC – Holding coilM – Operating motorMF – Fly-ball motorML – Load-limit motorMS – Speed adjusting, or SynchronizingmotorS – SolenoidSI – Seal-inTC – Trip coilV – Valve2. All auxiliary contacts <strong>and</strong> positioning <strong>and</strong>limit switches for such <strong>device</strong>s <strong>and</strong> equipment ascircuit breakers, contactors, valves <strong>and</strong> rheostats<strong>and</strong> contacts of relays. These are designated asfollows:abaabb– Contact that is open when the main<strong>device</strong> is in the st<strong>and</strong>ard referenceposition, commonly referred to as thenonoperated or deenergized position,<strong>and</strong> that closes when the <strong>device</strong>assumes the opposite position.– Contact that is closed when the main<strong>device</strong> is in the st<strong>and</strong>ard referenceposition, commonly referred to as thenonoperated or deenergized position,<strong>and</strong> that opens when the <strong>device</strong>assumes the opposite position.– Contact that is open when the operatingmechanism of the main <strong>device</strong> is in thenonoperated position <strong>and</strong> that closeswhen the operating mechanismassumes the opposite position.– Contact that is closed when the operatingmechanism of the main <strong>device</strong> is inthe nonoperated position <strong>and</strong> thatopens when the operating mechanismassumes the opposite position.St<strong>and</strong>ard reference positions of sometypical <strong>device</strong>s are as follows:DevicePower circuit breakerDisconnecting switchLoad-break switchValveGateClutchTurning gearPower electrodesRheostatAdjusting means 1)<strong>Relay</strong> 2)Contactor 2)<strong>Relay</strong> (latched-intype)Contactor (latched-intype)Temperature relay 3)Level detector 3)Flow detector 3)Speed switch 3)Vibration detector 3)Pressure switch 3)Vacuum switch 3)St<strong>and</strong>ardreference positionMain contacts openMain contacts openMain contacts openClosed positionClosed positionDisengaged positionDisengaged positionMaximum gap positionMaximum resistancepositionLow or Down positionDeenergized positionDeenergized positionNon-latched-in positionMain contacts openLowest temperatureLowest levelLowest flowLowest speedMinimum vibrationLowest pressureLowest pressure, i.e.,highest vacuumThe simple designation “a” or “b” is used in allcases where there is no need to adjust thecontacts to change position at any particular pointin the travel of the main <strong>device</strong> or where the partof the travel where the contacts change position isof no significance in the control or operatingscheme. Hence the “a” <strong>and</strong> “b” designationsusually are sufficient for circuit breaker auxiliaryswitches.Note: If several similar auxiliary switches arepresent on the same <strong>device</strong>, they should be designatednumerically 1, 2, 3, etc. when necessary.
<strong>ABB</strong> Network Partner<strong>Relay</strong> <strong>symbols</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong>;selection from IEC 617-, IEEE C37.2-1991<strong>and</strong> IEEE C37.2-19791MRK 590 006-BENPage 14IEEE <strong>device</strong> <strong>numbers</strong><strong>and</strong> functions (cont’d)St<strong>and</strong>ardDevicereference position1) These may be speed, voltage, current, load, orsimilar adjusting <strong>device</strong>s comprising rheostats,springs, levers, or other components for thepurpose.2) These electrically operated <strong>device</strong>s are of thenon-latched-in type, whose contact position isdependent only upon the degree of energizationof the operating or restraining or holdingcoil or coils which may or may not be suitablefor continuous energization. The deenergizedposition of the <strong>device</strong> is that with all coilsdeenergized.DEFHHRHSLMOFFON– Decelerating, or Detonate, or Down, orDisengaged– Emergency, or Engaged– Failure, or Forward– Hot, or High– H<strong>and</strong> reset– High speed– Left, or Local, or Low, or Lower, orLeading– Manual– Off– On3) The energizing influences for these <strong>device</strong>s areconsidered to be, respectively, risingtemperature, rising level, increasing flow, risingspeed, increasing vibration, <strong>and</strong> increasingpressure.PRST– Polarizing– Right, or Raise, or Reclosing, orReceiving, or Remote, or Reverse– Sending, or Swing– Test, or Trip, or TrailingTDC– Time-delay closingTDO– Time-delay openingU– UpOther switchesThese letters cover all other distinguishingfeatures or characteristics or conditions,which serve to describe the use of the <strong>device</strong>or its contacts in the equipment such as:ABC– Accelerating, or Automatic– Blocking, or Back-up– Close, or Cold