Vol. 54â2000 - NorthEastern Weed Science Society
Vol. 54â2000 - NorthEastern Weed Science Society Vol. 54â2000 - NorthEastern Weed Science Society
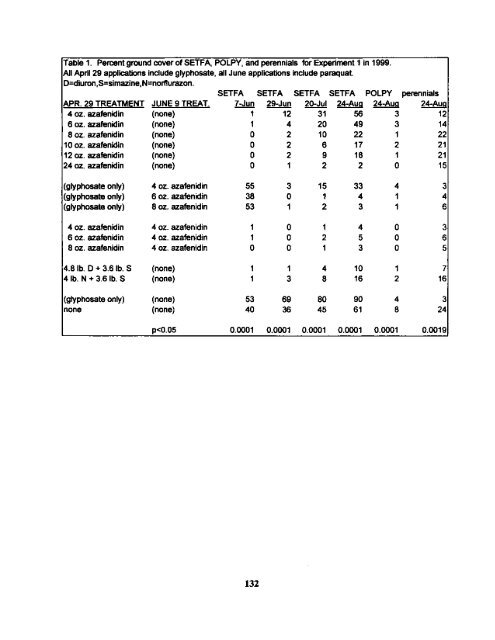
Table 1. Percentground cover of SETFA, POLPV,andperennialsforExperiment1 in 1999. AllApril 29 applicationsincludeglyphosate,allJuneapplicationsincludeparaquat D=diuron,S=simazine,N=norfturazon. SETFA SETFA SETFA SETFA POLPY perennials APR. 29 TREATMENT JUNE 9 TREAT. 7-Jun 29-Jun 2o-Jul 24-Aug 24-Aug 24-Aug 4 oz. azafenidin (none) 1 12 31 56 3 12 6 oz. azafentdin (none) 1 4 20 49 3 14 8 oz. azafenidin (none) a 2 10 22 1 22 10 oz. azafenidin (none) a 2 6 17 2 21 12 oz. azafenidin (none) a 2 9 18 1 21 24 oz. azafenidin (none) a 1 2 2 a 15 (glyphosate only) 4 oz.azafenidin 55 3 15 33 4 3 (glyphosate only) 6 oz. azafenidin 38 a 1 4 1 4 (glyphosate only) 8 oz. azafenidin 53 1 2 3 1 6 4 oz. azafenidin 4 oz. azafenidin 1 a 1 4 a 3 6 oz. azafenidin 4 oz. azafenidin 1 a 2 5 a 6 8 oz. azafenidin 4 oz. azafenidin a a 1 3 a 5 4.8 lb. D + 3.6 lb. 5 (none) 1 1 4 10 1 7 4 lb. N + 3.6 lb. 5 (none) 1 3 8 16 2 16 (glyphosate only) (none) 53 69 80 90 4 3 none (none) 40 36 45 61 8 24 p
HERBICIDE TOLERANCE IN CRANBERRIES A.O. Ayeni, B.A. Majek, J. Hammerstedt and J.L Coia 1 ABSTRACT More herbicideoptions are needed.to managethe dynamicsof weed flora in cranberry bogs in New Jersey.Severalherbicideswerecomparedwithotherspreviouslyidentified to have some potentials in cranberries. The study was conducted at Rutgers Agricultural Research and Extension Center under greenhouse conditions (75 to 85"1' day, 55 to 65"1' night, 16 h light) to determine herbicide safety on cranberries and subsequently identify those to take to the field for further evaluation. The herbicides compared were nicosulfuron, (0.062 IblA), cbIorimuron (0.02 Ib/A), rimsulfuron (0.032 Ib/A), rriflusulfuron (0.067 Ib/A), triasulfuron (0.026 & 0.052 IblA), tribenuron (0.004, om,& 0.02 IblA), MON 37503 (0.016, 0.032, & O.064lb/A), asularn (2 & 4 IblA), metolachlor (2 & 4Ib/A), carfentrazone (0.008 & 0.0161b1A), quinclorac (O.5lb/A), clomazone (0.25 & 0.50 IblA), ZA 1296 (0.19 & 0.38 IblA), and V-3153 (0.02 & 0.04 Ib/A). The cranberryplantstreatedwere raisedin the greenhousefrom 3- to 4-inch stem cuttings planted in 4-inch pots filled with Berryland sand soil that was collected from a herbicidefree site at the Blueberry/Cranberry Research Center, Chatsworth, NJ. Plants were 12 weeks old at the time of treatment. A calibrated greenhouse sprayer, fitted with 8002VSnozzle tip and operated at 30 psi and 68 gpo. was used for herbicide application. The experimentwas set up in four randomizedcomplete blocks and repeated.Herbicidal action was observed for eight weeks and plants were harvested to determine dry matter for the treated stock and regrowth (= new growth) after herbicide application. At two weeks after treatment, cranberry plants showed varying degrees of injury ranging from "non-phytotoxic" to "highly phytotoxic". Nicosulfuron, triasulfuron, quinclorac, and ZA 1296 were non-phytotoxic (injury :::1 on 0 to 10 scale); clomazone was slightly phytotoxic (injury 2 to 3); chlorimuron, rimsulfuron, triflusulfuron, tribenuron, and MON 37503 were quite phytotoxic (iqjury 4 to 5); while carfentrazone, metolach1or, and V 3153 were highly phytotoxic (injury ~). Asularn was highly phytotoxic (injury 7 to 8) but symptoms were not fully expressed until 5 to 6 weeks after treatment. Symptomatic expressions showed that asulam, carfentrazone, MON 37503, and V-3153 were strong apical dominance inhibitors (strong-ADI's); chlorimuron, metolachlor, and tribenuron were mild-ADI's and the remaining herbicides were non-ADI's. Regrowth potential, measured by regrowth dry weight as percent dry weight of treated stock, was highest (60 to 83%) in plants treated with ZA 1296, quinclorac, nicosulfuron, and clomazone in that order. Asularn caused the least regrowth (20%) eight weeks after treatment. Based on cranberry safety, it was concluded that ZA 1296, quinclorac, nicosulfuron, and clomazonearepotentialcandidateherbicidesforfurtherevaluation. I ResearchAssociatein WeedScience,Professorof Weed Science,ResearchTechnician, and Research Assistant, Rutgers Agric. Res. & Ext. Ctr., Bridgeton, NJ 08302. 133
- Page 81 and 82: IR-4 ORNAMENTAL RESEARCH PROGRESS F
- Page 83 and 84: personnel with many of the illegal
- Page 85 and 86: TOLERANCE OF ORNAMENTAL GROUNDCOVER
- Page 87 and 88: MUGWORT CONTROL WITH CLOPYRALID AND
- Page 89 and 90: POTENTIAL WEEDINESS OF SEVERAL NEW
- Page 91 and 92: Table I: Identification, morphologi
- Page 93 and 94: Trifolium tricolor 232 26 62 0 18 S
- Page 95 and 96: NUTRIENT REMOVAL BY WEEDS IN CONTAI
- Page 97 and 98: CONTROL OF POAANNUA FROM MULTIPLE S
- Page 99 and 100: ANNUAL BLUEGRASS (PDaannual CONTROL
- Page 101 and 102: LATERAL DEVELOPMENT OF PLANT oaowra
- Page 103 and 104: RE-ROOTING OF FOUR VARIETIES OF CRE
- Page 105 and 106: Table 2. Top growth weights (fresh)
- Page 107 and 108: CONTROL OF DALLISGRASS IN COOL SEAS
- Page 109 and 110: Kentucky bluegrass was rated to hav
- Page 111 and 112: Table 2. Fresh weight (grams) barve
- Page 113 and 114: MANAGING FENOXAPROP RESIST ANT CRAB
- Page 115 and 116: ADVANCED FORMULATION TECHNOLOGY FOR
- Page 117 and 118: Table I. Preemergence smooth crabgr
- Page 119 and 120: 0.57EW at O.l21bs ai/A plus Confron
- Page 121 and 122: EFFICACY OF DITHIOPYR FORMULATIONS
- Page 123 and 124: EFFECTS OF DROUGHT ON THE INTERFERE
- Page 125 and 126: WEED MANAGEMENT WITH HALOSULFURON I
- Page 127 and 128: WEED CONTROL IN SWEET CORN WITH CAR
- Page 129 and 130: COMPARISON OF USING LEAF AREA AND W
- Page 131: RESULTS OF NEW YORK VINEYARD TRIALS
- Page 135 and 136: Classification based on action on a
- Page 137 and 138: EFFECTS OF SEVERAL POTENTIALLY USEF
- Page 139 and 140: Supplement of the 53 rd Annual Meet
- Page 141 and 142: with society activities to anyone.
- Page 143 and 144: WINTER SQUASH CULTIVARS DIFFER IN R
- Page 145 and 146: INCORPORATING QUINCLORAC IN AUTUMN
- Page 147 and 148: Control efforts aim to eradicate bo
- Page 149 and 150: Table I Weed canopy, insect and dis
- Page 151 and 152: Table 1: Percent mortality of respr
Table 1. Percentground cover of SETFA, POLPV,andperennialsforExperiment1 in 1999.<br />
AllApril 29 applicationsincludeglyphosate,allJuneapplicationsincludeparaquat<br />
D=diuron,S=simazine,N=norfturazon.<br />
SETFA SETFA SETFA SETFA POLPY<br />
perennials<br />
APR. 29 TREATMENT JUNE 9 TREAT. 7-Jun 29-Jun 2o-Jul 24-Aug 24-Aug 24-Aug<br />
4 oz. azafenidin (none) 1 12 31 56 3 12<br />
6 oz. azafentdin (none) 1 4 20 49 3 14<br />
8 oz. azafenidin (none) a 2 10 22 1 22<br />
10 oz. azafenidin (none) a 2 6 17 2 21<br />
12 oz. azafenidin (none) a 2 9 18 1 21<br />
24 oz. azafenidin (none) a 1 2 2 a 15<br />
(glyphosate only) 4 oz.azafenidin 55 3 15 33 4 3<br />
(glyphosate only) 6 oz. azafenidin 38 a 1 4 1 4<br />
(glyphosate only) 8 oz. azafenidin 53 1 2 3 1 6<br />
4 oz. azafenidin 4 oz. azafenidin 1 a 1 4 a 3<br />
6 oz. azafenidin 4 oz. azafenidin 1 a 2 5 a 6<br />
8 oz. azafenidin 4 oz. azafenidin a a 1 3 a 5<br />
4.8 lb. D + 3.6 lb. 5 (none) 1 1 4 10 1 7<br />
4 lb. N + 3.6 lb. 5 (none) 1 3 8 16 2 16<br />
(glyphosate only) (none) 53 69 80 90 4 3<br />
none (none) 40 36 45 61 8 24<br />
p