Stroke Rehabilitation Across the Continuum of Care
Stroke Rehabilitation Across the Continuum of Care
Stroke Rehabilitation Across the Continuum of Care
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Rehabilitation</strong>Nurses:Champions forOptimizing <strong>Stroke</strong><strong>Rehabilitation</strong><strong>Across</strong> <strong>the</strong><strong>Continuum</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Care</strong>
PresentersSandra Melchiorre RN, MN, ACNP, CNN (c)Regional <strong>Stroke</strong> Acute <strong>Care</strong> Advanced PracticeNurse, SEODelanya Podgers BSc, RN<strong>Stroke</strong> Resource Nurse, Neuroscience Unit, KGHBarb Knapton RNSMOL, Neuro <strong>Rehabilitation</strong> NurseChristine Allison RN, HBScNSMOL, Neuro <strong>Rehabilitation</strong> Nurse
<strong>Rehabilitation</strong>Improves<strong>Stroke</strong>PatientOutcomes
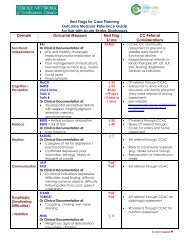
Workshop ObjectivesTo discuss <strong>the</strong> role <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> RN inimplementing stroke rehabilitation &<strong>Stroke</strong> Best Practice Guidelines(2003) across <strong>the</strong> continuum <strong>of</strong> careTo discuss common barriers andstrategies for effective transitionmanagement
Definition <strong>of</strong> <strong>Stroke</strong><strong>Rehabilitation</strong>“A progressive, dynamic, goal-orientedprocess aimed at enabling a personwith an impairment to reach his orher optimal physical, cognitive,emotional, communicative and/orsocial functional levels”(HSFO, 2000)
Goals <strong>of</strong> <strong>Stroke</strong> <strong>Rehabilitation</strong>• Prevent & treat complications• Restore independent functioning• Facilitate psychosocial coping• Promote community re-integration• Enhance quality <strong>of</strong> life
Do you as a nurseimplement strokerehabilitation as part<strong>of</strong> your plan <strong>of</strong> care?
<strong>Stroke</strong> <strong>Rehabilitation</strong>• A “process” that begins at onset• Early rehabilitation optimizesstroke outcomes• Apply principles throughout <strong>the</strong>continuum <strong>of</strong> care
<strong>Stroke</strong> <strong>Rehabilitation</strong> NursingPrinciples• Continuity <strong>of</strong> <strong>Care</strong> (repetition)• Holistic approach to care• Integrated interdisciplinary teamapproach
2003 Cochrane Database<strong>Stroke</strong> Unit Trials Review• <strong>Stroke</strong> patients who receiveorganized inpatient care in a strokeunit are more likely to be alive,independent, and living at homeone year after <strong>the</strong> stroke
<strong>Stroke</strong> Unit Characteristics• Patients cared for in a geographicallydistinct location• Nursing Specialization and team expertise• Nursing integration with multidisciplinaryplan <strong>of</strong> care
<strong>Stroke</strong> Unit Characteristics• Coordinated multidisciplinary care• Family centered care• Staff, patient and caregiver education
Case StudyMrs.Percy
Mrs Percy’s Hx• 77 year old retired teacher, very active• Married, supportive family• Found in bed awake at 0800, responsiveand talking• Left facial drooping with left hemiplegia• She was last seen normal at 10 pm <strong>the</strong>night before. Not a candidate for tPA• BP 165/100 in ER• No previous <strong>Stroke</strong> or TIAs
Diagnosis: Ischemic <strong>Stroke</strong>• CT Results: RtMCA IschemicInfarct
Mrs Percy’s Deficits• Left hemiplegia• Left shoulder sublexation with pain• Requires two person transfer• Dysphagia: pureed diet with thickenedfluids• Continent <strong>of</strong> bowel and bladder but needsassistance with dressing/undressing• Emotionally labile• Apraxia• Left body neglect
What are your plannedinterventions to preventcomplications andoptimize Mrs Percy’srecovery?
Maintaining Skin Integrity• Skin assessment weekly using Bradenscale• Collaborate with OT, PT, andNutritionist to manage risk factors• Turning/repositioning schedule
Promoting Early Remobilization• Complete risk for falls assessmentupon admission in collaboration withOT and PT• Post instructions for safetransferring, positioning, andambulation at <strong>the</strong> bedside and on <strong>the</strong>care plan• Educate <strong>the</strong> patient/family
Promoting Safe Swallowing andFeeding• Collaborate with SLP and Nutritionist withswallowing and nutritional assessment• Implement feeding strategies and dietmodifications as recommended to reducerisk <strong>of</strong> aspiration• Reinforce diet education for MrsPercy/family
Preventing Aspiration PneumoniaMalnutrition, & Dehydration• Ongoing swallowing nutrition andrespiratory assessments• Report progress or concerns to <strong>the</strong>SLP and Nutritionist and implementchanges to diet and feedingstrategies suggested
Restoring MaximalIndependence with ADL• Collaborate with <strong>the</strong>rapists• Provide education/coaching• Reinforce <strong>the</strong>rapy at <strong>the</strong> bedside• On going assessment• Review Mrs Percy’s progress withInterdisciplinary team during <strong>Stroke</strong>Rounds, Discharge Rounds, and Familymeetings
Protecting Hemiplegic Shoulder• Provide mechanical support <strong>of</strong> left arm (ie. Laptray, positioning)• Move gently and allow her time to participate• When side-lying, never position her directly on <strong>the</strong>humeral head• Encourage Mrs Percy to pay attention to left arm
Pain Management- Assess for pain using a pain scale <strong>of</strong>1-10- Administer analgesia and evaluateeffectiveness- Collaborate with OccupationalTherapy and Physio<strong>the</strong>rapy for <strong>the</strong>appropriate positioning andtransferring techniques
Continence Promotion• Ensure bedpan and Commode chairare at <strong>the</strong> bedside• Ask family to bring in adaptive looseclothing to promote toileting• Encourage Mrs Percy to call forassistance when needed• Educate patient and family
Facilitating PsychosocialCoping and Adaptation• Assess behavior, mood, loss <strong>of</strong> interestin daily activities, sleeping pattern andloss <strong>of</strong> appetite• Assess risk <strong>of</strong> depression using aDepression scale (Score ResearchProject)• Encourage family participation dayswith <strong>the</strong>rapists
What education do youwant to provide MrsPercy and her family?
Promoting <strong>Stroke</strong> Awareness• What is a stroke• Complications/deficits• Plan <strong>of</strong> <strong>Care</strong>• Risk Factors• Recognize & Reactto S&S• Secondary<strong>Stroke</strong>prevention– Medication– Diet– Exercise– BP
SMOL <strong>Stroke</strong> RehabAdmission Criteria• >16 years <strong>of</strong> age• Recent stroke• Stable• Investigations completed• Agrees to participate in stroke rehab• Able to learn
<strong>Stroke</strong> <strong>Rehabilitation</strong>Mrs Percy isadmitted to<strong>the</strong> in-patient<strong>Stroke</strong><strong>Rehabilitation</strong>Program atSMOL
Mrs Percy’s Deficits: 3 weeks• One person pivot transfer• Left shoulder pain continues• Dysphagia: minced diet with thickenedfluids, but wants to eat regular meals anddrink water• Continues to need assistance withtoileting• Emotionally: Anxious to return home andresume her social activities and refusesto be discharged to a LTC home
What are yourinterventions for MrsPercy and her family?
<strong>Stroke</strong> <strong>Rehabilitation</strong> Nursing• Ongoing assessment• Prevention <strong>of</strong> complications• Achievement <strong>of</strong> patient goals• Ethical issues• Patient/family education• Community re-integration
Preventing Complications• Collaborate with SLP and Nutritionistto assess dysphagia and nutritionalstatus• Reinforce diet and safe feedingstrategies with patient and family• Complete risk for falls assessmentupon admission in collaboration withMrs Percy, OT, PT, and Nursing
Restoring Mobility andMaximal Independence• Post instructions for safe transferring,positioning and ambulation at <strong>the</strong> bedside• Promote toileting and mobilization• Educate Mrs. Percy/family aboutrehabilitation and <strong>the</strong> approach to care atSMOL
Restoring Mobility andMaximal Independence• Collaborate with Pain Team, PT OT andPhysiatrist to manage shoulder pain• Reinforce <strong>the</strong>rapeutic interventions at <strong>the</strong>bedside (e.g. dressing, safe transferring)• Prepare Mrs Percy for cortisone injectionstudy in collaboration with Physiatrist
Facilitating Psychosocial Coping& Community Re-integration• Provide emotional support and educationre: stroke, secondary stroke prevention,community support, and caregiver stress• Monitor behavior, mood and affect forS/S <strong>of</strong> depression• Advocate for Mrs Percy and family at<strong>Stroke</strong> Rounds and Discharge PlanningRounds• Collaborate with team to resolve ethicalissues
Transition Management• A stroke survivor mayundergo severaltransitions in care• Effective transitions arean integral part <strong>of</strong>improving strokemanagement(BPGs for <strong>Stroke</strong> <strong>Care</strong>, 2003)
Managing <strong>the</strong> TransitionAchieving excellence intransition management is• Collaboration amonghealthcare providers indifferent organizations• Sharing both informationresponsibility for <strong>the</strong> entireprocess”(BPGs for <strong>Stroke</strong> <strong>Care</strong>, 2003)
Barriers to EffectiveTransition• Unexpected orunexplained delays intransferring strokesurvivors to <strong>the</strong>appropriate placement(BPGs for <strong>Stroke</strong> <strong>Care</strong>, 2003)
Barriers to EffectiveTransition• Lack <strong>of</strong> communication• Inadequate informationupon admission• Lack <strong>of</strong> attention toemotional needs(BPGs for <strong>Stroke</strong> <strong>Care</strong>, 2003)
What Information Is MostHelpful?• Full discharge summary re:stroke interventions,education and supportprovided• Interdisciplinary team reportwith specific programsestablished
Direct Communication• Holistic approach• Complete picture <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> client andfamily / caregiver– Functional status <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> strokesurvivor– Prognosis, established goals– Family support available
Reflect on whatbarriers to effectivetransition managementexist in your facility?
<strong>Rehabilitation</strong> Nurses:Champions for Optimizing<strong>Stroke</strong> <strong>Rehabilitation</strong>• Begin rehabilitation in acute care– Continue across <strong>the</strong> continuum <strong>of</strong> care• Prevent & treat complications• Integrated team approach• Transition management
<strong>Rehabilitation</strong> Nursing Role• Clinician• Collaborator• Coach• Educator• Advocate• Researcher