The mnemonic keyword method: The effects of bidirectional retrieval ...
The mnemonic keyword method: The effects of bidirectional retrieval ...
The mnemonic keyword method: The effects of bidirectional retrieval ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
M. Wyra et al. / Learning and Instruction 17 (2007) 360e371<br />
367<br />
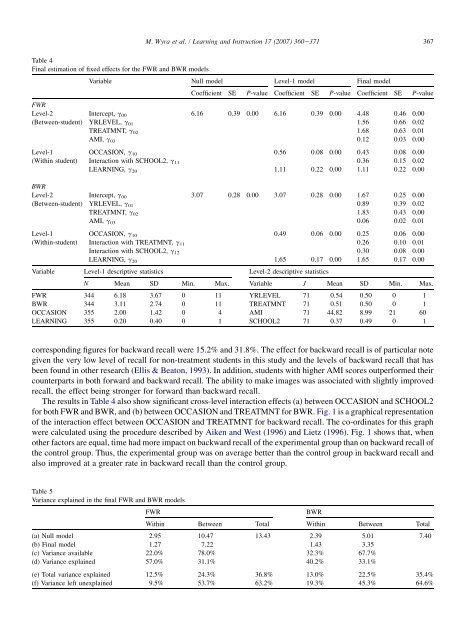
Table 4<br />
Final estimation <strong>of</strong> fixed <strong>effects</strong> for the FWR and BWR models<br />
Variable Null model Level-1 model Final model<br />
Coefficient SE P-value Coefficient SE P-value Coefficient SE P-value<br />
FWR<br />
Level-2 Intercept, g 00 6.16 0.39 0.00 6.16 0.39 0.00 4.48 0.46 0.00<br />
(Between-student) YRLEVEL, g 01 1.56 0.66 0.02<br />
TREATMNT, g 02 1.68 0.63 0.01<br />
AMI, g 03 0.12 0.03 0.00<br />
Level-1 OCCASION, g 10 0.56 0.08 0.00 0.43 0.08 0.00<br />
(Within student) Interaction with SCHOOL2, g 11 0.36 0.15 0.02<br />
LEARNING, g 20 1.11 0.22 0.00 1.11 0.22 0.00<br />
BWR<br />
Level-2 Intercept, g 00 3.07 0.28 0.00 3.07 0.28 0.00 1.67 0.25 0.00<br />
(Between-student) YRLEVEL, g 01 0.89 0.39 0.02<br />
TREATMNT, g 02 1.83 0.43 0.00<br />
AMI, g 03 0.06 0.02 0.01<br />
Level-1 OCCASION, g 10 0.49 0.06 0.00 0.25 0.06 0.00<br />
(Within-student) Interaction with TREATMNT, g 11 0.26 0.10 0.01<br />
Interaction with SCHOOL2, g 12 0.30 0.08 0.00<br />
LEARNING, g 20 1.65 0.17 0.00 1.65 0.17 0.00<br />
Variable Level-1 descriptive statistics Level-2 descriptive statistics<br />
N Mean SD Min. Max. Variable J Mean SD Min. Max.<br />
FWR 344 6.18 3.67 0 11 YRLEVEL 71 0.54 0.50 0 1<br />
BWR 344 3.11 2.74 0 11 TREATMNT 71 0.51 0.50 0 1<br />
OCCASION 355 2.00 1.42 0 4 AMI 71 44.82 8.99 21 60<br />
LEARNING 355 0.20 0.40 0 1 SCHOOL2 71 0.37 0.49 0 1<br />
corresponding figures for backward recall were 15.2% and 31.8%. <strong>The</strong> effect for backward recall is <strong>of</strong> particular note<br />
given the very low level <strong>of</strong> recall for non-treatment students in this study and the levels <strong>of</strong> backward recall that has<br />
been found in other research (Ellis & Beaton, 1993). In addition, students with higher AMI scores outperformed their<br />
counterparts in both forward and backward recall. <strong>The</strong> ability to make images was associated with slightly improved<br />
recall, the effect being stronger for forward than backward recall.<br />
<strong>The</strong> results in Table 4 also show significant cross-level interaction <strong>effects</strong> (a) between OCCASION and SCHOOL2<br />
for both FWR and BWR, and (b) between OCCASION and TREATMNT for BWR. Fig. 1 is a graphical representation<br />
<strong>of</strong> the interaction effect between OCCASION and TREATMNT for backward recall. <strong>The</strong> co-ordinates for this graph<br />
were calculated using the procedure described by Aiken and West (1996) and Lietz (1996). Fig. 1 shows that, when<br />
other factors are equal, time had more impact on backward recall <strong>of</strong> the experimental group than on backward recall <strong>of</strong><br />
the control group. Thus, the experimental group was on average better than the control group in backward recall and<br />
also improved at a greater rate in backward recall than the control group.<br />
Table 5<br />
Variance explained in the final FWR and BWR models<br />
FWR<br />
BWR<br />
Within Between Total Within Between Total<br />
(a) Null model 2.95 10.47 13.43 2.39 5.01 7.40<br />
(b) Final model 1.27 7.22 1.43 3.35<br />
(c) Variance available 22.0% 78.0% 32.3% 67.7%<br />
(d) Variance explained 57.0% 31.1% 40.2% 33.1%<br />
(e) Total variance explained 12.5% 24.3% 36.8% 13.0% 22.5% 35.4%<br />
(f) Variance left unexplained 9.5% 53.7% 63.2% 19.3% 45.3% 64.6%