Glia: sejttípusok és jellemzőik c - KOKI
Glia: sejttípusok és jellemzőik c - KOKI
Glia: sejttípusok és jellemzőik c - KOKI
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
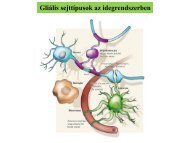
Gliális <strong>sejttípusok</strong> az idegrendszerben
Szatellitasejtekhttp://neurolex.org/wiki/Sao792373294Satellite glialcells (SGCs)- a neuronok sejttestjéhezközvetlenül illeszkedő sejtek- PNS-ben a ganglionokban- asztrocitákhoz hasonló funkciókPNS-ben- neural crest eredetűekGu, Huang 2010Afferent-stimulated ATP release from thesoma of a Dorsal Root Ganglion neuronand the excitatory (red arrow) andinhibitory (black arrow) control of theneuronal activity by SGCs.
SzatellitasejtekSatellite glial cells (SGCs)Érző neuron – SGC unit. A:egér DRG, SGC sejtekneuronok körül. A neuron-SGC egységeket kötőszövet(ct) választja el . *: nemmyelinált axonok Schwannsejtekkel körülvéve. sc: SGC.B: érző ganglion sematikusszerkezete.GS+ (glutamin szintáz)szatellitasejtek, nyíl:sejttestjükHanani 2005
Schwannsejtaxon- myelinálás a periférián- egy Schwann sejt – egy axont myelinál- minden internodus egy sejthez tartozik- neural crest eredetűek- 4 típus:- myelináló (nagy átmérőjű axon körül)- nem myelináló (kis axonnal kapcsolatossejt - axon-kötegeket különít el)- periszinaptikus (neuromuszkuláris)- terminális (érzőidegek)Schwann cellsforming myelinsheathes aroundaxons.nucleusnode of Ranvier
Schwann sejtPerifériánnem-myelinált axonmyelinált axon, Schwann sejttelhttp://www.wesapiens.org/file/2109169/Myelinated+nerve
SchwannsejtmitokondriumNem myelináltaxon, csak egyegyszerű Schwannmembránnalkörbekerítvekollagén rostok
Schwann sejtSchwann sejtek neural cresteredetűek, a növekvő axonokmentén vándorolnak.A korai Schwann prekurzorokaxonális kontakt nélkül nemélnek túl.(1) Schwann cell progenitorsproliferate and populate axonbundles(2) immature Schwann cells face abinary choice:(3) they either stay tightlyassociated with several axonsto form a Remak bundleNave, Schwab 2005Corfas, Ramsay 2003(4) or alternatively they single outlarger axons and differentiateinto myelinating Schwann cells(5) The entire path of Schwann celldevelopment and myelinationis remote controlled by theneurons through expression ofthe neuregulin-1 on theaxonal surface.
SchwannsejtMyelinP2, protein 2- FABP család tagja- myelincitoplazmatikusoldalánexpresszálódik- talánintracelluláriszsírsavtranszportban játszikPLP/DM20- Van PNS-ben is, de itt funkciója ?- PLP-KO egér: PNS myelináció OKMAG- periaxonális Schwann sejt membránban- funkciója is mint a CNS-ben: axon/myelinkapcsolat („axon-recognition”, adhézió,myelin-integritás fenntartása)MBP- jelen van, de nemolyan fontos, mintCNS-ben- shiverer mutánsbanCNS hypomyelinált dePNS nemVerrkhratsky, Butt 2007
SchwannsejtPMP22, Peripheral myelin protein 22- tetraspan membrane glycoprotein- trembler mutáns (PMP22 pontmuációk): PNSscpecifikusdismyelináció (P0 KO-hoz hasonló)- PMP22 KO: először hypermylináció majddemyelináció- myelináció kezdeti lép<strong>és</strong>eit, majd a myelinhüvelyvastagságát <strong>és</strong> stabilitását is szabályozza- valószínűleg integrin/laminin köt<strong>és</strong>ben is r<strong>és</strong>zt veszP0, Peripherial myelin protein zero- glycoprotein, IgCAM szupercsalád tagja- PNS myelin 50% -a- Schwann-sejt specifikus (ODC nemexpresszálja)- myelin lamellák adhéziójáért felel (mintPLP CNS-ben)- P0 KO egerek: komoly hiponyelináció <strong>és</strong>axondegeneráció - bár a myelinképz<strong>és</strong>kezdeti lép<strong>és</strong>ei nem értintettetekhttp://structbio.vanderbilt.edu/sanders/Research_Julia_Ver_1/Research.htmlP0-PMP22: ec. heterophilic interactionP0-P0: homophilic interactionBell, Haites 1998http://adc.bmj.com/content/78/4/296.full
Schwann sejtSchwann cells (blue) formmyelin by wrapping aninner process (arrow)around an axon (orange);initially loose wraps latercompact. The entire axon–Schwann cell unit issurrounded by a basallamina (gray). Schwanncells have two verydistinct surfaces: theadaxonal membranecontacting the axon andthe abaxonal membranecontacting the basallamina.Taveggia 2007Rat sciatic nerve, teasedfiber technique. Sudanblack. Nyílhegy: nodes ofRanvier;Szaggatott vonal:Schmidt-Lantermanincisures(„r<strong>és</strong>”) – ez PNS-rejellemző, CNS-ben ritka !!Oligodendroglia CNS-ben:nincs bazális membrán !!Piros kör: Schwann sejt magjaKrinke 2000Goodenough, Paul 2003
Schwann sejtCajal bands are cytoplasm-filled channels thatlie underneath the plasma membrane of theSchwann cell. Cajal bands contain microtubulesthat participate in the delivery of mRNA from thenucleus to distal sites at which it is translated.Court 2004a, Longitudinal and transverseprotoplasmic bands stained with silver byRamón y Cajal (Cajal bands).b, Teased fibres double-labelled withTRITC–phalloidin (actin) and an antibodyagainst DRP2 (dystrophin related protein2). Schwann cell cytoplasm is excludedfrom spheroidal clusters immunopositivefor DRP2.c, Immunostaining of fibres for theSchwann cell cytoplasmic protein S100.Sherman 2005
SchwannsejtPeriaxin„Teased fibers”, adult mousesciatic nerve, most superficiallayer of the Schwann cellmembrane.α-DG: a-disztroglikán;β-DG: b-disztroglikán; Drp2 :dystrophin related protein 2- PNS-specifikus glycoprotein, S <strong>és</strong> L-periaxin izoformák- L-periaxin: Schwann sejt cytoszkeleton-bazálismembrán kapcsolat- érett myelin-hüvely stabilizációja- mutációja: Charcot-Marie-Tooth diseaseCourt 2011Schwann cellabaxonaldomains.Appositions,Cajal-bands.
SchwannsejtConnexin32- főleg paranodálisrégióban <strong>és</strong> a Schmidt-Lanterman incisures –ban- r<strong>és</strong>-kapcsolatok amyelinben (Smidht-Lanterman incisures)- ÉS Schwann sejtekközött is- X-kromoszómás Cx32mutációk: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disesaseben- Cx32 KO egér hasonlófenotípusCompact myelin: halvány lila, ami teljesen leszigeteliaz axont, citoplazma-mentesNon-compacted myelin: sötét lila, csatornarendszer,melyen át a periaxonális térhez metabolitok juthatnakel: - SLIs: Schmidt–Lanterman incisures <strong>és</strong> paranodálisrégiókNave 2010
Olfactory nerve ensheating cells (ONEC, OEC)RágcsálószaglórendszerPuche AC.feromonok !Bulbusolfactorius
Olfactory nerve ensheatingcells (ONEC, OEC)Boyd 2005Olfactory receptor neuronok (ORN)bipoláris neuronok, dendritjük az orrüregfelé nyúlik, sok csillót bocsátva aszaglóhámot borító nyálkarétegbe.Axonjaik a szaglóideget alkotják, melyetONEC sejtek kísérnek eg<strong>és</strong>zen a bulbusig.Olfaktorikus axonok a glomerulusokban mitrálissejtek dendritjeivel képeznek szinapszisokat. AzONEC sejtek ezen axonokat borítják. Adendriteket asztrocita nyúlványok fedik.Raisman 2011
Olfactory nerve ensheatingcells (ONEC, OEC)Cross-section of the embryonic chickenolfactory bulb showing neural crest-derivedolfactory ensheathing cells. Axons; lowaffinityneurotrophin receptorClair BakerC: Olfactorikus lamina propria.OEC sejtmagok jellegzetesen oválisak.1: OEC sejtek egy nagy köteg nemmielináltolfaktorikus axon közelében.2: Egy nagyobb myelinált axon.3: Sok nem myelinált axon.FB: fibroblasztokBoyd 2005
Olfactory nerve ensheatingcells (ONEC, OEC)GFAP+, S100b+, nestin+, vimentin+fagocitálnak !- szaglóideg-regenerációértfelelős sejtek, eg<strong>és</strong>z életen át(fagocitotikus <strong>és</strong> antiinflammatorikusszerep)- implantációjukkalpróbálkoznak pl.gerincvelősérül<strong>és</strong>eknélOlfactory Ensheathing <strong>Glia</strong> (Sox10, Purple) surrounding theolfactory nerve which runs between receptor cells in the nose(right) and the brainRaisman 2006Regrowth of nerve fibres across a lesion of the rat corticospinal tracttransplanted with olfactory ensheathing cells. Reparative effect ofolfactory ensheathing cells (OEC) and their associated olfactory nervefibroblasts (fbl) on severed corticospinal axons. (a) During the firstweek, the axons advance, intimately surrounded by OECs and flanked byadvancing fibroblasts. (b) During the third and fourth weeks, the axonshave proceeded through the transplant, where they are now myelinated(myel) by OECs, thus forming a bridge from the oligodendrocytic myelinterritory (oli) at the cut, proximal end all the way through thetransplant to re-enter the oligodendrocytic territory at the distal end.http://thenode.biologists.com/wellcome-to-the-node/4_10x_sox10_e5-5_os/
Ependimasejtek3. kamra fala, 32 hetes fetus- agykamrákat <strong>és</strong> a gerincvelőcentrális csatornáját bélelőepitélsejtek- köbhám- mikrobolyhok <strong>és</strong> 1-többcsilló: liquor keverőáramaiCsillófejlőd<strong>és</strong> a laterális kamrában P0-P10.P10: érett állapotTissir 2010Gerincvelő, hibás ciliogenezis: hydrocephalusközponti csatornahttp://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/introductionneuropathttp://vanat.cvm.umn.edu/neurHistAtls/pages/glia6.htmlhology/Response%20_to_Injury/EpendymalCells.htmScanning electron micrographof the ciliated ependymallining of the floor of the 4thventricle of a 12-d-old Wistarrat. The 1-cm bar on thephotograph is equivalent to alength of 1.28 μmO Callaghan <strong>és</strong> mtsai., 1999; Luo <strong>és</strong> Conover 2008
Neuroblast migration parallelscerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flowIndia inkCell migrationCSF flowSawamoto, Alvarez-Buylla et al. 2006
Neuroblastmigrationparallelscerebrospinalfluid(CSF)flowCamera lucida drawingn=25 egérből !Sawamoto, Buylla et al. 2006Neuroblasts labeled witha retrovirus encodingalkaline phosphatase
Neuroblast migration parallelscerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flowWild typePSA-NCAM stainingTg737orpkmutant mice:hypomorphicallele for Polaris,which is essentialfor normalciliogenesisSawamoto, Buylla et al. 2006Choroid plexus kaudálisan: Slit2-t termel, ependyma Slit2gradienst alakit ki: kemorepulziv hatás, migrációorientációjának irányítása !!
Ependima – choroid plexusCP 3 kompertmentuma:- vaszkuláris zóna (20% of tissue volume),- intermedier intersticiális zóna (15% of tissuevolume): főleg intersticiális folyadék (ISF)- Külső epitélsejt – gyűrű (65% of tissuevolume)(mouse) cryofracturedpreparation of thechoroid plexusJohanson 2011http://visualsunlimited.photoshelter.com/image/I0000OTV7u.m4qegRichard Kessel
Lateral ventricleVentricle wallepenymalvcpcp epenyma50umb-galS100A10150mmRALDH2:RAProductionhttp://www.abcam.com/S100A10-antibody-ab50737.html#ab50737if.gif
Ependima – choroid plexus1918, Gray’sanatomyhttp://www.sci.uidaho.edu/med532/choroid.htmhttp://neuromedia.neurobio.ucla.edu/campbell/nervous/wp.htmhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Choroid_plexus
Ependima – choroid plexusN: nucleus V: ventricle L: lipid dropletblue arrow: microvilli red arrow: cilia
Ependima – choroid plexusThe free cellular surface of the choroid plexus. Note numerousmicrovilli (asterisk). Scale = 1 µm. (Rat, lateral ventricle.)http://synapses.clm.utexas.edu/atlas/4_1.stm
http://imueos.wordpress.com/2010/10/16/blood-brainbarrier/Ependima – choroid plexus- 3.-4. kamra- velőcső (neuroektodermális) eredetű- egyrétegű köbhám- intercelluláris r<strong>és</strong>ek: tight junction- szabad felszínén mikrobolyhok- aktív ion/metabolit transzport- vízre szabadon permeábilis (<strong>és</strong> alkoholra <strong>és</strong>koffeinre)- nem permeábilis: fehérjékre; fehérjekötötthormonokra, drogokra; erősenhidrofíl anyagokra (Na+, K+) – itt spec.carrier-mediált transzport
EpendimaMarkerek (well..)- egér gerincvelői ependyma Nkx6.1expresszáló ventrális neuroepitélsejtekből származik- egér előagyi ependyma radiális gliaeredetűGFAP, vimentin, cytokeratin- intermedier filamentumokRIL, Reversion-induced LIM- citoszkeleton-regulációTight junction proteins, CAMs– élekor/lokalizáció függőenType I-III kollagén, fibronektin,laminin, utrophin, alphadystrobrevin,beta-dystroglycan- bazális membránban, BM-melkapcsolatbanS100B-jelen van ependymábanCsillók – csilló proteinekDel Bigio 2010VEGF, vascular endothelial growthfactor- appears to be involved in ependymalstability- inhibition of VEGF in mice leads todisappearance of microvilliFGF2, HGF, GDNF, CTGF, IGFBP, BDNF,NT-4/5, Noggin, CD133, MAGI-3 kináz- termel<strong>és</strong> bizonyoséletkorokban/ependymaszubpopulációkbanCx26, Cx30, Cx43, Cx45AQP4, Aquaporin 4Glucokinase- inzulin-reszponzív enzim- pancreas b-sejtekben glükóz-szenzorGLUT1-4, glucose transporters- facilitative glucose carriers- water flux tooMonocarboxylate transporters (MCT)- uptake and release of lactate,pyruvate, and ketone bodies
Ependima- Ependyma: Őssejt ??? ... (SVZ oly közel...)Végdifferenciáltak vagy képesek de-differenciálódni ?Jonas Frisen1992, Reynolds, WeissRichards, L. J., Kilpatrick, T. J. & Bartlett, P. F. De novogeneration of neuronal cells from the adult mousebrain. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 8591–8595 (1992).
Mezodermáliseredetű sejtekMikrogliamicrogliasejtekaktivációja
MikrogliaJung S., Littman DR. et al MCB 2000 20(11):4106-14.