6. Digital simulation in Alecsis - LEDA
6. Digital simulation in Alecsis - LEDA
6. Digital simulation in Alecsis - LEDA
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
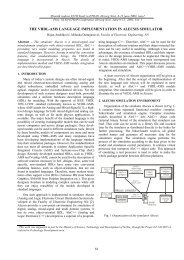
<strong>6.</strong> <strong>Digital</strong> <strong>simulation</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Alecsis</strong> 89<strong>6.</strong>2.1. Interpretation of signals <strong>in</strong> expressionsThe name of a signal can legally appear <strong>in</strong> the expressions of the process. (Be aware about the mask<strong>in</strong>g rulesgiven <strong>in</strong> the previous chapter.) However, they must be treated differently than C/C++-like variables. L<strong>in</strong>ks, andtherefore signals as digital l<strong>in</strong>ks, are complex entities, which can be differently treated <strong>in</strong> different situations. Thetreatment of the signal depends on the context.In all non- assignment expressions, the name of the signal refers to the memory stor<strong>in</strong>g the current valueof the signal. The size, dimensionality, and the type of the memory depend upon the type of the signal (scalars,vector, or a structure). In other words, <strong>in</strong> such expressions, the name of the signal refers to it value - it is used as avariable.Signals must not appear on the left side of the assignment operator (such as =, =+, ++, etc.) s<strong>in</strong>ce theyare not l-values. The change of the signal value can be performed exclusively us<strong>in</strong>g a special AleC++ assignmentoperator for signals