Chapter 5 Integumentary System.pdf
Chapter 5 Integumentary System.pdf
Chapter 5 Integumentary System.pdf
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
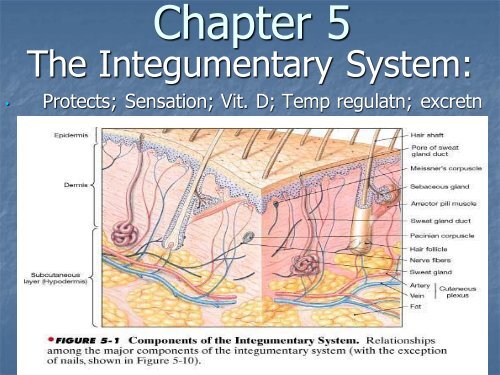
<strong>Chapter</strong> 5The <strong>Integumentary</strong> <strong>System</strong>:• Protects; Sensation; Vit. D; Temp regulatn; excretn
A. Skin1. Epidermis• Roof• Stratified squamousA. Stratum basale:• Bottom• Mitosis ~ every 19 days• 1 surfaces ~ 40-56 days later
C. Stratum Corneum• Upper• Protective: cells coated w/lipid• Top sloughs• Callus: friction ↑ cell layers• Corn: thickened area over bone
2. Dermis• House• Collagen (strength)• Cleavage Lines (fiber orientation)• resist stretching• parallel incision heal best• striae: stretch marks
Skin Cont.• Few fat cells/macrophages• Dermal papillae (upper)• Blood vessels (move matl’s, temp reg)• Shape finger/ft print• Grip of hand/ft
B. Skin Color1. Melanin:• Brn/blk pigment molecule• UV protection• Melanocytes:• Produce melanin vesicles: melanosomes• Vesicles phagocytized by epidermal cells• Freckles/moles: most• Palms/soles: least• # of melanocytes:• Same for all races- Skin cells
• Production based on:• Genetics: races• Albinism = recessive (no melanin)• Hormones: pregnancy mask• UV light: suntan
2. Tattoo: bluish hue: dermal fibers scatter light
3. Cyanosis: bluish hue: ↓ bld O2Irregular heart w/Undersized lungsCyanosis of nail beds with extremepulmonary dysfunction
4. Carotene: yellowish lipid-soluble pigment (carrots)5. Jaundice: yellow w/liver damage - bile in bldJaundice: Yellow skin discoloration caused by hyperbilirubinemiaAnatomy of the liver. An obstruction in the bileduct may lead to jaundice.
6. Birthmark: congenital disorder of dermal BVCapillary Malformation("Port-wine Stain")Most birthmarks are no risk to healthVascular birthmarks are caused by enlarged small blood vessels justbeneath the skin's surface. The most common are known as "angel'skisses“when located on the forehead or eyelids, and as "stork bites"when they appear on the back of the neck.
C. Hypodermis• Foundation• Subcutaneous (under skin)• ½ body fat (insulate/pad); TBF count• Injection site
D. Accessory Skin Structures1. Hair:A. Shaft (visible)B. Hair root (bulb) in follicle• Dermal papilla nourishes• Divide/keratinizehe cuticle, or outer layer,f a healthy shaft of hairA split end, caused whena hair shaft is pulled apart
• Phases• Growth: lash-30 dys/scalp-3 yrs• Rest: lash 105 dys/scalp-1-2 yrs
C. Pattern baldness: sex linked (hormone)
D. Color: determined by bulb melanocytes• Age: gray -↓ activity; white - no actvtyHow does hair turn gray? The melanocytes in hair stop producing melanins!
2. Muscles: arrector pili (smooth)A. Gooseflesh: hair perpendicularB. W/fur: insulate/fierceness
3. Glands:A. Sebaceous- sebum (oil) to follicleB. Eccrine- sweat (↑ H2O) to skinC. Apocrine- org-sweat to genital/axillary follicle• Active w/puberty – bacterial decay=odorAn apocrine gland, whichproduces little sweat but isresponsible for the body'snatural 'scent'.
E. Physiology• Temp reg (dermal BV); excretion (urea-sweat)• Vitamin D prodctn: in skin w/UV• Stimulates Ca/P uptake SI= muscle/bone health
• Burns: degree of depth
• Partial-thickness: part of basale viable(regenerate from edges, follicles)• 1°: epidermis – edema, no scar• 2°: epi/dermis-blister, may scarThe epidermis, the outer layer, is burned.Reddening occurs and swelling is possible.The epidermis is burned through, and the dermis,is also injured. An intense red discoloring isaccompanied by severe pain, swelling and blisters.
• Full-thickness:• 3°: epi/dermis destroyed-skin graftAll layers of skin are burned through to the fat, muscles and possiblyto the bone. There may be severe pain, but sometimes extensivenerve damage results in little or no pain.
First Degree BurnSecond Degree BurnThird Degree BurnSuperficial(epidermal burn)Intermediate(superficial dermal burn)Fourth degree burnDeep(sub-dermal burn)
• Skin Cancer:• most common type of cancer; UV exposure• Basal cell carcinoma: common; open ulcer; treatableMassive UlceratingBasal Cell CarcinomaHistology:basal cellcarcinoma,high power
• Squamous cell carc. : keratinized tumor;↓ metastasis
• Malignant melanoma: rare; melanocytes-mole:metastasis common (fatal)
Aging• ↓ skin activity & functn• Age spots w/↑ # of melanocytes (some areas)