Heavy Duty Balanced Opposed Compressors - Ariel Corporation
Heavy Duty Balanced Opposed Compressors - Ariel Corporation
Heavy Duty Balanced Opposed Compressors - Ariel Corporation
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
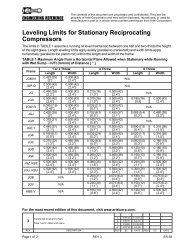
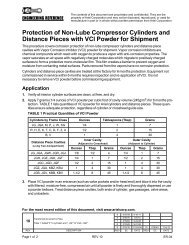
Section 4 Part Replacement For Models: JGH:E:K:T<br />
in place during piston and rod insertion.<br />
NOTE: Stagger ring gaps around the piston; do not align them.<br />
4. Follow the steps under “Piston and Rod Installation” on page 4-14.<br />
High-Pressure Face-Cut Piston Rings<br />
Face-cut piston rings are typically used in cylinders with 2500 psi MAWP or higher, and generally<br />
with notched and fluted wear bands. The rings install with the face cuts toward the highest pressure,<br />
or toward the nearest head. Gas pressure in the wear band area escapes past the piston rings via<br />
the face cuts during the suction stroke to prevent loading the wear band and increase service life.<br />
Also, do not align the ring end gaps; stagger them to minimize gas leakage.<br />
Crank<br />
End<br />
Piston<br />
Rod<br />
Piston<br />
Wear Bands<br />
Notches<br />
Pressure Pressure<br />
Most JGK and JGT pistons use a single, one-piece angle-cut filled Teflon wear band. High-pressure<br />
cylinders use two-piece thermoplastic wear bands (see Fig. 4-13).<br />
Since wear bands do not work as sealing rings, end gap is not critical. Wear band projection beyond<br />
the outer piston diameter is important. To check wear band projection, measure piston to cylinder<br />
bore clearance at the bottom of the bore. There is no need to remove the piston from the cylinder.<br />
Replace wear band before it wears enough to allow the piston to touch the cylinder bore. Install wear<br />
bands in the same way as piston rings, above. See Table B-5 in Appendix B for wear band end gap<br />
and radial projection tolerances.<br />
Piston Rod Packing<br />
Piston Rod Packing Removal<br />
Piston Rings Wear Band Piston Rings<br />
Staggered<br />
End Gaps<br />
Notches<br />
FIGURE 4-13 High-Pressure Face-Cut Piston Ring Orientation<br />
1. Remove piston and piston rod. See “Piston and Rod Removal” on page 4-8.<br />
2. Remove packing diaphragm (if applicable) and oil wiper packing.<br />
3. Disconnect all tubing and instrumentation (if applicable) from packing flange. Remove the twelvepoint<br />
capscrews that hold the pressure packing gland to the crank end of the cylinder/head.<br />
4. Do not remove the small nuts from the studs. They hold the packing case together for removal as<br />
PAGE 4-16 3/11<br />
Head<br />
End