Gas Chromatography (GC) (IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology):
Lecture 3. Gas chromathography. Split Injection. Used for samples with analyte concentration > 0.1 %. Only 0.2 – 2 % of the sample is delivered to column. Injector temperature is high, e.g. 350 ºC. 102 ml/min 1 ml/min 100 ml/min 1ml/min The sample is injected rapidly through the septum into evaporation zone. The injector temperature is kept high to promote fast evaporation. A brisk flow of the carrier gas sweeps the sample through the mixing chamber. At the split point, small fraction of vapors enters the column but most passes to waste vent. Split ratio (the proportion of the sample that does not reach the column) is typically 50:1 to 600:1. Septum purge gas flow: prevents the column during injection and chromatography from hot rubber septum gases and the excess of the sample vapors. ● ● ● Advantages of split injection: narrow solute peaks; suitable for qualitative analysis; minimize the solvent effect. Drawbacks: ● ● ● requires rather high concentration of analyte; split ratio makes the quantitative analysis more complex; not suitable for very expensive or toxic compounds. 22
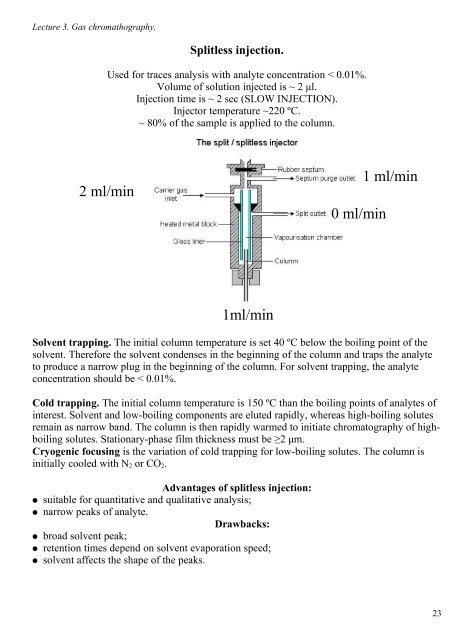
Lecture 3. Gas chromathography. Splitless injection. Used for traces analysis with analyte concentration < 0.01%. Volume of solution injected is ~ 2 μl. Injection time is ~ 2 sec (SLOW INJECTION). Injector temperature ~220 ºC. ~ 80% of the sample is applied to the column. 2 ml/min 0 ml/min 1 ml/min 1ml/min Solvent trapping. The initial column temperature is set 40 ºC below the boiling point of the solvent. Therefore the solvent condenses in the beginning of the column and traps the analyte to produce a narrow plug in the beginning of the column. For solvent trapping, the analyte concentration should be < 0.01%. Cold trapping. The initial column temperature is 150 ºC than the boiling points of analytes of interest. Solvent and low-boiling components are eluted rapidly, whereas high-boiling solutes remain as narrow band. The column is then rapidly warmed to initiate chromatography of highboiling solutes. Stationary-phase film thickness must be ≥2 μm. Cryogenic focusing is the variation of cold trapping for low-boiling solutes. The column is initially cooled with N 2 or CO 2 . ● ● ● ● ● Advantages of splitless injection: suitable for quantitative and qualitative analysis; narrow peaks of analyte. Drawbacks: broad solvent peak; retention times depend on solvent evaporation speed; solvent affects the shape of the peaks. 23
- Page 1 and 2: Lecture 3. Gas chromathography. Gas
- Page 3 and 4: Lecture 3. Gas chromathography. Adv
- Page 5 and 6: Film thickness, μm Lecture 3. Gas
- Page 7 and 8: Lecture 3. Gas chromathography. POL
- Page 9 and 10: Lecture 3. Gas chromathography. Non
- Page 11 and 12: Lecture 3. Gas chromathography. 11
- Page 13 and 14: Lecture 3. Gas chromathography. Col
- Page 15 and 16: Lecture 3. Gas chromathography. Eff
- Page 17 and 18: Lecture 3. Gas chromathography. GAS
- Page 19 and 20: Lecture 3. Gas chromathography. Tem
- Page 21: Lecture 3. Gas chromathography. Sam
- Page 25 and 26: Lecture 3. Gas chromathography. Com
- Page 27 and 28: Lecture 3. Gas chromathography. Pur
- Page 29 and 30: Lecture 3. Gas chromathography. Der
- Page 31 and 32: Lecture 3. Gas chromathography. Rea
- Page 33: Lecture 3. Gas chromathography. 33
Lecture 3. <strong>Gas</strong> chromathography.<br />
Splitless injection.<br />
Used for traces analysis with analyte concentration < 0.01%.<br />
Volume <strong>of</strong> solution injected is ~ 2 μl.<br />
Injection time is ~ 2 sec (SLOW INJECTION).<br />
Injector temperature ~220 ºC.<br />
~ 80% <strong>of</strong> the sample is applied to the column.<br />
2 ml/min<br />
0 ml/min<br />
1 ml/min<br />
1ml/min<br />
Solvent trapping. The initial column temperature is set 40 ºC below the boiling point <strong>of</strong> the<br />
solvent. Therefore the solvent condenses in the beginning <strong>of</strong> the column and traps the analyte<br />
to produce a narrow plug in the beginning <strong>of</strong> the column. For solvent trapping, the analyte<br />
concentration should be < 0.01%.<br />
Cold trapping. The initial column temperature is 150 ºC than the boiling points <strong>of</strong> analytes <strong>of</strong><br />
interest. Solvent and low-boiling components are eluted rapidly, whereas high-boiling solutes<br />
remain as narrow band. The column is then rapidly warmed to initiate chromatography <strong>of</strong> highboiling<br />
solutes. Stationary-phase film thickness must be ≥2 μm.<br />
Cryogenic focusing is the variation <strong>of</strong> cold trapping for low-boiling solutes. The column is<br />
initially cooled with N 2 or CO 2 .<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
●<br />
Advantages <strong>of</strong> splitless injection:<br />
suitable for quantitative and qualitative analysis;<br />
narrow peaks <strong>of</strong> analyte.<br />
Drawbacks:<br />
broad solvent peak;<br />
retention times depend on solvent evaporation speed;<br />
solvent affects the shape <strong>of</strong> the peaks.<br />
23