IEC 61508: Functional safety of electrical/electronic/programmable ...
IEC 61508: Functional safety of electrical/electronic/programmable ...
IEC 61508: Functional safety of electrical/electronic/programmable ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
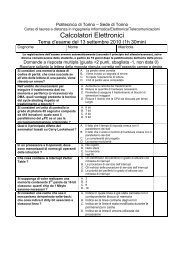
Tecniche per il progetto di sistemi elettronici tolleranti ai guasti, luglio 2006<br />
<strong>IEC</strong> <strong>61508</strong>: <strong>Functional</strong> <strong>safety</strong> <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>electrical</strong>/<strong>electronic</strong>/<strong>programmable</strong><br />
<strong>electronic</strong> <strong>safety</strong>-related systems<br />
Maurizio Rebaudengo,<br />
Matteo Sonza Reorda<br />
Politecnico di Torino<br />
Dipartimento di Automatica e Informatica<br />
The challange<br />
• Electrical, <strong>electronic</strong> or <strong>programmable</strong> <strong>electronic</strong><br />
systems increasingly carry out <strong>safety</strong> functions.<br />
These systems are usually complex, making it<br />
impossible in practice to fully determine every<br />
failure mode or to test all possible behaviours.<br />
• It is difficult to predict the <strong>safety</strong> performance,<br />
although testing is still essential.<br />
• The challenge is to design the system in such a<br />
way as to prevent dangerous failures or to control<br />
them when they arise.<br />
2<br />
Examples <strong>of</strong> systems, subsystems &<br />
devices under consideration<br />
• electro-mechanical<br />
• solid state <strong>electronic</strong><br />
• <strong>programmable</strong> <strong>electronic</strong><br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
Low complexity<br />
Low complexity/Complex<br />
Complex<br />
<strong>programmable</strong> Controllers<br />
<strong>programmable</strong> Logic Controllers<br />
microprocessor based systems;<br />
application specific integrated circuits (ASICs)<br />
intelligent sensors/transmitters/actuators etc.<br />
digital communication systems (e.g. bus systems)<br />
internet based technologies<br />
3<br />
Safety Requirements<br />
Specifications (SRS)<br />
• Specifications containing all the<br />
requirements <strong>of</strong> the <strong>safety</strong> functions that<br />
have to be performed by the <strong>safety</strong>-related<br />
systems.<br />
4<br />
Safety Integrity Level (SIL)<br />
• The basic concept <strong>of</strong> <strong>IEC</strong> <strong>61508</strong> is the<br />
definition <strong>of</strong> SIL:<br />
• discrete level for specifying the <strong>safety</strong> integrity<br />
requirements <strong>of</strong> the <strong>safety</strong> functions to be<br />
located to the E/E/PE <strong>safety</strong>-related systems.<br />
Safe Failure Fraction (SFF)<br />
• The ratio between the safe failures (i.e.,<br />
failures which don't have the potential to<br />
put the <strong>safety</strong>-related system in a<br />
hazardous state) and detected dangerous<br />
failures over the sum <strong>of</strong> all the possible<br />
failures (safe + dangerous).<br />
5<br />
6<br />
M. Rebaudengo, M. Sonza Reorda, M. Violante 1
Tecniche per il progetto di sistemi elettronici tolleranti ai guasti, luglio 2006<br />
Hardware Fault Tolerance (HFT)<br />
• A hardware fault tolerance <strong>of</strong> N means that<br />
N+1 faults could cause a loss <strong>of</strong> the <strong>safety</strong><br />
function.<br />
SIL/SFF/HFT<br />
HFT<br />
SFF 0 1 2<br />
< 60% SIL1 SIL2<br />
60% - 90% SIL1 SIL2 SIL3<br />
90% - 99% SIL2 SIL3 SIL4<br />
> 99% SIL3 SIL4 SIL4<br />
7<br />
8<br />
SIL/SFF/HFT (cont.)<br />
• With a HFT equal to 0, a SFF equal or<br />
greater than 99% is required in order that<br />
the system or component can be granted<br />
as SIL3.<br />
FMEA<br />
• The commonly used way to provide the<br />
information required by the SRS is to<br />
perform a FMEA<br />
9<br />
10<br />
Sensible zone<br />
• A set <strong>of</strong> sensible zones are identified from the<br />
design.<br />
• A sensible zone is the elementary failure point in<br />
which one or more faults converge to lead a<br />
failure<br />
• Valid definitions <strong>of</strong> sensible zones are:<br />
• memory elements such registers, flip-flops<br />
• primary input and primary outputs<br />
• critical nets<br />
Observation point<br />
• The observation points are selected where<br />
the main effect <strong>of</strong> each sensible zone<br />
failure mode is evaluated.<br />
• The observation point is:<br />
• a primary output<br />
• an alarm <strong>of</strong> the diagnostic.<br />
11<br />
12<br />
M. Rebaudengo, M. Sonza Reorda, M. Violante 2
Tecniche per il progetto di sistemi elettronici tolleranti ai guasti, luglio 2006<br />
Fault injection<br />
• The <strong>IEC</strong> <strong>61508</strong> highly recommends the use<br />
<strong>of</strong> Fault Injection in order to estimate the<br />
behavior <strong>of</strong> the sensible zones<br />
Faults and failures<br />
• <strong>IEC</strong> <strong>61508</strong> specifies faults or failures to be<br />
detected or to be analyzed in the derivation<br />
<strong>of</strong> Safe Failure Fraction.<br />
13<br />
14<br />
<strong>IEC</strong> <strong>61508</strong> flow<br />
SRS<br />
FMEA<br />
Fault Injection<br />
SFF report<br />
15<br />
M. Rebaudengo, M. Sonza Reorda, M. Violante 3