Euler's partition theorem and the combinatorics of -sequences
Euler's partition theorem and the combinatorics of -sequences Euler's partition theorem and the combinatorics of -sequences
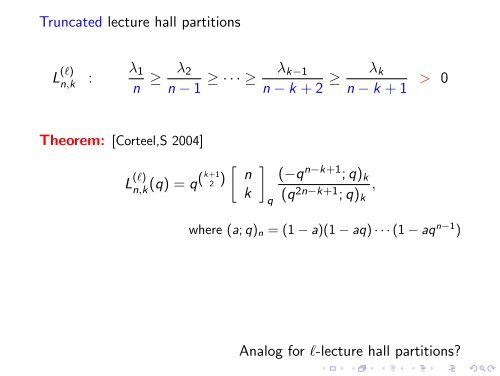
Truncated lecture hall partitions L (l) n,k : λ 1 n ≥ λ 2 n − 1 ≥ · · · ≥ λ k−1 n − k + 2 ≥ λ k n − k + 1 > 0 Theorem: [Corteel,S 2004] [ L (l) n,k (q) = q(k+1 2 ) n k ] q (−q n−k+1 ; q) k (q 2n−k+1 ; q) k , where (a; q) n = (1 − a)(1 − aq) · · · (1 − aq n−1 ) Analog for l-lecture hall partitions?
Truncated lecture hall partitions L (l) n,k,j : j ≥ λ 1 n ≥ λ 2 n − 1 ≥ · · · ≥ λ k−1 n − k + 2 ≥ λ k n − k + 1 > 0 Theorem: [Corteel,S 2004] [ L (l) n,k (q) = q(k+1 2 ) n k Theorem [Corteel,Lee,S 2005] ( ) L (l) n n,k,j (1) = jk k ] q (−q n−k+1 ; q) k (q 2n−k+1 ; q) k , where (a; q) n = (1 − a)(1 − aq) · · · (1 − aq n−1 ) Analog for l-lecture hall partitions?
- Page 1 and 2: Euler’s partition theorem and the
- Page 3 and 4: Overview Euler’s partition theore
- Page 5 and 6: Overview 1, 2, 3, . . . l-sequences
- Page 7 and 8: Overview 1, 2, 3, . . . l-sequences
- Page 9 and 10: Sylvester’s Bijection
- Page 11 and 12: l-sequences For integer l ≥ 2, de
- Page 13 and 14: l-sequences For integer l ≥ 2, de
- Page 15 and 16: l = 2 The l-Euler theorem [BME2]: T
- Page 17 and 18: l = 3 The l-Euler theorem [BME2]: T
- Page 19: The insertion step To insert a k +
- Page 22 and 23: Binary numeration system 1 0 1 1 0
- Page 24 and 25: Binary numeration system 1 0 1 1 0
- Page 26: Theorem [Fraenkel 1985] Every nonne
- Page 31 and 32: Lecture Hall Partitions
- Page 33 and 34: The Lecture Hall Theorem [BME1] The
- Page 35 and 36: Θ (l) n : Bijection for the l-Lect
- Page 46 and 47: Theorem [Corteel,S 2004] Given posi
- Page 48 and 49: The l-nomial coefficient Example (
- Page 50 and 51: Let u l and v l be the roots of the
- Page 52 and 53: Let u l and v l be the roots of the
- Page 54 and 55: An l-nomial theorem [LS]: An analog
- Page 56 and 57: A coin-flipping interpretation of t
- Page 58 and 59: Define a q-analog of the l-nomial:
- Page 60 and 61: Another q-analog of the l-nomial Le
- Page 62 and 63: Question: When l = 2, several refin
- Page 64 and 65: Question: What is the generating fu
- Page 66 and 67: CanaDAM 2009 2nd Canadian Discrete
Truncated lecture hall <strong>partition</strong>s<br />
L (l)<br />
n,k<br />
:<br />
λ 1<br />
n ≥ λ 2<br />
n − 1 ≥ · · · ≥<br />
λ k−1<br />
n − k + 2 ≥<br />
λ k<br />
n − k + 1 > 0<br />
Theorem: [Corteel,S 2004]<br />
[<br />
L (l)<br />
n,k<br />
(q) = q(k+1 2 ) n<br />
k<br />
]<br />
q<br />
(−q n−k+1 ; q) k<br />
(q 2n−k+1 ; q) k<br />
,<br />
where (a; q) n = (1 − a)(1 − aq) · · · (1 − aq n−1 )<br />
Analog for l-lecture hall <strong>partition</strong>s?