Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
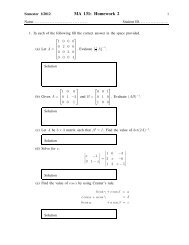
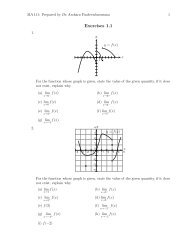
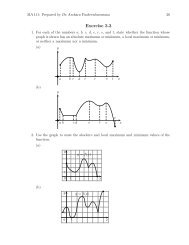
MA112 Section 750001: Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 48kijGeometric Properties of the Cross ProductThe follow<strong>in</strong>g theorem shows that the cross product of two vectors is orthogonal to bothfactors.Theorem 3.11 If u and v are vectors <strong>in</strong> 3-space, then:(a) u·(u×v) = 0 (u×v is orthogonal to u)(b) v·(u×v) = 0 (u×v is orthogonal to v)Example 3.22 Let u and v be vectors as <strong>in</strong> Example 3.21. Show that u×v is orthogonalto both u and v.Solution .........Theorem 3.12 Let u and v be nonzero vectors <strong>in</strong> 3-space, and let θ be the angle betweenthese vectors when they are positioned so their <strong>in</strong>itial po<strong>in</strong>ts co<strong>in</strong>cide.(a) ‖u×v‖ = ‖u‖‖v‖s<strong>in</strong>θ(b) The area A of the parallelogram that has u and v as adjacent sides isA = ‖u×v‖ (3.19)(c) u×v = 0 if and only if u and v are parallel vectors, that is, if and only if they arescalar multiples of one another.Example 3.23 F<strong>in</strong>d the area of the parallelogram with two adjacent sides formed by thevectors u = 〈1,2,−2〉 and v = 〈3,0,1〉.Solution .........Example 3.24 F<strong>in</strong>d the area of the triangle that is determ<strong>in</strong>ed by the po<strong>in</strong>ts P 1 (2,2,0),P 2 (−1,0,2), and P 3 (0,4,3).Solution .........