Living Standards Measurements Study - Serbia 2002 - 2007
Living Standards Measurements Study - Serbia 2002 - 2007
Living Standards Measurements Study - Serbia 2002 - 2007
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
situations relating to using services for chronic<br />
diseases was noticed among those living below the<br />
poverty line and among Roma people (70 percent<br />
and 66 percent respectively). There was no<br />
significant change in the usage of health services<br />
among the overall population compared to 2003.<br />
The percentage of the population which<br />
reported that due to their chronic diseases they were<br />
limited in performing everyday activities was 19<br />
percent, whereas the percentage for population over<br />
60 years was 48 percent. Respondents from the two<br />
lowest quintiles had more frequent problems due to<br />
their diseases than those in the two highest quintiles<br />
(25 percent as opposed to 14 percent). Compared to<br />
2003, the proportion of respondents limited in their<br />
everyday activities was lower by 2 percentage<br />
points (from 21 percent in 2003 to 19 percent in<br />
<strong>2007</strong>).<br />
Every tenth respondent (or 10 percent of the<br />
population) suffered from an acute disease or injury<br />
one month prior to the survey. The frequency of<br />
illnesses was higher only among the population<br />
older than 60 years (15 percent).<br />
7.4. Use of Health Services<br />
In <strong>2007</strong>, 35 percent of the population used<br />
health services in health institutions (outpatient<br />
health services in the month preceding the study,<br />
and hospital treatment in the preceding 12 months).<br />
Females were more likely to use services than<br />
males, as well as those aged over 45 years,<br />
particularly those aged of 65 years and older (58<br />
percent). Urban residents were more likely to use<br />
health services (37 percent compared to 32 percent<br />
in other areas). Significantly less usage was<br />
observed by the poor and socially vulnerable (24<br />
percent of those living below the poverty line, 26<br />
percent of the uninsured, 22 percent of the<br />
unemployed and 25 percent of Roma). In the period<br />
67 percent of the both chronically and acutely ill<br />
population used health services. Characteristics of<br />
the use of health services in the ill population,<br />
regarding all the observed variables, correspond to<br />
those previously described for the overall<br />
population. The only observed difference was in the<br />
fact that the groups of ill refugees and IDPs joined<br />
the group of those who used health services<br />
significantly less. Significantly less use of services<br />
was observed among the ill population below<br />
poverty the poverty line (52 percent compared to 68<br />
percent above the line), and the uninsured as<br />
opposed to insured persons (56 percent and 68<br />
percent respectively) (Graph 3).<br />
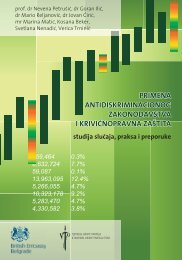
Graph 7.3. Overall and ill population that<br />
used health services (percent)<br />
% population<br />
0 20 40 60 80<br />
Total<br />
Male<br />
Female<br />
35<br />
30<br />
40<br />
67<br />
64<br />
68<br />
0 - 14<br />
29<br />
76<br />
15 - 29<br />
30 - 44<br />
20<br />
24<br />
57<br />
61<br />
45 - 59<br />
38<br />
64<br />
60+<br />
58<br />
70<br />
Urban<br />
Rural<br />
Non poor<br />
37<br />
32<br />
36<br />
68<br />
64<br />
68<br />
Poor 24<br />
52<br />
Poorest<br />
30<br />
59<br />
2<br />
3<br />
4<br />
Richest<br />
Yes<br />
34<br />
35<br />
37<br />
40<br />
36<br />
68<br />
70<br />
70<br />
67<br />
68<br />
No<br />
Roma<br />
26<br />
25<br />
56<br />
61<br />
Refugees &<br />
IDPs<br />
34<br />
64<br />
Unemployed 22<br />
57<br />
Ill citizens who used health services<br />
Citizens who used health services<br />
Gender<br />
Age<br />
Type of<br />
settlement<br />
Poverty<br />
line<br />
Quantiles of consalla<br />
Insurance<br />
In comparison to 2003, in <strong>2007</strong> there was an<br />
increase in the use of health services in general<br />
population by 5 percentage points, and in the ill<br />
population by 8 percentage points (from 30 percent<br />
in 2003 to 35 percent in <strong>2007</strong> and from 59 percent<br />
in 2003 to 67 percent in <strong>2007</strong>).<br />
86 <strong>Living</strong> <strong>Standards</strong> <strong>Measurements</strong> <strong>Study</strong> - <strong>Serbia</strong> <strong>2002</strong> - <strong>2007</strong>