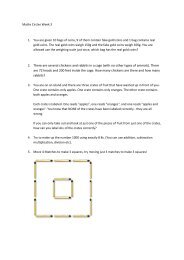
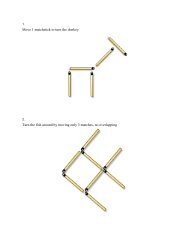
Fourier Transforms
Fourier Transforms
Fourier Transforms
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
substituted into the original equation to check that it is correct.The final result is found to be of the formfx A exp−ax 2 where the constants A and a are determined as part of the solution process (determinethem!). If we had been given this at the start, then A and a could have been determined bysubstituting directly into the integral equation without having to employ FTs.Note: Step1 requires the use of contour integration to determine gk and the result−e −x2 dx .3.3.4 Signal ProcessingSignal processing usually involves the time t and frequency as the two variables, givingrise to time-domain and frequency domain modelling. These quantities are related via theFT, i.e.Fft f ft eitdt .−If the signal ft is such that ft 0 for all |t| ≥ T, then the signal is called Time-Limitedand corresponds to a signal of finite length. If the signal is such that f 0 for all|| ≥ L, then the signal is called Band Limited and is restricted to a range of frequencies. Aband limited signal can be obtained by passing a full signal through a low-pass filter. It canbe shown, though we do not provide a proof, that a signal cannot be both time- andband-limited.The Shannon Sampling Theorem demonstrates the link between FT and FS for aband-limited signal. Let ft be the measured time signal and f be its band-limitedtransform. Using the inverse FT givesft 12 f e−itd 1−2L−L f e−itdand at the point t n/L, we obtainf nL 12L−L f exp −i nLd .Let H be a periodic complex-valued function of period 2L, defined to be equal to the18