Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
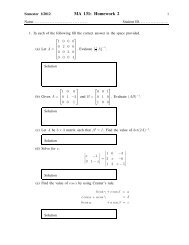
•••••MA112 Section 750001: Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 5Substitut<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> (3.22) and squar<strong>in</strong>g yieldsand after simplify<strong>in</strong>g(x−p) 2 +y 2 = (x+p) 2 (1.3)y 2 = 4px (1.4)The derivations of the other equations <strong>in</strong> the previous Figure are similar.Example 1.1 F<strong>in</strong>d the focus and directrix of the parabola x 2 = −6y and sketch its graph.Solution .........Example 1.2(a) F<strong>in</strong>d an equation of a parabola that has vertex at the orig<strong>in</strong>, opens right, and passesthrough the po<strong>in</strong>t P(7,−3).(b) F<strong>in</strong>d the focus.Solution .........Equations of Ellipses <strong>in</strong> Standard PositionIt is traditional <strong>in</strong> the study of ellipse to denote the length of the major axis by 2a, thelength of the m<strong>in</strong>or axis by 2b, and the distance between the foci by 2c.ccbbaaThe number a is called the semimajor axis and the number b the semim<strong>in</strong>or axis.There is a basic relationship between a, b, and c that can be obta<strong>in</strong>ed by exam<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g thesum of the distances to the foci from a po<strong>in</strong>t P at the end of the major axis and from apo<strong>in</strong>t Q at the end of the m<strong>in</strong>or axis.√b2 +c 2Qbc c a−c√b2 +c 2•P