Scanner 2000 Steam Mass Flow Transmitter ... - Spirax Sarco
Scanner 2000 Steam Mass Flow Transmitter ... - Spirax Sarco
Scanner 2000 Steam Mass Flow Transmitter ... - Spirax Sarco
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
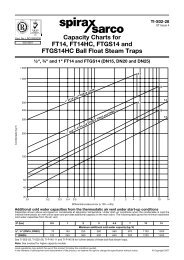
<strong>Scanner</strong> ® <strong>2000</strong> microEFM Section 1<br />
NuFlo Cone Meter (DP Input). The <strong>Scanner</strong> <strong>2000</strong> supports steam measurement using industry-recognized<br />
algorithms identified in the NuFlo Cone Meter User Manual. Fluid properties for steam are calculated<br />
in accordance with the IAPWS Industrial-Formulation 1997 (IF-97) standard. Temperature is calculated<br />
according to IF-97 for saturated steam, based on static pressure. Therefore, an RTD is not required. The<br />
optional Steven wet correction method is supported for the measurement of vapor and fluid.<br />
Averaging Pitot Tube Meter (Annubar ® ). The <strong>Scanner</strong> <strong>2000</strong> supports steam measurement based on ASME<br />
MFC-12M -2006 flow rate methods for averaging pitot tube meters. Fluid properties are calculated in<br />
accordance with the IAPWS Industrial-Formulation 1997 (IF-97) standard. Temperature is calculated<br />
according to IF-97 for saturated steam, based on static pressure. Therefore, an RTD is not required. Wet<br />
correction methods are not supported.<br />
Compensated Liquid<br />
The <strong>Scanner</strong> <strong>2000</strong> measures compensated petroleum liquid flow using an orifice, cone, liquid turbine, or<br />
averaging pitot tube (Annubar ® ) flowmeter. Users can select either of two fluid property calculation methods<br />
for use with any of these flowmeters.<br />
• The “generic” fluid properties calculation method is used to measure liquids such as water or emulsions,<br />
based on user-supplied viscosity values and either user-supplied density values or user-supplied liquid<br />
thermal expansion coefficients.<br />
• The API-2540 calculation method provides temperature corrections for the following petroleum liquids:<br />
crude oil, gasoline, jet fuel, fuel oils, and lube oil.<br />
Orifice Plate (DP Input). The <strong>Scanner</strong> <strong>2000</strong> calculates flow rates in accordance with AGA Report No. 3, Part<br />
1 (1990) or ISO-5167 (2003) methods. When measuring liquids, the expansion factor (Y) is always equal to<br />
1.0. Fluid property calculations for temperature-compensated measurements are based on API-2540 (1980),<br />
Petroleum Measurement Tables.<br />
NuFlo Cone Meter (DP Input). The <strong>Scanner</strong> <strong>2000</strong> calculates flow rates in accordance with industryrecognized<br />
algorithms identified in the NuFlo Cone Meter User Manual. When measuring liquids, the<br />
expansion factor (Y) is always equal to 1.0. Fluid property calculations for temperature-compensated liquids<br />
are based on API-2540 (1980), Petroleum Measurement Tables.<br />
Liquid Turbine Meter (Frequency Input). The <strong>Scanner</strong> <strong>2000</strong> calculates flow rates in accordance with the<br />
measurement principles upon which the AGA-7 standard is based. The user supplies a linear or multi-point<br />
calibration factor, and the instrument performs the required compensation calculations, based on the RTD<br />
input.<br />
Averaging Pitot Tube Meter (Annubar ® ). The <strong>Scanner</strong> <strong>2000</strong> calculates flow rates in accordance with the<br />
ASME MFC-12M-2006 measurement standard. When measuring liquids, the expansion factor (Y) is always<br />
equal to 1.0. Fluid property calculations for temperature-compensated liquids are based on API-2540 (1980),<br />
Petroleum Measurement Tables.<br />
Uncompensated Liquid<br />
The <strong>Scanner</strong> <strong>2000</strong> measures uncompensated liquid flow based on the input from a liquid turbine meter or PD<br />
meter.<br />
Liquid Turbine Meter (Frequency Input) or PD Meter (Pulse Input). The <strong>Scanner</strong> <strong>2000</strong> calculates flow rate<br />
from a liquid turbine meter via a frequency input, or from a contact closure (which requires the pulse input on<br />
the optional expansion board). <strong>Flow</strong> rates and totals are calculated using a user-supplied linear or multi-point<br />
calibration factor in accordance with API Manual of Petroleum Measurement Standards, Chapter 5, Section 3,<br />
Measurement of Liquid Hydrocarbons by Turbine Meters (2005).<br />
9