Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
Chapter 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
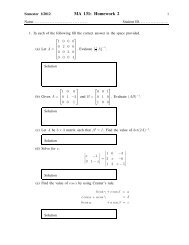
MA112 Section 750001: Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 10Ellipse with center (h,k) and major axis parallel to x-axis(x−h) 2a 2+(y −k)2b 2 = 1 (a > b)Ellipse with center (h,k) and major axis parallel to y-axis(x−h) 2b 2+(y −k)2a 2 = 1 (a > b)Hyperbola with center (h,k) and focal axis parallel to x-axis(x−h) 2a 2−(y −k)2b 2 = 1Hyperbola with center (h,k) and focal axis parallel to y-axis(y −k) 2a 2− (x−h)2b 2 = 1Example 1.7 F<strong>in</strong>d an equation of the parabola with vertex V(−4,2) and directrix y = 5.Solution .........Sometimes the equations of translated conics occur <strong>in</strong> expanded form, <strong>in</strong> which case weare faced with the problem of identify<strong>in</strong>g the graph of a quadratic equation <strong>in</strong> x and y:Ax 2 +Cy 2 +Dx+Ey +F = 0The basic procedure for determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g the nature of such a graph is to complete the squaresof the quadratic terms and then try to match up the result<strong>in</strong>g equation with one of theforms of a translated conic.Example 1.8 Show that the curveis a parabola.Solution .........y = 6x 2 −12x+8Example 1.9 Discuss and sketch the graph of the equationSolution .........16x 2 +9y 2 +64x−18y−71 = 0.