- Page 3 and 4: EEA Report No 12/2012Climate change
- Page 5: ContentsContentsAcknowledgements...
- Page 10 and 11: ContentsMap 4.1 Change in the numbe
- Page 12 and 13: ContentsList of boxesBox 1.1 The IP
- Page 14 and 15: AcknowledgementsAblain, Gilles Larn
- Page 16: AcknowledgementsComments from the E
- Page 20: Executive summaryThe causes of the
- Page 23: Technical summaryTable TS.1 Observe
- Page 26 and 27: Technical summaryTable TS.1 Observe
- Page 28 and 29: Technical summaryMountain areasThe
- Page 30: Technical summaryTable TS.2 Key obs
- Page 33 and 34: IntroductionIt should be noted that
- Page 35 and 36: IntroductionBox 1.1The IPCC Fifth A
- Page 37 and 38: Introduction1. develop and improve
- Page 39 and 40: Introduction1.4.3 Overview of main
- Page 41 and 42: IntroductionThe next generation of
- Page 44 and 45: Introductionimmigration will be low
- Page 46 and 47: Introduction7. projection of a clim
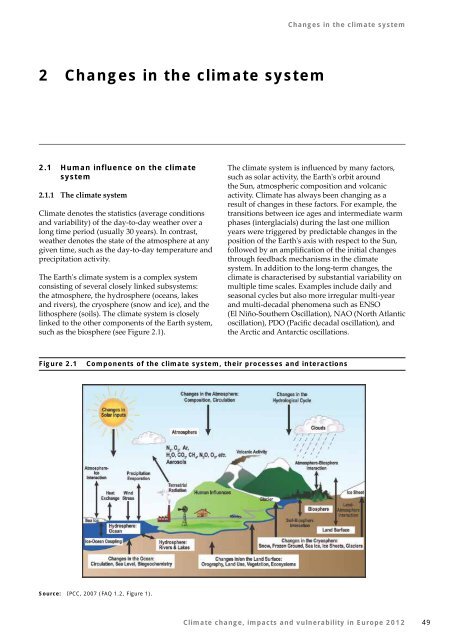
- Page 49: IntroductionThe term risk is also i
- Page 53 and 54: Changes in the climate systemdammin
- Page 55 and 56: Changes in the climate system2.1.4
- Page 57 and 58: Changes in the climate systemSelect
- Page 59 and 60: Changes in the climate systemPast t
- Page 61 and 62: Changes in the climate systemEurope
- Page 63 and 64: Changes in the climate systemSevera
- Page 65 and 66: Changes in the climate systemMap 2.
- Page 67 and 68: Changes in the climate systemMap 2.
- Page 69 and 70: Changes in the climate systemMap 2.
- Page 71 and 72: Changes in the climate systemMap 2.
- Page 73 and 74: Changes in the climate systemclosel
- Page 75 and 76: Changes in the climate system2.3 Cr
- Page 77 and 78: Changes in the climate systemPast t
- Page 79 and 80: Changes in the climate systemof up
- Page 81 and 82: Changes in the climate systemFigure
- Page 83 and 84: Changes in the climate systemFigure
- Page 85 and 86: Changes in the climate system2.3.5
- Page 87 and 88: Changes in the climate systemBox 2.
- Page 89 and 90: Changes in the climate systemFigure
- Page 91 and 92: Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 93 and 94: Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 95 and 96: Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 97 and 98: Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 99 and 100: Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 101 and 102:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 103 and 104:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 105:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 108 and 109:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 110 and 111:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 112 and 113:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 114 and 115:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 116 and 117:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 118 and 119:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 120:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 123 and 124:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 125 and 126:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 127 and 128:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 129 and 130:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 131 and 132:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 133 and 134:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 135 and 136:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 137 and 138:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 139:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 142 and 143:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 144 and 145:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 146 and 147:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 148 and 149:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 150 and 151:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 152 and 153:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 154 and 155:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 156 and 157:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 158 and 159:
Climate impacts on environmental sy
- Page 160 and 161:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 162 and 163:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 164 and 165:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 166 and 167:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 168 and 169:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 170 and 171:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 172 and 173:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 174 and 175:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 176 and 177:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 178 and 179:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 180 and 181:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 182 and 183:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 184 and 185:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 186 and 187:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 188 and 189:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 190 and 191:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 192 and 193:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 194 and 195:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 196 and 197:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 198 and 199:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 200 and 201:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 202 and 203:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 204 and 205:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 206 and 207:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 208 and 209:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 210 and 211:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 212 and 213:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 214 and 215:
Climate impacts on socio-economic s
- Page 216 and 217:
Vulnerability to climate changein f
- Page 218 and 219:
Vulnerability to climate change5.3
- Page 220 and 221:
Vulnerability to climate changeMap
- Page 222 and 223:
Vulnerability to climate changeasse
- Page 224 and 225:
Vulnerability to climate change5.3.
- Page 226 and 227:
Vulnerability to climate changeBox
- Page 228 and 229:
Vulnerability to climate changeMap
- Page 230 and 231:
Vulnerability to climate change5.5
- Page 232 and 233:
Vulnerability to climate changeFigu
- Page 234 and 235:
Vulnerability to climate changeFigu
- Page 236 and 237:
Vulnerability to climate changeFina
- Page 238 and 239:
Vulnerability to climate changefact
- Page 240 and 241:
Indicator and data needsA key polic
- Page 242 and 243:
Indicator and data needsWEI and res
- Page 244 and 245:
Indicator and data needsDirectorate
- Page 246 and 247:
Indicator and data needs6.2.2 Globa
- Page 248 and 249:
Abbreviations and acronyms7 Abbrevi
- Page 250 and 251:
Abbreviations and acronymsAcronym o
- Page 252 and 253:
Abbreviations and acronymsAcronym o
- Page 254 and 255:
Abbreviations and acronymsProject a
- Page 256 and 257:
Referenceset al. (2010) DEMIFER: De
- Page 258 and 259:
ReferencesNovember to 11 December 2
- Page 260 and 261:
ReferencesEEA (2011a) Mapping the i
- Page 262 and 263:
References19 December 2009. UNFCCC,
- Page 264 and 265:
ReferencesIsaksen, K., Sollid, J. L
- Page 266 and 267:
Referencesfür Hydrologie und Limno
- Page 268 and 269:
Referencescirculation models. Journ
- Page 270 and 271:
Referencesin Geophysics 32(4-5), 58
- Page 272 and 273:
ReferencesVermeer, M. and Rahmstorf
- Page 274 and 275:
ReferencesDevelopment. http://ec.eu
- Page 276 and 277:
ReferencesMooij, W. M., Hulsmann, S
- Page 278 and 279:
ReferencesAraújo, M. B., Thuiller,
- Page 280 and 281:
ReferencesPeninsula (1952-2004). Ec
- Page 282 and 283:
ReferencesMenzel, A., Sparks, T. H.
- Page 284 and 285:
ReferencesUrban, M. C., Tewksbury,
- Page 286 and 287:
ReferencesM., Palosuo, T., Bellamy,
- Page 288 and 289:
ReferencesApplied Climatology 74, 4
- Page 290 and 291:
Referencesepidemiologic evidence. E
- Page 292 and 293:
ReferencesEnvironmental Health Pers
- Page 294 and 295:
Referencestemperature. Epidemiology
- Page 296:
ReferencesEEA (2012) Annual Europea
- Page 299 and 300:
ReferencesChapter 5:Vulnerability t
- Page 301 and 302:
ReferencesSchool. http://www.jbs.ca
- Page 303 and 304:
European Environment AgencyClimate