Tsubaki Complete Energy Series
Tsubaki Complete Energy Series
Tsubaki Complete Energy Series
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
®<br />
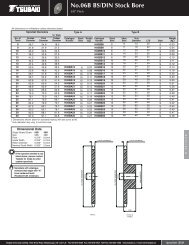
Model Number<br />
Inch <strong>Series</strong>: PL 1 AD<br />
AD <strong>Series</strong><br />
Shaft Dia. (inch)<br />
POWER-LOCK ®<br />
AD Inch <strong>Series</strong><br />
Features & Applications<br />
• Over 2 times larger transmissible torque<br />
than that of AS <strong>Series</strong><br />
• Interchangeable with Power-Lock ® AS <strong>Series</strong><br />
Has the same size inside and outside diameter as<br />
AS <strong>Series</strong> Power-Lock ® in most cases<br />
• Self-centering function<br />
Straight and narrow hubs can be used with<br />
AD <strong>Series</strong> Power-Lock ®<br />
• Easy and precise positioning<br />
Note:<br />
AD series is referred to as ADN and AD-N in other parts of<br />
the world. All three describe an identical product.<br />
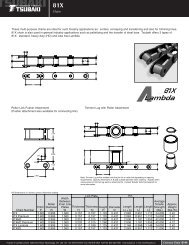
AS Selection<br />
AS Inch/Metric<br />
Guide<br />
<strong>Series</strong><br />
AS Selection<br />
AS Inch/Metric<br />
AS Inch/Metric Guide<br />
<strong>Series</strong><br />
<strong>Series</strong><br />
Power-Lock ®<br />
Selection Guide:<br />
AD Selection Guide<br />
Selection Guide:<br />
Selection Selection Guide: Guide:<br />
Power-Lock<br />
Power-Lock<br />
Power-Lock<br />
www.tsubaki.ca<br />
1. a) Determine the required maximum torque (MtC) to be transmitted:<br />
Torque MtC = 5252 x HP (ft-lb)<br />
RPM<br />
1. a) Determine the required maximum torque (MtC) to be transmitted:<br />
1. a) b) Determine If combined the required torsionalmaximum and axialtorque loads(MtC) are to be be transmitted,<br />
1. Torque a) Determine MtC = 5252 thexrequired HP (ft-lb)<br />
transmitted:<br />
calculate the resulting torque as<br />
maximum<br />
follows:<br />
torque (MtC) to be transmitted:<br />
Torque MtC = 5252 RPMx HP (ft-lb)<br />
b) If combined torsional RPM and axial loads are to be transmitted,<br />
b) calculate If combined the resulting torsional and torque and axial axial asloads follows:<br />
M<br />
loads are are to be totransmitted, be transmitted, calculate the resulting torque as follows:<br />
calculate t res =<br />
MtC +( 2 Fxd ) 2 < M t<br />
24<br />
the resulting torque as follows:<br />
Where:<br />
M t res =<br />
MtC +( 2<br />
M t res MtC +( Fxd ) 2 Fxd 2 < 2<br />
M t<br />
24<br />
Mt res = resultant torque to be transmitted < M t<br />
24<br />
MtC = actual or maximum torque to be transmitted (ft-lb). This value is calculated in step 1 a) above.<br />
Where:<br />
F = axial load/thrust torque to be be transmitted transmitted (lbs)<br />
Where: Mt res = resultant torque to be transmitted<br />
d = shaft actual diameter or maximum (inches)<br />
MtC res = = actual resultant or maximum torque torque torque be transmitted be to transmitted be transmitted (ft-lb). (ft-lb). This value This value is calculated is calculated in step in 1 a) step above. 1 a) above.<br />
Mt axial = maximum load/thrust transmissible to be transmitted torque (lbs) (ft-lb) of the Power Lock as specified in the AS Power-Lock specification tables.<br />
MtC F = axial = actual load/thrust or maximum to be transmitted torque to be(lbs)<br />
transmitted (ft-lb). This value is calculated in step 1 a) above.<br />
F d = shaft<br />
axial shaftdiameter load/thrust (inches) (inches)<br />
Mt 2. Select maximum aPower-Lock<br />
to be<br />
transmissible for<br />
transmitted<br />
torque the shaft (ft-lb) diameter<br />
(lbs)<br />
of the Power-Lock (d) from the ® as ASspecified Power-Lock in the specification AD Power-Lock tables ® specification in this catalogue tables. and verify that the<br />
d Mt = = shaft maximum diameter transmissible (inches) torque (ft-lb) of the Lock as specified in the AS Power-Lock specification tables.<br />
2. Select<br />
corresponding<br />
a Power-Lock<br />
maximum ® for the<br />
transmissible<br />
shaft diameter<br />
torque<br />
(d) from<br />
(Mt)<br />
the<br />
meets<br />
AD Power-Lock<br />
the torque ® specification<br />
requirement<br />
tables<br />
that was<br />
in this<br />
calculated<br />
catalogue<br />
in<br />
and<br />
step<br />
verify<br />
1a)<br />
that<br />
above.<br />
the<br />
If torque is<br />
Mt = maximum transmissible torque (ft-lb) of the Power as specified in the AS Power-Lock specification tables.<br />
corresponding<br />
the primary requirement,<br />
maximum transmissible<br />
select the necessary<br />
torque (Mt)<br />
torque<br />
meets the<br />
(Mt)<br />
torque<br />
from the<br />
requirement<br />
same specification<br />
that was calculated<br />
tables and step<br />
determine<br />
1 a) above.<br />
the<br />
If<br />
corresponding<br />
torque<br />
shaft<br />
2. Select aPower-Lock for the shaft diameter (d) from the AS Power-Lock specification tables in this catalogue and verify that the<br />
2. is diameter the Select primary (d).<br />
corresponding aPower-Lock requirement, maximumfor select transmissible the shaft the necessary diameter torque torque (d) (Mt) from meets (Mt) the from ASthe torque Power-Lock same requirement specification specification that tables was tables and calculated determine this catalogue inthe step corresponding 1a) and above. verifyIf that torque theis<br />
corresponding shaft Note: diameter Required (d). peak torque should never exceed specified transmissible torque (Mt).<br />
the primary requirement, maximum select transmissible the necessary torque (Mt) torque meets (Mt) the fromtorque the same requirement specification that was tables calculated and determine stepthe 1a) corresponding above. If torque shaft is<br />
the Note: diameter primary Required (d). requirement, peak torque select should the never necessary exceed torque specified (Mt) transmissible from the same torque specification (Mt).<br />
To increase transmissible torque (Mt):<br />
tables and determine the corresponding shaft<br />
diameter Note: Required (d). peak torque should never exceed specified transmissible torque (Mt).<br />
Install 2 or 3 Power-Locks in series, increasing transmissible torque as follows:<br />
Note: To increase Required transmissible peak torque torque should (Mt):<br />
- with 2Power-Locks: Mtrans.= 2 x<br />
never<br />
Mt<br />
exceed specified transmissible torque (Mt).<br />
Install To increase 2 or 3 Power-Locks transmissiblein torque series, (Mt): increasing transmissible torque as follows:<br />
To -<br />
with<br />
with<br />
increase 3Power-Locks:<br />
Power-Locks: transmissible Mtrans.<br />
Mtrans.=<br />
torque = 2 x<br />
3<br />
(Mt):<br />
x Mt<br />
Install 2 or 3 Power-Locks in series, increasing transmissible torque as follows:<br />
Install The hub<br />
32 must be long<br />
or 3 Mtrans.<br />
enough<br />
in= series, 3<br />
to<br />
x Mt<br />
accommodate the assemblies.<br />
- with 2Power-Locks: Mtrans.= 2 x Mt increasing transmissible torque as follows:<br />
The - with hub 2Power-Locks: 3Power-Locks: must be long enough Mtrans.= to accommodate 23 x Mt the assemblies.<br />
3. Determine the recommended minimum hub outside diameter (DN) for the Power-Lock selected from the specification tables (which<br />
3. Determine -The withub 3Power-Locks: must the recommended be long Mtrans.= enough minimum to3 accommodate x Mt hub outside diameter the assemblies. (DN) for the Power-Lock ® selected from the<br />
show the DN for material with ayield point of 32,000 p.s.i.) For other yield point materials, calculate the hub outside diameter (DN) by<br />
The specification hub must tables be long (which enough show the to accommodate DN for material with the assemblies.<br />
a yield point of 32,000 p.s.i.). For other yield point<br />
using the following equation:<br />
materials, 3. Determine calculate the recommended the hub outside minimum diameter hub (DN) by outside using diameter the following (DN) equation: for the Power-Lock selected from the specification tables (which<br />
3. show Determine the DN for thematerial recommended with ayield minimum point hub of 32,000 outside p.s.i.) diameter For other (DN) for yield thepoint Power-Lock materials, selected calculate from the the hubspecification outside diameter tables (DN) (which by<br />
show using the DN following for material YP equation: + (K<br />
D<br />
with ayield point of 32,000 p.s.i.) For other yield point materials, calculate the hub outside diameter (DN) by<br />
using N > D x<br />
3 x pH)<br />
(inches or mm)<br />
the followingYP equation: - (K 3 x pH)<br />
Fig. 1 (Long Hub with Guide)<br />
where B > 2l<br />
Where<br />
YP + (K<br />
D N > D x<br />
3 x pH)<br />
(inches or mm) K3 = 0.6<br />
Where = Outer diameter of YPthe + - (K Power-Lock 3 ® and hub counter<br />
D<br />
bore N > D x<br />
x pH)<br />
(inches or mm)<br />
D= Outer inside diameter YP (inches of- the (K 3 Power-Lock or x mm). pH) and hub counter bore inside diameter (inches or mm).<br />
YP = yield point of of hub hub material (p.s.i. (p.s.i. or MPa). or MPa)<br />
Where<br />
pH = Contact pressure between the the Power-Lock ® and hub bore. See specification tables (p.s.i. or MPa).<br />
Where D= Outer diameter of the Power-Lock and hub counter bore inside diameter (inches or mm).<br />
and K3 = hub 0.6 bore. (oneSee Power-Lock) specification tables (p.s.i. or MPa).<br />
D= YP Outer yield<br />
Form diameter point of<br />
factor depending of hubthematerial Power-Lock (p.s.i.<br />
on hub design. and or MPa) hub counter bore inside diameter (inches or mm).<br />
K3 = 0.8 (2 3Power-Locks in series)<br />
YP pH Fig. yield Contact<br />
1, Fig. point pressure<br />
2 or ofFig. hub3.<br />
material between(p.s.i. the Power-Lock or MPa) and hub bore. See specification tables (p.s.i. or MPa).<br />
See Hub layout diagram on next page for more detail on value of K3<br />
pH K3<br />
Note:<br />
= 0.6<br />
Use Contact (one<br />
either<br />
Power-Lock)<br />
pressure all imperial between values (inches/p.s.i.) the Power-Lock or all and hub bore. See specification tables (p.s.i. or MPa).<br />
K3<br />
metric = 0.6 0.8 values (one (2 or(mm/MPa) Power-Lock)<br />
3Power-Locks when calculating series)<br />
Note: Use either all imperial values (inches/p.s.i.) the value of or DN. all metric values (mm/MPa) when calculating the value of DN.<br />
K3 See= Hub 0.8 (2layout or 3Power-Locks diagram on next in series) page for more detail on value of K3<br />
4. Verify that the hub length (B) is adequate for the<br />
See Hub layout diagram<br />
selected Power-Lock ® on next page for more detail on value of K3<br />
.<br />
Note: Use either all imperial values (inches/p.s.i.) or all metric values (mm/MPa) when calculating the value of DN.<br />
5. Check Note: the Useapplicable either allmachining imperial values tolerance (inches/p.s.i.) for the shaft or all metric Fig. values 2 (Short (mm/MPa) Hub with when Guide) calculating Fig. 3 the (Short value Hub ofwithout DN. Guide)<br />
and hub bore in the specification tables. A surface finish of where Lt < B < 2l<br />
K3 = 1.0<br />
125 micro-inches for shafts and bores is generally adequate. K3 = 1.0<br />
38<br />
39