Nausea and vomiting - Palliative Care Resources
Nausea and vomiting - Palliative Care Resources
Nausea and vomiting - Palliative Care Resources
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
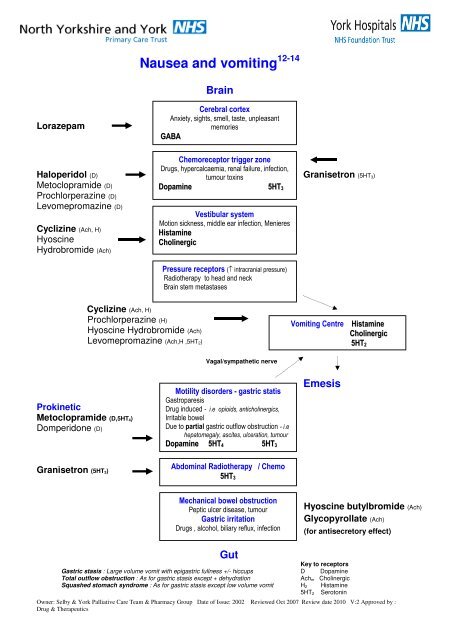
<strong>Nausea</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>vomiting</strong> 12-14BrainLorazepamCerebral cortexAnxiety, sights, smell, taste, unpleasantmemoriesGABAChemoreceptor trigger zoneDrugs, hypercalcaemia, renal failure, infection,Haloperidol (D) tumour toxinsGranisetron (5HT 3)Metoclopramide (D)Dopamine 5HT 3Prochlorperazine (D)Levomepromazine (D)Cyclizine (Ach, H)HyoscineHydrobromide (Ach)Vestibular systemMotion sickness, middle ear infection, MenieresHistamineCholinergicPressure receptors (↑ intracranial pressure)Radiotherapy to head <strong>and</strong> neckBrain stem metastasesCyclizine (Ach, H)Prochlorperazine (H)Hyoscine Hydrobromide (Ach)Levomepromazine (Ach,H ,5HT 2)Vomiting CentreHistamineCholinergic5HT 2Vagal/sympathetic nerveProkineticMetoclopramide (D,5HT 4)Domperidone (D)Granisetron (5HT 3)Motility disorders - gastric statisGastroparesisDrug induced - i.e opioids, anticholinergics,Irritable bowelDue to partial gastric outflow obstruction - i.ehepatomegaly, ascites, ulceration, tumourDopamine 5HT 4 5HT 3Abdominal Radiotherapy / Chemo5HT 3EmesisMechanical bowel obstructionPeptic ulcer disease, tumourGastric irritationDrugs , alcohol, biliary reflux, infectionHyoscine butylbromide (Ach)Glycopyrollate (Ach)(for antisecretory effect)GutGastric stasis : Large volume vomit with epigastric fullness +/- hiccupsTotal outflow obstruction : As for gastric stasis except + dehydrationSquashed stomach syndrome : As for gastric stasis except low volume vomitKey to receptorsD DopamineAch m CholinergicH 2 Histamine5HT 2 SerotoninOwner: Selby & York <strong>Palliative</strong> <strong>Care</strong> Team & Pharmacy Group Date of Issue: 2002 Reviewed Oct 2007 Review date 2010 V:2 Approved by :Drug & Therapeutics
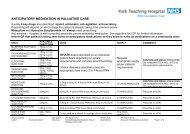
Summary of anti-emetics commonly used in <strong>Palliative</strong> careReceptor action Main site of action Choice of antiemetic for :Haloperidol Dopamine antagonist +++ Chemoreceptor trigger zone o Chemical causee.g. drugs, ↑Ca, uraemiaProchlorperazine Dopamine antagonist ++ Chemoreceptor trigger zone o Chemical causesHistamine antagonist +Levomepromazine Dopamine antagonist ++Histamine antagonist +++Muscarinic antagonist ++5HT 2 antagonist +++Chemoreceptor trigger zoneVestibular centreVomiting CentreoPersisting nausea <strong>and</strong> <strong>vomiting</strong>(especially if mechanismuncertain)Cyclizine Histamine antagonist ++Muscarinic antagonist ++VestibularVomiting centreo Vagal stimulationeg mechanical bowel obstructiono Raised intracranial pressureo Motion sicknessHyoscine hydrobromide Muscarinic antagonist +++ Vomiting centre As for cyclizineMetoclopramide Dopamine antagonist ++5HT 4 agonist++Gut – increases peristalsisChemoreceptor trigger zoneDomperidone Dopamine antagonist ++ Gut – increases peristalsisChemoreceptor trigger zoneOctreotide Somatostatin analogue Gut – reduces GI secretions<strong>and</strong> motilityHyoscine butylbromide Muscarinic antagonist +++ Gut – reduces GI secretions& antispasmodicGranisetron 5HT 3 antagonist +++ Vagal 5HT 3 stimulationChemoreceptor trigger zoneo Prokinetic – gastric stasis,functional bowel obstructiono Chemical causesAs for metoclopramideo Bowel obstruction with largevolume vomituso Bowel Obstructiono Colico ChemotherapyDoses of anti-emetics commonly used in <strong>Palliative</strong> careGeneric nameUsual oral doseUsual Subcutaneous doseStat Rangeover 24hrsMaximumover 24 hrsCyclizine (Valoid) 25-50mg 8hrly 50mg 100-150mg 150mgDomperidone (Motilium)10-20mg 8hrly po(30-60mg 8hrly rectally)- - -Haloperidol (Serenace/Haldol) 1.5 - 5mg nocte 1.5mg 3-5mg 10mgHyoscine Hydrobromide (sl = Kwells) 150-300mcg s/l 8hrly 400mcg 400-2,400mcg 2400mcgLevomepromazine (Nozinan)6.25-12.5mg nocte 5-6.25mg 5-25mg 200mg forBroad spectrum antiemeticagitationMetoclopramide (Maxalon) 10-20mg tds (pre meal) 10mg 40-60mg 100mgGranisetron (Kytril)Chemotherapy induced nausea onlyAdjuvantsLorazepam (Ativan)Octreotide (S<strong>and</strong>ostatin)Dexamethasone (Decadron)1mg bd po1mg stat s/l-4-12mg po3mgintravenous----150-600mcg4-12mg9mgintravenous-1000mcg-Note• Important to fully assess patient <strong>and</strong> diagnose cause of nausea or <strong>vomiting</strong> <strong>and</strong> treat reversible causes.• Prescribe most appropriate first line antiemetic regularly.• If symptoms severe may need to use a syringe driver.• If combining antiemetics combine those with different actions (e.g Haloperidol <strong>and</strong> Cyclizine)• Do not usually combine antikinetics (i.e antimuscarinic e.g Cyclizine) with prokinetics (e.g Metoclopramide)• Levomepromazine oral : ( formerly called Methotrimeprazine) - available as a named patient supply from Link in a6mg tablet strength . Otherwise use ¼-½ of a commercially available 25mg tablet.• Also consider non-pharmacological methods of nausea control e.g Sea-B<strong>and</strong>s.Ginger is a natural antiemeticOwner: Selby & York <strong>Palliative</strong> <strong>Care</strong> Team & Pharmacy Group Date of Issue: 2002 Reviewed Oct 2007 Review date 2010 V:2 Approved by :Drug & Therapeutics