Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
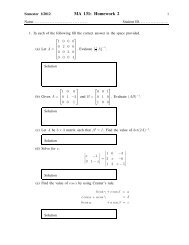
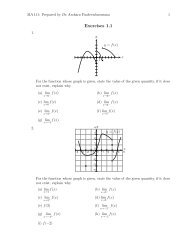
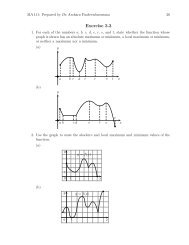
•••MA112 Section 750001: Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 56P•0Theorem 3.16 The distance D between a po<strong>in</strong>t P 0 (x 0 ,y 0 ,z 0 ) and the plane ax+by+cz+d =0 isD = |ax 0 +by 0 +cz 0 +d|√a2 +b 2 +c 2 (3.34)Example 3.41 F<strong>in</strong>d the distance D between the po<strong>in</strong>t (1,−4,−3) and the planeSolution .........Example 3.42 The planes2x−3y +6z = −1x+2y −2z = 3 and 2x+4y −4z = 7are parallel s<strong>in</strong>ce their normals, 〈1,2,−2〉 and 〈2,4,−4〉, are parallel vectors. F<strong>in</strong>d thedistance between these planes.Solution .........Example 3.43 It was shown <strong>in</strong> Example 3.29 of Section2.5 that the l<strong>in</strong>eare skew. F<strong>in</strong>d the distance between them.Solution .........3.7 Quadric SurfacesQuadric SurfacesL 1 : x = 1+4t, y = 5−4t, z = −1+5tL 2 : x = 2+8t, y = 4−3t, z = 5+tIn the discussion of Formula (1.11) <strong>in</strong> Section 1.2 we noted that a second-degree equationAx 2 +Bxy +Cy 2 +Dx+Ey +F = 0represents a conic section. The analog of this equation <strong>in</strong> an xyz-coord<strong>in</strong>ate system isAx 2 +By 2 +Cz 2 +Dxy +Exz +Fyz +Gx+Hy +Iz +J = 0 (3.35)which is called a second-degree equation <strong>in</strong> x, y, and z. The graphs of such equationsare called quadric surfaces or sometimes quadrics.Six common types of quadric surfaces are ellipsoids, hyperboloids of one sheet,hyperboloids of two sheet, elliptic cones, elliptic paraboloids, and hyperbolicparaboloids.