第22回 ロボット聴覚特集 - 奥乃研究室 - 京都大学
第22回 ロボット聴覚特集 - 奥乃研究室 - 京都大学
第22回 ロボット聴覚特集 - 奥乃研究室 - 京都大学
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
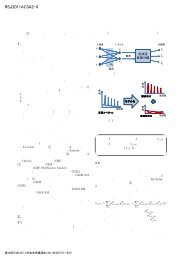
ンターフェースはスパイクイベントと 決 まっており、その 時 間 情 報 に 位 相 、 強 度 、 周 波 数 など 必 要 な 情 報が 準 備 されているので、 受 け 側 で 選 択 し 利 用 すればいい。また、 個 々の 処 理 が 単 純 なため、 冗 長 ではあるが 多 数 のニューロンを 用 意 し 関 係 付 けることで、時 間 的 にも 空 間 的 にも 補 完 的 な 処 理 が 可 能 になる。このモデルは 学 習 発 達 型 でも 利 用 可 能 である。 発達 型 にするのであれば、2.2.1 などを 参 考 に、 低 周 波選 択 で 位 相 発 火 型 の 聴 神 経 をベースに 内 側 上 オリーブ- 下 丘 間 の 結 合 を 学 習 し、 下 丘 に 方 向 マップを 概ね 作 成 した 後 に 外 側 オリーブや 外 側 毛 帯 を 導 入 し、上 下 で 挟 むことで 学 習 を 進 めればいい。また、このモデルにおいてマスクを 形 成 する 外 側毛 帯 の 活 動 は、 一 時 の 入 力 に 対 し 20 ミリ 秒 ほどの 継続 的 発 火 を 伴 うものなのだが、そのような 特 性 も 細胞 特 性 に 組 み 込 むだけでよい。IID などは、 計 算 方 式はアルゴリズムで 記 述 するものと 異 なるが 内 容 に 大きな 差 はないが、 同 じ 計 算 原 理 で Fig.7 のモデルをすべて 動 かせることが 何 よりも 重 要 である。しかし、3.1 で 述 べたように 原 理 は 実 時 間 向 きでも、 処 理 が 実時 間 でないことは 大 きな 課 題 であり、ロボット 応 用に 向 けてはさらなる 技 術 蓄 積 が 必 要 である。。4. おわりに脳 型 情 報 処 理 の 立 場 から、ロボット 聴 覚 を 考 察 した。 本 稿 ではスパイキングニューロンの 処 理 に 関 してのみ 述 べたが、3 節 冒 頭 で 述 べたように、 脳 型 情 報処 理 はシステム、 回 路 、 素 子 の 3 要 素 からなり、それらの 相 乗 効 果 が 大 きい。 三 位 一 体 の 研 究 展 開 が 重要 である。ロボット 聴 覚 は 情 報 処 理 として 求 められる 動 的 特 性 、 学 習 能 力 の 観 点 から、 脳 型 情 報 処 理 の研 究 において 最 適 な 課 題 といえる。 今 後 、 両 研 究 領域 の 相 互 発 展 を 期 待 したい。参 考 文 献1) Berg, BO., Principles of Child Neurology, McGraw-Hill,New York NY, 1995.2) Brooks, RA. : A Robust Layered Control System for aMobile Robot, IEEE Journal of Robotics and Automation 2(1), 14–2, 1986.3) Clifton RK., The development of spatial hearing in humaninfants, in Werner LA, Rubel EW (eds): Developmental Psycholoacoutics.,American psychological Association, Washington,DC, 135-157, 1992.4) Damasio, H., Tranel, D., Grabowski, T., Adolphs, R.,Damasio, A., Neural systems behind word and concept re-trieval, Cognition, 92, 179-229, 2004.5) Dayan, P., Abbott, LF., Theoretical Neuroscience: Computationaland Mathematical Modeling of Neural Systems,MIT Press, Cambridge MA, 2001.6) Dominey PF.,Hoen M.,Blanc JM.,Lelekov-Boissard T.,7)Neurological basis of language and sequential cognition:evidence from simulation, aphasia, and ERP studies., Brainand Language, 86(2),207-25, 2003.D’Esposito M, Alexander MP., Subcortical aphasia: distinctprofiles following left putaminal hemorrhage. Neuorol-ogy, 45, 38–41, 1995.8) Ewert, J.-P. and Arbib, M.A., Eds., Visuomotor Coordina-Amphibians, Comparisons, Models and Robots, Newtion:York: Plenum Press, 1989.9) Jordan, MI. (Ed.), Learning in graphical models., MITPress, Cambridge MA, 1999.10) Koch, C. (ed.), Biophysics of Computation, Oxford UniversityPress, New York, 1999.11) Koerner, E., Gewaltig, M-O., Koerner, U., Richter, A. andRodemann, T., A model of computation in neocorticalarchitecture., Neural Networks, 12:989–1006, 1999.12) Koerner, E., Tsujino, H. and Masutani, T.: A Cortical-typeModular Neural Network for Hypothetical Reasoning,Neural Networks 10, 791-814, 1997.13) Lieberman, P., On the nature and evolution of the neuralbases of human language, Yearbook of physical anthropology,45, 36-62, 2002.14) Litovsky RY, Colburn HS, Yost WA, Guzman SJ., Theprecedence effect, J Acoust Soc Am.,106(4 Pt 1),1633-54,1999.15) Litovsky RY, Shinn-Cunningham BG., Investigation of therelationship among three common measures of precedence:fusion, localization dominance, and discrimination suppression,J Acoust Soc Am., 109(1),346-58, 2001.16) Maas W., Bishop, CM. (eds), Pulsed neural networks, MITPress, Cambridge MA, 1998.17) McCarthy, J., Minsky ML., Rochester, N., Shannon CE., Aproposal for the Dartmouth summer research project on artificialintelligence”, 1955.18) McCulloch, W.S. and Pitts, W.H., A logical calculus of theideas immanent in neural nets, Bulletin of MathematicalBiophysics, 5 : 115-133, 1943.19) Nilsson, NJ. : Shakey The Robot, Technical Note 323. AICenter, SRI International, 1984.20) Poeppel, D., Hickok, G., Towards a new functional anatomyof language, Cognition, 92(1-2), 1-12, 2004.21) Pollak GD, Burger RM, Klug A., Dissecting the circuitryof the auditory system, Trends Neuroscience, 26(1),33-9,2003.22) Tsujino, H., Output-driven operation and memory-basedarchitecture principles embedded in a real-world device,Journal of Integrative Neuroscience, 3(2), 133-42, 2004.23) Ullman, MT., Contribution of memory circuits to language:the declarative/procedural model, Cognition, 92, 231-270,2004.24) Watkins KE, Vargha-Khadem F, Ashburner J, PassinghamRE, Connelly A, Friston KJ, Frackowiak RS, Mishkin M,Gadian DG., MRI analysis of an inherited speech and languagedisorder: structural brain abnormalities., Brain, 125( Pt3), 465-78, 2002.25) Werner LA., Gillenwater JM., Pure-tone sensitivity of 2-to5-week-old infants, Infant Behavior and Development,13(355), 355-375, 1990.26 ) Wolpert D, Kawato M: Multiple paired forward and inversemodels for motor control. Neural Networks11,1317-1329, 1998.27) Yang X, Grantham DW., Echo suppression and discriminationsuppression aspects of the precedence effect, PerceptPsychophys, 59(7),1108-17, 1997.28) 井 上 博 充 : 人 間 型 ロボットが 拓 く 未 来 社 会 と 新 産 業の 創 成 , 日 本 ロボット 学 会 誌 , 22 (1), 2-5 , 2004.29) 奥 乃 博 , 中 臺 一 博 , ロボット 聴 覚 の 課 題 と 現 状 , 情 報処 理 , 44(11), 104-113, Nov. 2003.30) 松 本 元 、 辻 野 広 司 : 脳 のこころ、「 情 と 意 の 脳 科 学 」、松 本 元 ・ 小 野 武 年 共 編 、 培 風 館 , 2002.40