Corrosion Inhibitors for Waterborne Alkyd Technology - Halox
Corrosion Inhibitors for Waterborne Alkyd Technology - Halox
Corrosion Inhibitors for Waterborne Alkyd Technology - Halox
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Corrosion</strong> <strong>Inhibitors</strong><br />
<strong>for</strong> <strong>Waterborne</strong> <strong>Alkyd</strong><br />
<strong>Technology</strong><br />
28 th Biennial Western Coatings<br />
Societies Symposium & Show<br />
Las Vegas, Nevada<br />
October 2007
Outline:<br />
• <strong>Corrosion</strong> <strong>Inhibitors</strong><br />
– Background & Mechanisms<br />
• Applications & Formulating Strategies<br />
– Background & Mechanisms
<strong>Corrosion</strong> <strong>Inhibitors</strong>
What is <strong>Corrosion</strong>:<br />
• The electrochemical deterioration of a<br />
metal due to the reaction with its<br />
environment involving the oxidation of<br />
a metal and the reduction of another<br />
material.
<strong>Corrosion</strong> Simplified:<br />
ELECTRON CONDUCTOR<br />
IONIC CONDUCTOR<br />
ELECTRON ACCEPTOR<br />
+ - + - + - + - + - + - + - + - + - + - + -<br />
Ionic Conductance<br />
Electron Conductance
The Result:<br />
FACTORS INFLUENCING:<br />
Presence of Water<br />
Presence of Oxygen<br />
Presence of Ions<br />
Temperature<br />
e<br />
pH<br />
Grain Structure of Metal<br />
Stresses from Fabrication
<strong>Corrosion</strong> Cell Diagram:<br />
Electron Conductor: Metal<br />
Ionic Conductor: Water<br />
Electron Acceptor: Oxygen<br />
3/2 O 2<br />
n H 20<br />
2HO<br />
2 2 Fe 2+<br />
Fe 2 O 3 • H 2 0<br />
4H +<br />
O 2<br />
2 Fe<br />
4 e⎯<br />
Anodic Site<br />
Cathodic Site
How Can We Use<br />
Coatings to Protect Metal<br />
from <strong>Corrosion</strong> ?:
PASSIVE<br />
Protect through the barrier properties<br />
of resin or pigment having low H 2 O<br />
transmission. (i.e. epoxies, chlorinated<br />
rubbers)<br />
ACTIVE<br />
Inorganic Inhibitive Pigments<br />
Organic <strong>Corrosion</strong> <strong>Inhibitors</strong><br />
Ion Exchange<br />
Vapor Phase<br />
SACRIFICIAL<br />
Zinc-rich primers protect through the<br />
preferential oxidation of zinc metal
Passivation Mechanism<br />
(Active-Direct Inorganic Inhibitor)<br />
Specific Example:<br />
Zinc phosphate<br />
-<br />
+<br />
- + -<br />
+ +<br />
-<br />
+<br />
+<br />
-<br />
Zn 3 (PO 4 ) 2<br />
-<br />
+<br />
Hydrolysis<br />
ys s<br />
-<br />
+<br />
-<br />
Fe 2+<br />
H 2 O<br />
Insoluble<br />
FePO 4<br />
Precipitate<br />
M x (OH) x<br />
e -<br />
Substrate<br />
Fe<br />
Anode<br />
e<br />
Cathode
Applications &<br />
Formulating Strategies
Water Based <strong>Alkyd</strong>s
Uses:<br />
• Lower cost corrosion protection<br />
• Light duty industrial applications<br />
Moderate per<strong>for</strong>mance on machinery, tanks, etc.<br />
Lower VOC compared to S/B<br />
Fast Drying<br />
Good adhesion to steel, plastic, & aluminum
Types:<br />
• Water Reducible <strong>Alkyd</strong>s (WRA)<br />
COO - COO<br />
-<br />
COO - COO- COO<br />
COO - -<br />
COO -<br />
COO -<br />
COO-<br />
COO - COO -<br />
COO -<br />
COO -<br />
• Water Dispersible ibl <strong>Alkyd</strong>s (WDA)<br />
ACRYLIC<br />
POLYMER SHELL<br />
ALKYD CORE
Properties:<br />
Feature<br />
Water Reducible<br />
<strong>Alkyd</strong> (WRA)<br />
Water Dispersible<br />
<strong>Alkyd</strong> (WDA)<br />
Ability to achieve low VOC + ++<br />
High gloss + ++<br />
Hydrolysis resistance + ++<br />
<strong>Corrosion</strong> resistance ++ +<br />
Shear stability - ++<br />
Gloss retention ti<br />
++ +<br />
Dry time (wet edge/open time) - -<br />
Alkaline resistance - +<br />
Moisture resistance - -<br />
Gelling with basic pigments - +<br />
Drier kick-out resistance ++ -<br />
Yellowing - -
Hydrolysis of <strong>Alkyd</strong>s:<br />
Reversible Reaction in<br />
the Presence of Water<br />
‣ System pH is critical<br />
‣ Amine selection is critical
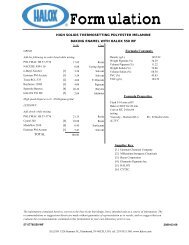
Typical Formulation<br />
(Water Reducible Epoxy Ester)<br />
INGREDIENTS % WEIGHT FUNCTION<br />
Resydrol AX237w/70BG 33.16 Resin<br />
Ammonium hydroxide 0.62 Amine<br />
Triethylamine 1.86 Amine<br />
Additol VXW-6206 0.38 Drier<br />
Troymax Antiskin B 0.18 Antiskin<br />
Patcote 577 0.09 Defoamer<br />
De-Ionized Water 9.22<br />
RO-4097 Kroma Red 8.32 Pigment<br />
Anticorrosive Pigment* 6.02 <strong>Corrosion</strong> Inhibitor<br />
Micro Talc AT Extra 5.23 Filler<br />
Millicarb 6.52 Filler<br />
Bartex 65 6.62 Filler<br />
Aerosil 200 037 0.37 Rheology modifier<br />
De-Ionized Water 21.41<br />
TOTAL 100.0<br />
Fast<br />
(25%)<br />
Amine Package<br />
Slow<br />
(75%)
Formulating with WRA’s:<br />
• Recommended system pH of 8.00 – 8.50<br />
• Use 100% triethylamine (TEA) <strong>for</strong> excellent<br />
stability & good salt spray resistance.<br />
• Use a blend of TEA and ammonium hydroxide<br />
<strong>for</strong> good stability & excellent salt spray<br />
resistance.
Changes to the Amine Package:<br />
Water Epoxy Ester - Cold Rolled Steel – 2.0 mils - 336 hrs SS<br />
Best<br />
Stability<br />
Best<br />
Per<strong>for</strong>mance<br />
100%<br />
Triethylamine<br />
75:25 TEA and<br />
Ammonium Hydroxide
Stability vs. Amine Package:<br />
4<br />
Heat Aged Stability<br />
Weeks<br />
@ 50o<br />
C<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
0<br />
100 75/25 50/50 25/75<br />
TEA to Ammonium Hydroxide Ratio
Base Strengths via pKa & pH:<br />
Amine<br />
pKa @<br />
Amine pH<br />
20°C<br />
TEA 10.78 10.6<br />
(0.005 N aq. Solution)<br />
AMP 9.82 10.3<br />
(2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol)<br />
Ammonia 9.24 10.0
Formulating with WRA’s:<br />
Effect of <strong>Corrosion</strong> Inhibitor<br />
• Zinc phosphate with low levels of zinc oxide<br />
showed better corrosion resistance (Salt<br />
Spray Testing).<br />
• Better solvent resistance with Zn than Ca<br />
(MEK Double Rubs).<br />
• Higher electrochemical impedance with Zn<br />
than Ca (EIS Testing).<br />
• Synergy witnessed with organic inhibitor.
Formulating with WRA’s:<br />
Role of zinc oxide<br />
• Improves the cross link density of film<br />
• It is an active “cathodic” inhibitor which<br />
works synergistically with zinc phosphate.<br />
• Can react with mono- & di- carboxylic acid<br />
binder breakdown products
<strong>Corrosion</strong> Per<strong>for</strong>mance:<br />
ZnO 0% 0% 2% 17%<br />
MEK 6 8 7 12
Impedance Spectra<br />
(Bode Plots):<br />
Strontium zinc phosphosilicate<br />
p<br />
Calcium phosphosilicate<br />
Zinc phosphate<br />
Blank
Inorganic-Organic <strong>Corrosion</strong><br />
Inhibitor Synergy:<br />
Water Reducible <strong>Alkyd</strong> - Cold Rolled Steel – 1.0 mil - 500 hrs SS<br />
Blank 6% Mod ZnPO4 6% Mod ZnPO4<br />
2% Organic CI
Summary:<br />
• Balancing the amine package is key to<br />
<strong>for</strong>mulating hydrolytically stable WR alkyd<br />
primers.<br />
• Modified (i.e., containing ZnO) zinc phosphate<br />
pigments provide excellent e corrosion os o resistance<br />
sta compared to non-zinc or traditional zinc<br />
phosphate corrosion inhibitors.<br />
• Salt spray and electrochemical impedance<br />
corrosion testing correlated well!
Acknowledgements<br />
Hexion Specialty Chemicals<br />
Melissa DeGroot, R&D Chemist<br />
Guy Lopez – Senior Technical Specialist<br />
Natalie Wilson – Technical Service Representative<br />
High Solids, <strong>Waterborne</strong> and Latex: Three Approaches to Compliance
Contact In<strong>for</strong>mation:<br />
Andrew Thorn – HALOX Technical Service Manager<br />
Phone: (219) 933-1560 X 243<br />
Fax: (219) 933-1575<br />
Email:<br />
Athorn@halox.com