Solution to Laplace's Equation in Cylindrical Coordinates 1 ...
Solution to Laplace's Equation in Cylindrical Coordinates 1 ...
Solution to Laplace's Equation in Cylindrical Coordinates 1 ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
potential over the enclos<strong>in</strong>g surface. In Cartesian coord<strong>in</strong>ates this means that the potential<br />
at a po<strong>in</strong>t is approximately the average of the sum of the potentials over its nearest neighbors.<br />
V l,m,n = 1/6[V l−1,m,n + V l+1,m,n + V l,m−1,n +<br />
V l,m+1,n + V l,m−1,n + V l,m,n−1 + V l,m,n+1 ]<br />
One beg<strong>in</strong>s by tak<strong>in</strong>g the exact potential values on the surface and assign<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>itial<br />
values <strong>to</strong> the potential at all the grid po<strong>in</strong>ts. The <strong>in</strong>itial values can be any guesses. The<br />
average values at each po<strong>in</strong>t are then obta<strong>in</strong>ed, keep<strong>in</strong>g the correct potential on the surface.<br />
The process is iterated <strong>to</strong> convergence. The thechnique is called the relaxation method. It<br />
is stable by iteration and converges rapidly <strong>to</strong> the potential with<strong>in</strong> a volume. This technique<br />
(f<strong>in</strong>ite element analysis) is generally applied <strong>to</strong> any process which is described by Laplace’s<br />
equation, and this <strong>in</strong>cludes a number of physical processes <strong>in</strong> addition <strong>to</strong> electrostatics.<br />
If charge is present, we must have a solution <strong>to</strong> Poisson’s equation. For a sphere of<br />
radius, r, the potential at the center relative <strong>to</strong> the surface is;<br />
∆V = ρr 2 /(6ǫ 0 )<br />
This would be <strong>in</strong>cluded <strong>in</strong> the equation above when comput<strong>in</strong>g the average. As an example,<br />
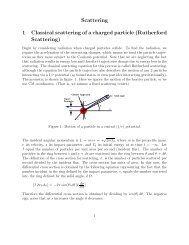
Figure 7 shows a numerical valuation of a potential at the center of a set of grounded<br />
metal boundaries and wires which are held at constant potential.<br />
9