Crystal Structure 1 3.1 Some Basic Concepts of Crystal Structure ...
Crystal Structure 1 3.1 Some Basic Concepts of Crystal Structure ...
Crystal Structure 1 3.1 Some Basic Concepts of Crystal Structure ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Crystal</strong> <strong>Structure</strong><br />
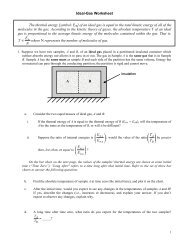
Fig. 3.25 The Ewald construction for the powder method. (a) The Ewald sphere is the smaller sphere. It is<br />
centered on the tip <strong>of</strong> the incident wavevector k with radius k, so that the origin 0 is on its surface. The<br />
larger sphere is centered on the origin and has a radius K. The two spheres intersect in a circle<br />
(foreshortened to an ellipse). Bragg reflections will occur for any wavevector k’ connecting any point on<br />
the circle <strong>of</strong> intersection to the tip <strong>of</strong> the vector k. The scattered rays therefore lie on the cone that opens in<br />
the direction opposite to k. (b) A plane section <strong>of</strong> (a), containing the incident wavevector. The triangle is<br />
isosceles, and thus K = 2ksin(/2).<br />
19



![arXiv:1303.7274v2 [physics.soc-ph] 27 Aug 2013 - Boston University ...](https://img.yumpu.com/51679664/1/190x245/arxiv13037274v2-physicssoc-ph-27-aug-2013-boston-university-.jpg?quality=85)