Heavy Duty Balanced Opposed Compressors - Ariel Corporation
Heavy Duty Balanced Opposed Compressors - Ariel Corporation
Heavy Duty Balanced Opposed Compressors - Ariel Corporation
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
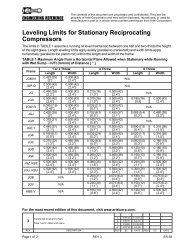
Section 3 - Maintenance For Models: JGH:E:K:T<br />
1. For new divider valves, verify working piston section fastener torque is 75 lb-in. Loosen the section<br />
fasteners, then step-torque them first to 40 lb-in, and then to 75 lb-in. Used divider valves<br />
can be tested “as is”, with approximate section fastener torque verified after testing.<br />
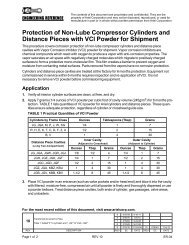
6. Place the distribution block in an open container with all base outlets open. Connect purge gun<br />
filled with room temperature (65°F) 10 wt. (ISO 32) mineral oil to the divider block inlet. Pump the<br />
purge gun to purge air from the divider block assembly. Verify that oil flows freely from all outlets<br />
(see Fig. 3-8 “Divider Block All Outlets Open”).<br />
Testing with 10 wt. mineral oil at 65°F simulates divider block operation at 120°F with 40 wt. (ISO<br />
150) mineral oil. If 10 wt. mineral oil is unavailable, use 40 wt. (ISO 150); however, the pressure<br />
test will be less sensitive in detecting a bypassing divider valve.<br />
7. The divider block assembly should cycle at less than 300 psi while purging at a steady rate.<br />
Cycle pressures above 300 psi indicate inhibited piston movement, possibly caused by the piston<br />
rubbing the bore, oil contamination, part geometry, or bore distortion due to over-tightening the<br />
section fastners.<br />
8. For divider valves stamped with a “T” (for “twin”), use a 1/8 inch pipe or tubing plug to plug only<br />
one base outlet when testing that side of the piston, and leave all other outlets open. Plug and<br />
test each base outlet of divider valves stamped with a “T” one side at a time. See Fig. 3-8 “Testing<br />
‘T’ Divider Valve”. Individual testing of each outlet ensures both sides of the piston build adequate<br />
pressure. For all divider valves stamped with an “S” on the front (for “single”), leave the one<br />
side plugged and plug the other outlet as well to test both sides of the piston for by-passing<br />
simultaneously. See Fig. 3-8 “Testing ‘S’ Divider Valve”.<br />
9. Pump the purge gun until the pressure gauge indicates 3000 psi. Hold this pressure for 5 seconds,<br />
then increase it to 3500 psi. Stop pumping at 3500 psi.<br />
10. Start timer and monitor the pressure drop from 3500 psi for 30 seconds. Check discharge outlet(s)<br />
plug(s) to confirm no external leaks. If the valve bypasses rapidly, repeat the test to ensure<br />
the bypass wasn’t due to trapped air. New valves should not exceed a 400 psi pressure drop in<br />
30 seconds. Used valves should not exceed 1000 psi pressure drop in 30 seconds. If pressure<br />
drops exceed these limits, the divider valve fails the test.<br />
11. Repeat Steps 4 thru 6 for the remaining outlets on the divider block assembly.<br />
NOTE: Test distribution blocks at higher pressures if the application dictates higher system<br />
operating pressure.<br />
If a divider valve fails, replace it. Discard worn divider valves. If the tested valve passes the test,<br />
relieve the pressure, move the plug to the next outlet, and repeat the test for all divider valves. When<br />
all divider valves either pass this pressure test or are replaced, reassemble the distribution block,<br />
purge it with the proper force feed lubricant, and put it into service.<br />
This distribution block pressure test procedure is not infallible. <strong>Ariel</strong> recommends periodic tests for<br />
proper cylinder bore lubrication rates and/or aftermarket devices that measure flow.<br />
Balance Valves<br />
Install balance valves on low-pressure lube lines to artificially increase lube line pressure and reduce<br />
differential pressure between lube points downstream of a divider block. Important considerations:<br />
• Set and maintain balance valves downstream of a divider block within 500 psi (3400kPa) of each<br />
other or less. The closer the balance valve set pressures, the more reliable the system.<br />
• Avoid situations in which the balance valve set pressure is the greatest contributor of pressure to<br />
the divider block immediately upstream.<br />
• With a balanced divider block, the upstream divider block pressure gauge should exhibit no erratic<br />
needle movement as the divider block cycles.<br />
PAGE 3-18 3/11