Palliative Care Guidelines - NHS Lanarkshire
Palliative Care Guidelines - NHS Lanarkshire
Palliative Care Guidelines - NHS Lanarkshire
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
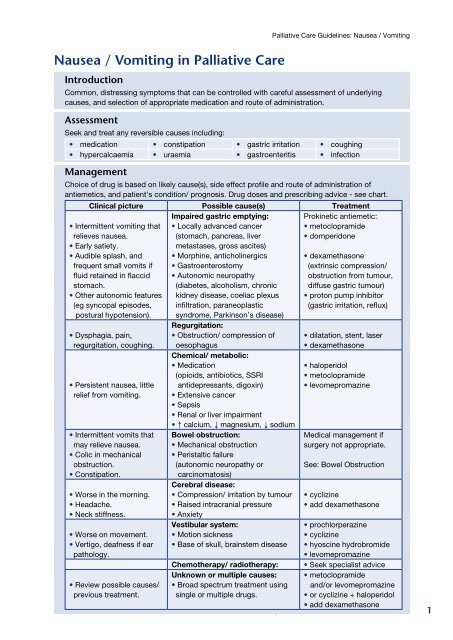
Nausea / Vomiting in <strong>Palliative</strong> <strong>Care</strong>Introduction<strong>Palliative</strong> <strong>Care</strong> <strong>Guidelines</strong>: Nausea / VomitingCommon, distressing symptoms that can be controlled with careful assessment of underlyingcauses, and selection of appropriate medication and route of administration.AssessmentSeek and treat any reversible causes including:• medication • constipation • gastric irritation • coughing• hypercalcaemia • uraemia • gastroenteritis • infectionManagementChoice of drug is based on likely cause(s), side effect profile and route of administration ofantiemetics, and patient’s condition/ prognosis. Drug doses and prescribing advice - see chart.Clinical picture Possible cause(s) Treatment• Intermittent vomiting thatrelieves nausea.• Early satiety.• Audible splash, andfrequent small vomits iffluid retained in flaccidstomach.• Other autonomic features(eg syncopal episodes,postural hypotension).• Dysphagia, pain,regurgitation, coughing.• Persistent nausea, littlerelief from vomiting.• Intermittent vomits thatmay relieve nausea.• Colic in mechanicalobstruction.• Constipation.• Worse in the morning.• Headache.• Neck stiffness.• Worse on movement.• Vertigo, deafness if earpathology.Impaired gastric emptying:• Locally advanced cancer(stomach, pancreas, livermetastases, gross ascites)• Morphine, anticholinergics• Gastroenterostomy• Autonomic neuropathy(diabetes, alcoholism, chronickidney disease, coeliac plexusinfiltration, paraneoplasticsyndrome, Parkinson’s disease)Regurgitation:• Obstruction/ compression ofoesophagusChemical/ metabolic:• Medication(opioids, antibiotics, SSRIantidepressants, digoxin)• Extensive cancer• Sepsis• Renal or liver impairment• ↑ calcium, ↓ magnesium, ↓ sodiumBowel obstruction:• Mechanical obstruction• Peristaltic failure(autonomic neuropathy orcarcinomatosis)Cerebral disease:• Compression/ irritation by tumour• Raised intracranial pressure• AnxietyVestibular system:• Motion sickness• Base of skull, brainstem diseaseProkinetic antiemetic:• metoclopramide• domperidone• dexamethasone(extrinsic compression/obstruction from tumour,diffuse gastric tumour)• proton pump inhibitor(gastric irritation, reflux)• dilatation, stent, laser• dexamethasone• haloperidol• metoclopramide• levomepromazineMedical management ifsurgery not appropriate.See: Bowel Obstruction• cyclizine• add dexamethasone• prochlorperazine• cyclizine• hyoscine hydrobromide• levomepromazine• Seek specialist advice• metoclopramideand/or levomepromazine• or cyclizine + haloperidolChemotherapy/ radiotherapy:Unknown or multiple causes:• Review possible causes/ • Broad spectrum treatment usingprevious treatment. single or multiple drugs.© <strong>NHS</strong> Lothian Issue date: January 2009• add dexamethasoneReview date: March 20121