Read or Download - National Institute of Foundry & Forge Technology
Read or Download - National Institute of Foundry & Forge Technology Read or Download - National Institute of Foundry & Forge Technology
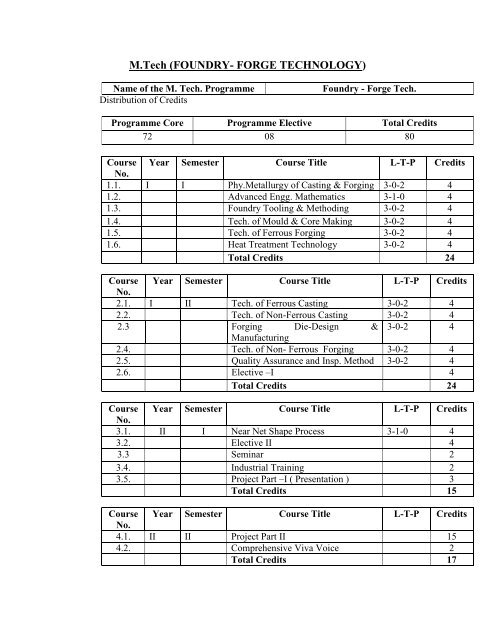
- Page 2 and 3: Total Credits = 802.6 Elective -I2.
- Page 4 and 5: Technology of open- die forging; Al
- Page 7 and 8: Solid Mechanics: The Potential Ener
Total Credits = 802.6 Elective –I2.6 (a) Energy Conservation & Pollution Control2.6 (b) Finite Element method and Applications2.6 (c ) Modern Casting Process2.6 (d) Industrial Engg. & Operation research.2.6 (e) Rapid Prototyping3.2 Elective –II3.2 (a) Modeling & Simulation3.2 (b) Recent Trends in F<strong>or</strong>ging Tech.3.2 (c) Non Traditional Machining3.2 (d) Computer Aided Design3.2 (e) CNC & ProgrammingNote: Students feedback is invariably obtained in all semesters in all subjectsME:MME:Fdy:F<strong>or</strong>ge:Manufacturing EngineeringMaterials & Metallurgical Engineering<strong>Foundry</strong> <strong>Technology</strong>F<strong>or</strong>ge <strong>Technology</strong>M. TECH. FOUNDRY FORGE TECHNOLOGYCOURSE SYLLABIIST SEMESTER1.1. Physical Metallurgy <strong>of</strong> Casting & F<strong>or</strong>ging. ( 3 0 2)Solid solutions- the<strong>or</strong>ies <strong>of</strong> alloying, Intermediate phases and intermetalliccompounds. Common binary equilibrium diagrams and their interpretation, Introductionto ternary equilibrium diagram. Diffusional & diffusionless tramf<strong>or</strong>mation, Concepts <strong>of</strong>structure property processing co- relation Strengthening <strong>of</strong> metals & alloys and itsmechanism.Solidification <strong>of</strong> metals & alloys, Casting grain structure; Ingot structure dendritic andcellular dendritic growth, multiphase microstructures. Micro & Macro segregation, Micro& Macro p<strong>or</strong>osity and residual stresses in casting.Hot and cold w<strong>or</strong>king <strong>of</strong> metals & alloys, recovery, recrystallisation and grain growth.Evolution <strong>of</strong> microstructure in hot & cold f<strong>or</strong>ged alloy.1.2 Advanced Engg. Mathematics (3 1 0 )
Vect<strong>or</strong> calculus; Gauss, Stoke’s and Green’s The<strong>or</strong>ems; Tens<strong>or</strong> analysis;Computational Fluid Dynamics; Discontinuous Flow; V<strong>or</strong>tices and Viscosity; BoundaryLayer The<strong>or</strong>yMatrices and Determinants Equations; Cayley- Hamilton’s The<strong>or</strong>em; Inversion <strong>of</strong> largematrices Ordinary Differential Equations; Exact Defferential Equations; TotalDifferential Equations; Partial Differential Equatins; Mongee’s Method, Separation <strong>of</strong>Variables. Special functions: Bessel, Legendre, Hypergeometric Hermite, Lagurve andGreen’s Funcions Fourier Series; Fourier Transf<strong>or</strong>ms, Laplace Transf<strong>or</strong>ms; HankelTransf<strong>or</strong>m; Application in solution to Laplace, wave and heat conduction equations.Complex variables; Conf<strong>or</strong>mal mapping; Contour Integrals. Numerical Methods;Interpolation, Differentiation, Solution <strong>of</strong> <strong>or</strong>dinary differential equations and Algebraicand Transudental equations. Finite element technique; Weighted residual and variationalmethods.1.3 <strong>Foundry</strong> Tooling and Methoding (3 0 2)Pattern Equipment f<strong>or</strong> quality production <strong>of</strong> castings : Pattern plates: types,materials used; design and constructional features suiting to various moulding machines.Special design features f<strong>or</strong> high pressure moulding machines.C<strong>or</strong>e Boxes: type , materials used, design and constructional features f<strong>or</strong> c<strong>or</strong>e blowingand shooting machines. Special features f<strong>or</strong> shell c<strong>or</strong>e shooters .C<strong>or</strong>e print. Gravity Diecasting: Die-Types, and design features. Pressure Die-casting: die- design features.Gating : Elements <strong>of</strong> the gating system. Design <strong>of</strong> Gating system f<strong>or</strong> cast iron & steel.Fluidity and its significance in casting.Risering : Solidification <strong>of</strong> iron and steel with reference to Fe-C diagram. Riserclassification. Design <strong>of</strong> riser. Methods to achieve directional solidification.1.4 <strong>Technology</strong> <strong>of</strong> mould and c<strong>or</strong>e Making (3 0 2)Sand :occurrence, classification and characteristics <strong>of</strong> different types <strong>of</strong> sand, grainsize, shape and distributions.Binders :Clay, Linseed oil, dextrin, sodium silicate, molasses, their characteristics andquality tests.Green and dry sand practices, carbon dioxide and shell process. Role and function <strong>of</strong>additives & washes in conventional mould & c<strong>or</strong>e making processes.Moulding practices, Odd side, three part, loam, sweep & pit moulding, skeleton patterns,stack moulding, c<strong>or</strong>e assembly.C<strong>or</strong>e making practices :- small and large c<strong>or</strong>es, sweptc<strong>or</strong>es ,loam c<strong>or</strong>es, skeleton c<strong>or</strong>es.Mould and c<strong>or</strong>e venting, reinf<strong>or</strong>cement & drying.Machines f<strong>or</strong> sand mixing and preparation <strong>of</strong> moulds & c<strong>or</strong>es like mixer, muller, jolting,Squeezing, jolt-squeezing, slinging, blowing and shooting machines. Their functions &characteristics, C<strong>or</strong>e location, closing and weighting <strong>of</strong> moulds. Sand reclamationmethods & equipments.Casting defects mainly attributed to moulding and c<strong>or</strong>e makingpractices and materials.1.5 <strong>Technology</strong> <strong>of</strong> Ferrous F<strong>or</strong>ging ( 3 0 2)
<strong>Technology</strong> <strong>of</strong> open- die f<strong>or</strong>ging; Allowance and tolerances f<strong>or</strong> free f<strong>or</strong>ging; Processchart f<strong>or</strong> manufacture <strong>of</strong> typical components such as straight, stepped and hollow shaft,rings, discs, crank shaft, etc; F<strong>or</strong>ging defects and their remedial measuresClassification, and characterization <strong>of</strong> f<strong>or</strong>ging equipments; Load and energycharacteristics; Classification viz, pneumatic hammer, drop hammer, counter blowhammer, mechanical and hydraulic presses, upsetters, HERF machines, etc; Foundation<strong>of</strong> hammer; Recent development in f<strong>or</strong>ging equipment Methods <strong>of</strong> blank preparation;Acceptance criteria f<strong>or</strong> bars & billets in f<strong>or</strong>ging industry, Advanced technology f<strong>or</strong>production <strong>of</strong> large f<strong>or</strong>ging ingots, Fact<strong>or</strong>s affecting metal flow in the die, such asf<strong>or</strong>geability, friction, lubrication, die temperature, shape and size fact<strong>or</strong>s; F<strong>or</strong>ging <strong>of</strong>steel, F<strong>or</strong>ging <strong>of</strong> Stainless Steel, F<strong>or</strong>ging <strong>of</strong> high Speed Steel, Problems <strong>of</strong> gases,overheating and burning <strong>of</strong> steels.1.6 Heat Treatment <strong>Technology</strong> (3 0 2)Decomposition <strong>of</strong> austenite, Diffusion controlled and diffusionless transf<strong>or</strong>mations;Nucleation and growth <strong>of</strong> phases; Pearlitic and bainitic transf<strong>or</strong>mations; Mechanism <strong>of</strong>martensitic transf<strong>or</strong>mations; Determination <strong>of</strong> grain size; TTT and CCT curvesHeat treatment processes; Hardening, Tempering, Annealing, N<strong>or</strong>malizing, SurfaceHardening, Carburizing, Nitriding, Electron Beam Hardening and Laser Hardening;Application <strong>of</strong> Plasma in heat treating. High Temperature Carburising. Heat Treatment<strong>of</strong> tool and alloy Steels; Heat treatment <strong>of</strong> cast iron ; Heat Treatment <strong>of</strong> tool and alloysSteels; Heat treatment <strong>of</strong> weldments; Thermomechanical treatment; Heat treatment <strong>of</strong>non-ferrous metals and alloys; The<strong>or</strong>y <strong>of</strong> age-hardening; Heat Treatment defects incastings, f<strong>or</strong>gings and weldments and their remedial measures. Automation &computerization <strong>of</strong> heat treating process & equipments. Controlling heat treating furnaceatmosphere.IInd Semester2.1 <strong>Technology</strong> <strong>of</strong> Ferrous castings ( 3 0 2)Fe-C phase diagrams; classification, properties and applications <strong>of</strong> cast irons andsteel. Solidification behavi<strong>or</strong> and effect <strong>of</strong> alloy additions.Melting furnaces used f<strong>or</strong> iron and steel: electric arc furnace, induction furnace, cupola,rotary furnace. Melting practices and melt controls f<strong>or</strong> iron and steel. De-oxidation anddegassing <strong>of</strong> steel;Inoculation and alloying <strong>of</strong> cast irons. Production <strong>of</strong> grey, S.G., C.G. and malleable irons.Moulding and c<strong>or</strong>e making practice f<strong>or</strong> iron and steel. Gating and feeding practices f<strong>or</strong>iron and steel. Fettling, cleaning and heat treatments <strong>of</strong> castings; Defect analysis.2.2 <strong>Technology</strong> <strong>of</strong> Non-Ferrous castings (3 0 2)
Non-ferrous alloys based on Al, Cu, Zn and Mg. Their properties and applications.Solidification and microstructure <strong>of</strong> imp<strong>or</strong>tant non ferrous alloys.Melting, fluxing, degassing and pouring practices . Filtration <strong>of</strong> non- ferrous melts. Melttreatment : modification and grain refinement.Charge calculation, hardeners. Oxidation and gas abs<strong>or</strong>ption in metals and alloys,detection <strong>of</strong> gases.Mould and c<strong>or</strong>e practices, metal-mould reaction, gating and feeding practices. Defectanalysis, salvaging <strong>of</strong> castings.2.3 F<strong>or</strong>ging Die Design & Manufacture ( 3 0 2 )Study <strong>of</strong> f<strong>or</strong>ging drawing and its simplification from die design point <strong>of</strong> view.Determination <strong>of</strong> stock size, tensile strength <strong>of</strong> material at the finishing temperaturewhile f<strong>or</strong>ging. Calculation <strong>of</strong> weight <strong>of</strong> falling parts <strong>or</strong> die <strong>of</strong> a drop hammer, Mechanicalpress, Selection <strong>of</strong> the size <strong>of</strong> massive die blocks <strong>or</strong> insert dies. Production <strong>of</strong> die blocksand fact<strong>or</strong>s controlling their quality.Location <strong>of</strong> parting line, Selection <strong>of</strong> flash gutter.Determination <strong>of</strong> flash thickness and volume <strong>of</strong> fin, Calculation <strong>of</strong> wall thickness anddistance between two impressions. Design <strong>of</strong> edger, fuller, bender , blocker, finishingimpression, dovetail , cross, key and tapered key. Laws governing the design <strong>of</strong> the dies<strong>of</strong> h<strong>or</strong>izontal f<strong>or</strong>ging machine. Design <strong>of</strong> punches and heading tools f<strong>or</strong> upsetter(h<strong>or</strong>izontal f<strong>or</strong>ging machine).upsetting rule, coning Tool Design Method.Determination <strong>of</strong> capacity <strong>of</strong> trimming press. Design <strong>of</strong> trimming and piercing tool,die clearance between punch and die. Design <strong>of</strong> stripping and clipping tools. Assemblydetail f<strong>or</strong> trimming. Technical requirements f<strong>or</strong> sinking, re-sinking and rectification <strong>of</strong>dies, Die sinking methods like copy-milling, EDM, ECM etc. Instruction f<strong>or</strong> mounting,setting and w<strong>or</strong>king <strong>of</strong> dies, Reduced Roll design, saved perf<strong>or</strong>m design. Die lifeimprovement Computer aided design <strong>of</strong> f<strong>or</strong>ging dies, Optimization <strong>of</strong> die designparameters, Optimum material utilization, Modeling and analysis <strong>of</strong> f<strong>or</strong>ging processusing s<strong>of</strong>tware.2.4 <strong>Technology</strong> <strong>of</strong> Non-Ferrous F<strong>or</strong>ging (3 0 2)Classification & properties <strong>of</strong> commercial aluminum alloys & their metallurgicalcharacteristics, F<strong>or</strong>ging behavi<strong>or</strong> <strong>of</strong> aluminum alloys; Heat treatment technology andindustrial application <strong>of</strong> the alloysDesignation, properties and application <strong>of</strong> copper and magnesium alloys f<strong>or</strong>gings;F<strong>or</strong>ging practices <strong>of</strong> copper, copper alloys and magnesium alloysHeat treating practices and their applications, f<strong>or</strong>ging practices f<strong>or</strong> titanium alloys,current f<strong>or</strong>ging technology f<strong>or</strong> aerospace materials. F<strong>or</strong>ging <strong>of</strong> Aluminum. Lithiumalloys. Tribological behavi<strong>or</strong> during f<strong>or</strong>ging.2.5 Quality Assurance and Inspection Methods ( 3 0 2)Statistical parameters f<strong>or</strong> quality assurance; Probability desirability distributioncurves f<strong>or</strong> discrete and continuous random variables; Control charts f<strong>or</strong> attributes andvariables; Special control charts; Process capability; Acceptance sampling; On-line
Solid Mechanics: The Potential Energy Approach, Galerkin Approach, The FiniteElement Equations f<strong>or</strong> One Dimensional Problems and Treatment <strong>of</strong> <strong>Foundry</strong> Conditions,Temperature Effects, Plane Trusses, Two Dimensional Problems using Constant StrainTriangles, Beams.Introduction to Mass Transfer, Fluid Flow and Plate BendingLocal Co<strong>or</strong>dinate System: Shape Functions in Local Co<strong>or</strong>dinate System and Evaluation <strong>of</strong>Element Characteristic Matrices and Element Characteristic Vect<strong>or</strong>s.2.6 ( c) Modern Casting processesProcess details, in gradients used, process variables and economy <strong>of</strong> the processes usingsodium silicate as binder and <strong>or</strong>ganic binder processes e.g hot box, cold box, ABC,silicate- ester, catalyzed no-bake and warm box.Fluid sand, full mould, magnetic moulding, investment casting, frozen mould, vacuumsealed moulding, high pressure moulding, impact moulding; explosion moulding andsqueeze casting processes. Centrifugal casting and continuous casting processes.2.6 (d) Industrial Engg. & Operation research.Introduction to Production, planning and control, Invent<strong>or</strong>y Control, MRP, Design <strong>of</strong>experiments, Taguchi Methods and Multivariate analysis, Netw<strong>or</strong>k models, CPM andPERT. Times cost trade <strong>of</strong>f and generation <strong>of</strong> the project cost curye in determining thenetw<strong>or</strong>ks. Fulkerson's flow alg<strong>or</strong>ithm, Non-linear programming, Integer and Dynamicprogramming, waiting line the<strong>or</strong>y and its applications2.6 ( e ) Rapid PrototypingBasic Principal <strong>of</strong> RP processes, Classification <strong>of</strong> RP Processes, Various Industrial RPSystems like Sterolithography, Fused Deposition Modeling, Selective Laser Sintering,Laminated Object Manufacturing, 3D Printing, Ballistic particle modeling etc., Role <strong>of</strong>Rapid Prototyping and Rapid Tooling in Product Development. Process planning f<strong>or</strong>rapid prototyping, STL file generation Defects in STL files and repairing alg<strong>or</strong>ithms, Slicingand various slicing procedures, Accuracy issues in Rapid Prototyping, Strength <strong>of</strong> RP Parts,Surface roughness problem in Rapid Prototyping, Part deposition <strong>or</strong>ientation and issues likeaccuracy, surface finish, build time, supp<strong>or</strong>t structure, cost etc., Rapid tooling techniquessuch as laminated metallic tooling, direct metal laser sintering. Introduction to reverseengineering Integration <strong>of</strong> reverse engineering and rapid prototyping.3.2 Elective II3.2 (a ) Modelling & Simulation3-D modelling <strong>of</strong> molds & f<strong>or</strong>ging dies using solid modeller; Simulation and analysis <strong>of</strong>close die f<strong>or</strong>ging <strong>of</strong> f<strong>or</strong>ged components, such as gear blank connecting rod, crank shaft,rocker arm using FEM based s<strong>of</strong>tware packages. Simulation <strong>of</strong> metal flow in moulds,
solidification pattern analysis, microstructure and stress distribution in castings usingindustry standard FEM based s<strong>of</strong>tware packages.3.2 (b ) Recent Trends in F<strong>or</strong>ging <strong>Technology</strong>F<strong>or</strong>ging processes involving the use <strong>of</strong> electrical upsetters, <strong>or</strong>bital f<strong>or</strong>ging presses;Automatic h<strong>or</strong>izontal f<strong>or</strong>ging presses and multiram f<strong>or</strong>ging presses. Transverse rolling.Isothermal f<strong>or</strong>ging, super plastic f<strong>or</strong>ging, Net-shape technology, Powder f<strong>or</strong>ging,Precision f<strong>or</strong>ging, Flashless f<strong>or</strong>ging, Rheo F<strong>or</strong>ging, Liquid f<strong>or</strong>ging, warm f<strong>or</strong>gingtechnology, long f<strong>or</strong>ging machine, HERF.3.2 (c) Non Traditional MachiningNewer Processes in Manufacturing - Process Principles, Process Parameters, Advantages& Limitations and Industrial Applications <strong>of</strong> Processes such as Abrasive Jet Machining(AJM), Water Jet Machining (WJM), Abrasive Water Jet Machining (AWJM), AbrasiveFlow Machining (AFM), Ultrasonic Machining (UM), Electro Chemical Machining(ECM), Electro Chemical Grinding (ECG), Electro Chemical Discharge Grinding(ECDG), Shaped-Tube Electrolytic Machining (STEM), Electro Stream Drilling (ESD),Chemical Machining (CM), Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), Electrical DischargeWire Cutting (EDWC), Electron Beam Machining (EBM), Laser Machining (LM),Plasma Arc Cutting (PAC), Thermal Energy Method Deburring (TEM),Ion BeamMachining (IBM),Introduction to Micro-Machining.3.2 (d ) Computer Aided DesignPrinciples <strong>of</strong> computer aided designn. Computer graphics fundamentals. Points andlines. Transf<strong>or</strong>mations and projections. Plane curves. Space curves. Surfacedescription and generation. Surface modelling. Solid modelling, Representation <strong>of</strong> 3-Dobjects.Modelling using Solid Modeler. Part Modelling, Creating Geometry , Operations ,Modifying parts, Parametric design, Surface Modelling .3.2 (e ) CNC & ProgrammingIntroduction to NC/CNC/DNC, Basics elements <strong>of</strong> CNC, Introduction to Part Programming,Radius and Length Compensation Schemes, Tooling & W<strong>or</strong>k-holding f<strong>or</strong> CNC machinetools, Advanced Programming Features & Canned Cycles, Geometric Modeling f<strong>or</strong> NCmachining & Machining <strong>of</strong> Free-f<strong>or</strong>m Surfaces, NC program generation from CAD models,Introduction to APT programming, Post process<strong>or</strong>, NC Program verification and Virtual NC,Recent developments in CNC machine tools