Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
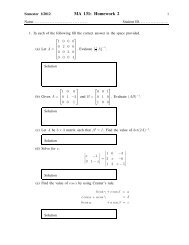
MA112 Section 750001: Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 37the vector is translated. The norm of a vector v = 〈v 1 ,v 2 〉 <strong>in</strong> 2-space is given by‖v‖ =√v 2 1 +v 2 2and the norm of a vector v = 〈v 1 ,v 2 ,v 3 〉 <strong>in</strong> 3-space is given by‖v‖ =√v 2 1 +v 2 2 +v 2 3Example 3.7 F<strong>in</strong>d the norm of v = 〈4,−2〉, and w = 〈−1,3,5〉.Solution .........is,For any vector v and scalar k, the length of kv must be |k| times the length of v; that‖kv‖ = |k|‖v‖Thus, for example,‖5v‖ = |5|‖v‖ = 5‖v‖‖−3v‖ = |−3|‖v‖ = 3‖v‖‖−v‖ = |−1|‖v‖ = ‖v‖This applies to vectors <strong>in</strong> 2-space and 3-space.Unit VectorsA vector of length 1 is called a unit vector. In an xy-coord<strong>in</strong>ate system the unit vectorsalong the x-axis and y-axis are denoted by i and j, respectively; and <strong>in</strong> xyz-coord<strong>in</strong>atesystem the unit vectors along the x-axis, y-axis and z-axis are denoted by i, j, and k,respectively.yz(0,1)(0,0,1)ji (1,0)xikj(0,1,0)y(1,0,0)Thus,xi = 〈1,0〉, j = 〈0,1〉 In 2-spacei = 〈1,0,0〉, j = 〈0,1,0〉, k = 〈0,0,1〉 In 3-space