Cornea - ARVO
Cornea - ARVO
Cornea - ARVO
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
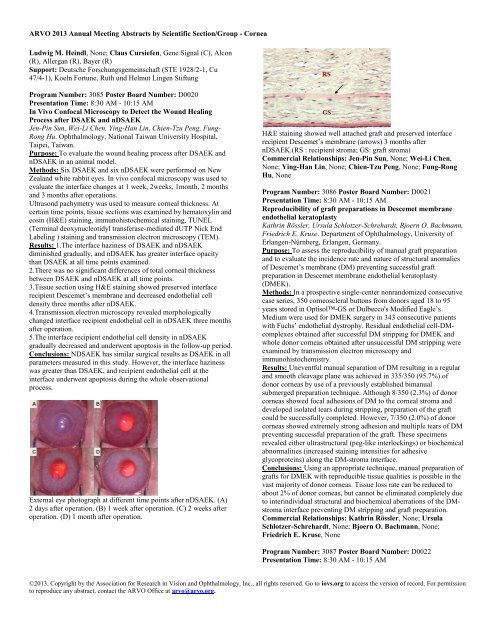
<strong>ARVO</strong> 2013 Annual Meeting Abstracts by Scientific Section/Group - <strong>Cornea</strong>Ludwig M. Heindl, None; Claus Cursiefen, Gene Signal (C), Alcon(R), Allergan (R), Bayer (R)Support: Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (STE 1928/2-1, Cu47/4-1), Koeln Fortune, Ruth und Helmut Lingen StiftungProgram Number: 3085 Poster Board Number: D0020Presentation Time: 8:30 AM - 10:15 AMIn Vivo Confocal Microscopy to Detect the Wound HealingProcess after DSAEK and nDSAEKJen-Pin Sun, Wei-Li Chen, Ying-Han Lin, Chien-Tzu Peng, Fung-Rong Hu. Ophthalmology, National Taiwan University Hospital,Taipei, Taiwan.Purpose: To evaluate the wound healing process after DSAEK andnDSAEK in an animal model.Methods: Six DSAEK and six nDSAEK were performed on NewZealand white rabbit eyes. In vivo confocal microscopy was used toevaluate the interface changes at 1 week, 2weeks, 1month, 2 monthsand 3 months after operations.Ultrasond pachymetry was used to measure corneal thickness. Atcertain time points, tissue sections was examined by hematoxylin andeosin (H&E) staining, immunohistochemical staining, TUNEL(Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP Nick EndLabeling ) staining and transmission electron microscopy (TEM).Results: 1.The interface haziness of DSAEK and nDSAEKdiminished gradually, and nDSAEK has greater interface opacitythan DSAEK at all time points examined.2.There was no significant differences of total corneal thicknessbetween DSAEK and nDSAEK at all time points.3.Tissue section using H&E staining showed preserved interfacerecipient Descemet’s membrane and decreased endothelial celldensity three months after nDSAEK.4.Transmission electron microscopy revealed morphologicallychanged interface recipient endothelial cell in nDSAEK three monthsafter operation.5.The interface recipient endothelial cell density in nDSAEKgradually decreased and underwent apoptosis in the follow-up period.Conclusions: NDSAEK has similar surgical results as DSAEK in allparameters measured in this study. However, the interface hazinesswas greater than DSAEK, and recipient endothelial cell at theinterface underwent apoptosis during the whole observationalprocess.External eye photograph at different time points after nDSAEK. (A)2 days after operation. (B) 1 week after operation. (C) 2 weeks afteroperation. (D) 1 month after operation.H&E staining showed well attached graft and preserved interfacerecipient Descemet’s membrane (arrows) 3 months afternDSAEK.(RS : recipient stroma; GS: graft stroma)Commercial Relationships: Jen-Pin Sun, None; Wei-Li Chen,None; Ying-Han Lin, None; Chien-Tzu Peng, None; Fung-RongHu, NoneProgram Number: 3086 Poster Board Number: D0021Presentation Time: 8:30 AM - 10:15 AMReproducibility of graft preparations in Descemet membraneendothelial keratoplastyKathrin Rössler, Ursula Schlotzer-Schrehardt, Bjoern O. Bachmann,Friedrich E. Kruse. Department of Ophthalmology, University ofErlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany.Purpose: To assess the reproducibility of manual graft preparationand to evaluate the incidence rate and nature of structural anomaliesof Descemet’s membrane (DM) preventing successful graftpreparation in Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty(DMEK).Methods: In a prospective single-center nonrandomized consecutivecase series, 350 corneoscleral buttons from donors aged 18 to 95years stored in Optisol-GS or Dulbecco's Modified Eagle’sMedium were used for DMEK surgery in 343 consecutive patientswith Fuchs’ endothelial dystrophy. Residual endothelial cell-DMcomplexesobtained after successful DM stripping for DMEK andwhole donor corneas obtained after unsuccessful DM stripping wereexamined by transmission electron microscopy andimmunohistochemistry.Results: Uneventful manual separation of DM resulting in a regularand smooth cleavage plane was achieved in 335/350 (95.7%) ofdonor corneas by use of a previously established bimanualsubmerged preparation technique. Although 8/350 (2.3%) of donorcorneas showed focal adhesions of DM to the corneal stroma anddeveloped isolated tears during stripping, preparation of the graftcould be successfully completed. However, 7/350 (2.0%) of donorcorneas showed extremely strong adhesion and multiple tears of DMpreventing successful preparation of the graft. These specimensrevealed either ultrastructural (peg-like interlockings) or biochemicalabnormalities (increased staining intensities for adhesiveglycoproteins) along the DM-stroma interface.Conclusions: Using an appropriate technique, manual preparation ofgrafts for DMEK with reproducible tissue qualities is possible in thevast majority of donor corneas. Tissue loss rate can be reduced toabout 2% of donor corneas, but cannot be eliminated completely dueto interindividual structural and biochemical aberrations of the DMstromainterface preventing DM stripping and graft preparation.Commercial Relationships: Kathrin Rössler, None; UrsulaSchlotzer-Schrehardt, None; Bjoern O. Bachmann, None;Friedrich E. Kruse, NoneProgram Number: 3087 Poster Board Number: D0022Presentation Time: 8:30 AM - 10:15 AM©2013, Copyright by the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology, Inc., all rights reserved. Go to iovs.org to access the version of record. For permissionto reproduce any abstract, contact the <strong>ARVO</strong> Office at arvo@arvo.org.